This content originally appeared on
A List Apart: The Full Feed and was authored by The fine folks at A List Apart
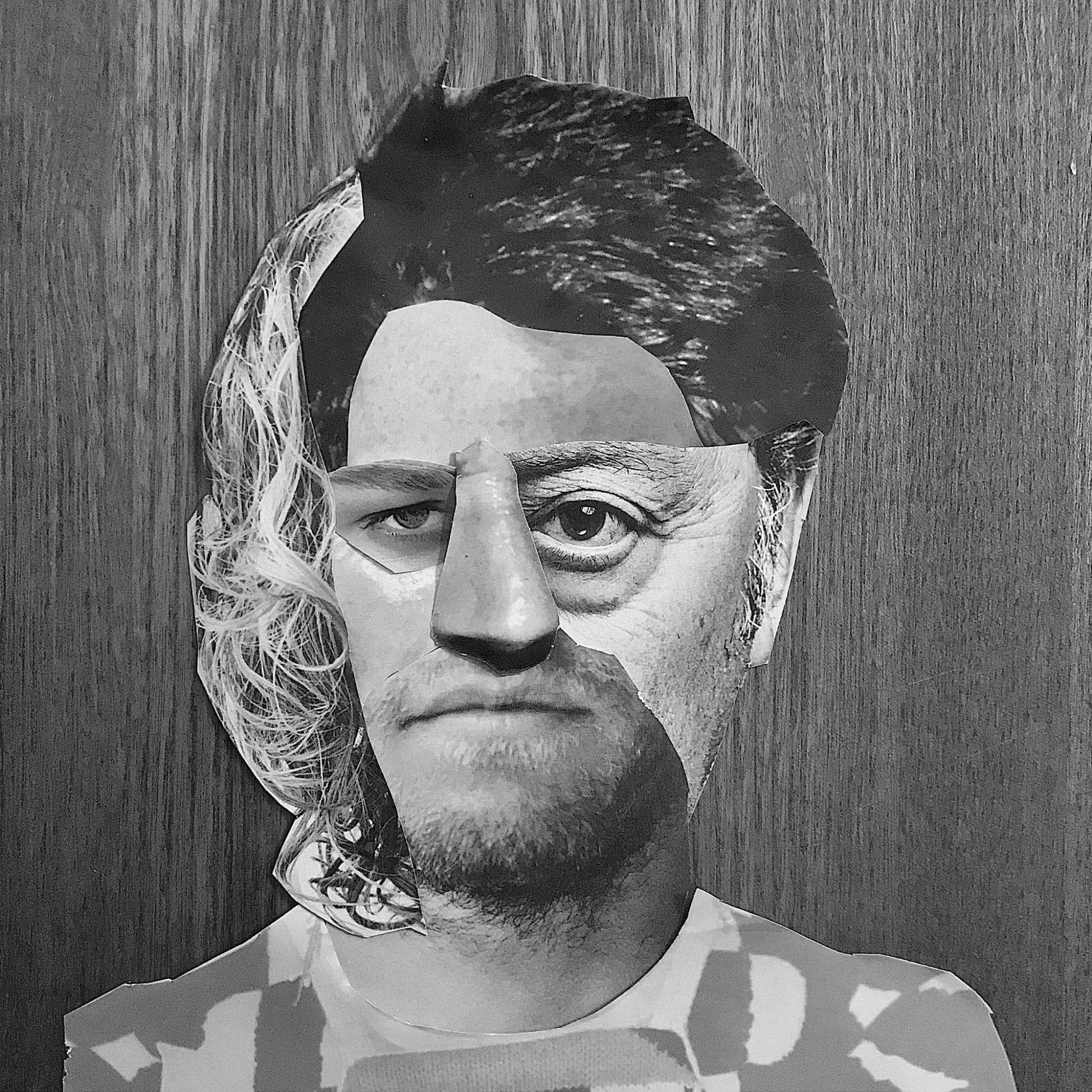
This Person Does Not Exist is a website that generates human faces with a machine learning algorithm. It takes real portraits and recombines them into fake human faces. We recently scrolled past a LinkedIn post stating that this website could be useful “if you are developing a persona and looking for a photo.”
We agree: the computer-generated faces could be a great match for personas—but not for the reason you might think. Ironically, the website highlights the core issue of this very common design method: the person(a) does not exist. Like the pictures, personas are artificially made. Information is taken out of natural context and recombined into an isolated snapshot that’s detached from reality.
But strangely enough, designers use personas to inspire their design for the real world.
Personas: A step back
Most designers have created, used, or come across personas at least once in their career. In their article “Personas - A Simple Introduction,” the Interaction Design Foundation defines personas as “fictional characters, which you create based upon your research in order to represent the different user types that might use your service, product, site, or brand.” In their most complete expression, personas typically consist of a name, profile picture, quotes, demographics, goals, needs, behavior in relation to a certain service/product, emotions, and motivations (for example, see Creative Companion’s Persona Core Poster). The purpose of personas, as stated by design agency Designit, is “to make the research relatable, [and] easy to communicate, digest, reference, and apply to product and service development.”
The decontextualization of personas
Personas are popular because they make “dry” research data more relatable, more human. However, this method constrains the researcher’s data analysis in such a way that the investigated users are removed from their unique contexts. As a result, personas don’t portray key factors that make you understand their decision-making process or allow you to relate to users’ thoughts and behavior; they lack stories. You understand what the persona did, but you don’t have the background to understand why. You end up with representations of users that are actually less human.
This “decontextualization” we see in personas happens in four ways, which we’ll explain below.
Personas assume people are static
Although many companies still try to box in their employees and customers with outdated personality tests (referring to you, Myers-Briggs), here’s a painfully obvious truth: people are not a fixed set of features. You act, think, and feel differently according to the situations you experience. You appear different to different people; you might act friendly to some, rough to others. And you change your mind all the time about decisions you’ve taken.
Modern psychologists agree that while people generally behave according to certain patterns, it’s actually a combination of background and environment that determines how people act and take decisions. The context—the environment, the influence of other people, your mood, the entire history that led up to a situation—determines the kind of person you are in each specific moment.
In their attempt to simplify reality, personas do not take this variability into account; they present a user as a fixed set of features. Like personality tests, personas snatch people away from real life. Even worse, people are reduced to a label and categorized as “that kind of person” with no means to exercise their innate flexibility. This practice reinforces stereotypes, lowers diversity, and doesn’t reflect reality.
Personas focus on individuals, not the environment
In the real world, you’re designing for a context, not for an individual. Each person lives in a family, a community, an ecosystem, where there are environmental, political, and social factors you need to consider. A design is never meant for a single user. Rather, you design for one or more particular contexts in which many people might use that product. Personas, however, show the user alone rather than describe how the user relates to the environment.
Would you always make the same decision over and over again? Maybe you’re a committed vegan but still decide to buy some meat when your relatives are coming over. As they depend on different situations and variables, your decisions—and behavior, opinions, and statements—are not absolute but highly contextual. The persona that “represents” you wouldn’t take into account this dependency, because it doesn’t specify the premises of your decisions. It doesn’t provide a justification of why you act the way you do. Personas enact the well-known bias called fundamental attribution error: explaining others’ behavior too much by their personality and too little by the situation.
As mentioned by the Interaction Design Foundation, personas are usually placed in a scenario that’s a “specific context with a problem they want to or have to solve”—does that mean context actually is considered? Unfortunately, what often happens is that you take a fictional character and based on that fiction determine how this character might deal with a certain situation. This is made worse by the fact that you haven’t even fully investigated and understood the current context of the people your persona seeks to represent; so how could you possibly understand how they would act in new situations?
Personas are meaningless averages
As mentioned in Shlomo Goltz’s introductory article on Smashing Magazine, “a persona is depicted as a specific person but is not a real individual; rather, it is synthesized from observations of many people.” A well-known critique to this aspect of personas is that the average person does not exist, as per the famous example of the USA Air Force designing planes based on the average of 140 of their pilots’ physical dimensions and not a single pilot actually fitting within that average seat.
The same limitation applies to mental aspects of people. Have you ever heard a famous person say, “They took what I said out of context! They used my words, but I didn’t mean it like that.” The celebrity’s statement was reported literally, but the reporter failed to explain the context around the statement and didn’t describe the non-verbal expressions. As a result, the intended meaning was lost. You do the same when you create personas: you collect somebody’s statement (or goal, or need, or emotion), of which the meaning can only be understood if you provide its own specific context, yet report it as an isolated finding.
But personas go a step further, extracting a decontextualized finding and joining it with another decontextualized finding from somebody else. The resulting set of findings often does not make sense: it’s unclear, or even contrasting, because it lacks the underlying reasons on why and how that finding has arisen. It lacks meaning. And the persona doesn’t give you the full background of the person(s) to uncover this meaning: you would need to dive into the raw data for each single persona item to find it. What, then, is the usefulness of the persona?

The relatability of personas is deceiving
To a certain extent, designers realize that a persona is a lifeless average. To overcome this, designers invent and add “relatable” details to personas to make them resemble real individuals. Nothing captures the absurdity of this better than a sentence by the Interaction Design Foundation: “Add a few fictional personal details to make the persona a realistic character.” In other words, you add non-realism in an attempt to create more realism. You deliberately obscure the fact that “John Doe” is an abstract representation of research findings; but wouldn’t it be much more responsible to emphasize that John is only an abstraction? If something is artificial, let’s present it as such.
It’s the finishing touch of a persona’s decontextualization: after having assumed that people’s personalities are fixed, dismissed the importance of their environment, and hidden meaning by joining isolated, non-generalizable findings, designers invent new context to create (their own) meaning. In doing so, as with everything they create, they introduce a host of biases. As phrased by Designit, as designers we can “contextualize [the persona] based on our reality and experience. We create connections that are familiar to us.” This practice reinforces stereotypes, doesn’t reflect real-world diversity, and gets further away from people’s actual reality with every detail added.
To do good design research, we should report the reality “as-is” and make it relatable for our audience, so everyone can use their own empathy and develop their own interpretation and emotional response.
Dynamic Selves: The alternative to personas
If we shouldn’t use personas, what should we do instead?
Designit has proposed using Mindsets instead of personas. Each Mindset is a “spectrum of attitudes and emotional responses that different people have within the same context or life experience.” It challenges designers to not get fixated on a single user’s way of being. Unfortunately, while being a step in the right direction, this proposal doesn’t take into account that people are part of an environment that determines their personality, their behavior, and, yes, their mindset. Therefore, Mindsets are also not absolute but change in regard to the situation. The question remains, what determines a certain Mindset?
Another alternative comes from Margaret P., author of the article “Kill Your Personas,” who has argued for replacing personas with persona spectrums that consist of a range of user abilities. For example, a visual impairment could be permanent (blindness), temporary (recovery from eye surgery), or situational (screen glare). Persona spectrums are highly useful for more inclusive and context-based design, as they’re based on the understanding that the context is the pattern, not the personality. Their limitation, however, is that they have a very functional take on users that misses the relatability of a real person taken from within a spectrum.
In developing an alternative to personas, we aim to transform the standard design process to be context-based. Contexts are generalizable and have patterns that we can identify, just like we tried to do previously with people. So how do we identify these patterns? How do we ensure truly context-based design?
Understand real individuals in multiple contexts
Nothing is more relatable and inspiring than reality. Therefore, we have to understand real individuals in their multi-faceted contexts, and use this understanding to fuel our design. We refer to this approach as Dynamic Selves.
Let’s take a look at what the approach looks like, based on an example of how one of us applied it in a recent project that researched habits of Italians around energy consumption. We drafted a design research plan aimed at investigating people’s attitudes toward energy consumption and sustainable behavior, with a focus on smart thermostats.
1. Choose the right sample
When we argue against personas, we’re often challenged with quotes such as “Where are you going to find a single person that encapsulates all the information from one of these advanced personas[?]” The answer is simple: you don’t have to. You don’t need to have information about many people for your insights to be deep and meaningful.
In qualitative research, validity does not derive from quantity but from accurate sampling. You select the people that best represent the “population” you’re designing for. If this sample is chosen well, and you have understood the sampled people in sufficient depth, you’re able to infer how the rest of the population thinks and behaves. There’s no need to study seven Susans and five Yuriys; one of each will do.
Similarly, you don’t need to understand Susan in fifteen different contexts. Once you’ve seen her in a couple of diverse situations, you’ve understood the scheme of Susan’s response to different contexts. Not Susan as an atomic being but Susan in relation to the surrounding environment: how she might act, feel, and think in different situations.
Given that each person is representative of a part of the total population you’re researching, it becomes clear why each should be represented as an individual, as each already is an abstraction of a larger group of individuals in similar contexts. You don’t want abstractions of abstractions! These selected people need to be understood and shown in their full expression, remaining in their microcosmos—and if you want to identify patterns you can focus on identifying patterns in contexts.
Yet the question remains: how do you select a representative sample? First of all, you have to consider what’s the target audience of the product or service you are designing: it might be useful to look at the company’s goals and strategy, the current customer base, and/or a possible future target audience.
In our example project, we were designing an application for those who own a smart thermostat. In the future, everyone could have a smart thermostat in their house. Right now, though, only early adopters own one. To build a significant sample, we needed to understand the reason why these early adopters became such. We therefore recruited by asking people why they had a smart thermostat and how they got it. There were those who had chosen to buy it, those who had been influenced by others to buy it, and those who had found it in their house. So we selected representatives of these three situations, from different age groups and geographical locations, with an equal balance of tech savvy and non-tech savvy participants.
2. Conduct your research
After having chosen and recruited your sample, conduct your research using ethnographic methodologies. This will make your qualitative data rich with anecdotes and examples. In our example project, given COVID-19 restrictions, we converted an in-house ethnographic research effort into remote family interviews, conducted from home and accompanied by diary studies.
To gain an in-depth understanding of attitudes and decision-making trade-offs, the research focus was not limited to the interviewee alone but deliberately included the whole family. Each interviewee would tell a story that would then become much more lively and precise with the corrections or additional details coming from wives, husbands, children, or sometimes even pets. We also focused on the relationships with other meaningful people (such as colleagues or distant family) and all the behaviors that resulted from those relationships. This wide research focus allowed us to shape a vivid mental image of dynamic situations with multiple actors.
It’s essential that the scope of the research remains broad enough to be able to include all possible actors. Therefore, it normally works best to define broad research areas with macro questions. Interviews are best set up in a semi-structured way, where follow-up questions will dive into topics mentioned spontaneously by the interviewee. This open-minded “plan to be surprised” will yield the most insightful findings. When we asked one of our participants how his family regulated the house temperature, he replied, “My wife has not installed the thermostat’s app—she uses WhatsApp instead. If she wants to turn on the heater and she is not home, she will text me. I am her thermostat.”
3. Analysis: Create the Dynamic Selves
During the research analysis, you start representing each individual with multiple Dynamic Selves, each “Self” representing one of the contexts you have investigated. The core of each Dynamic Self is a quote, which comes supported by a photo and a few relevant demographics that illustrate the wider context. The research findings themselves will show which demographics are relevant to show. In our case, as our research focused on families and their lifestyle to understand their needs for thermal regulation, the important demographics were family type, number and nature of houses owned, economic status, and technological maturity. (We also included the individual’s name and age, but they’re optional—we included them to ease the stakeholders’ transition from personas and be able to connect multiple actions and contexts to the same person).

To capture exact quotes, interviews need to be video-recorded and notes need to be taken verbatim as much as possible. This is essential to the truthfulness of the several Selves of each participant. In the case of real-life ethnographic research, photos of the context and anonymized actors are essential to build realistic Selves. Ideally, these photos should come directly from field research, but an evocative and representative image will work, too, as long as it’s realistic and depicts meaningful actions that you associate with your participants. For example, one of our interviewees told us about his mountain home where he used to spend every weekend with his family. Therefore, we portrayed him hiking with his little daughter.
At the end of the research analysis, we displayed all of the Selves’ “cards” on a single canvas, categorized by activities. Each card displayed a situation, represented by a quote and a unique photo. All participants had multiple cards about themselves.
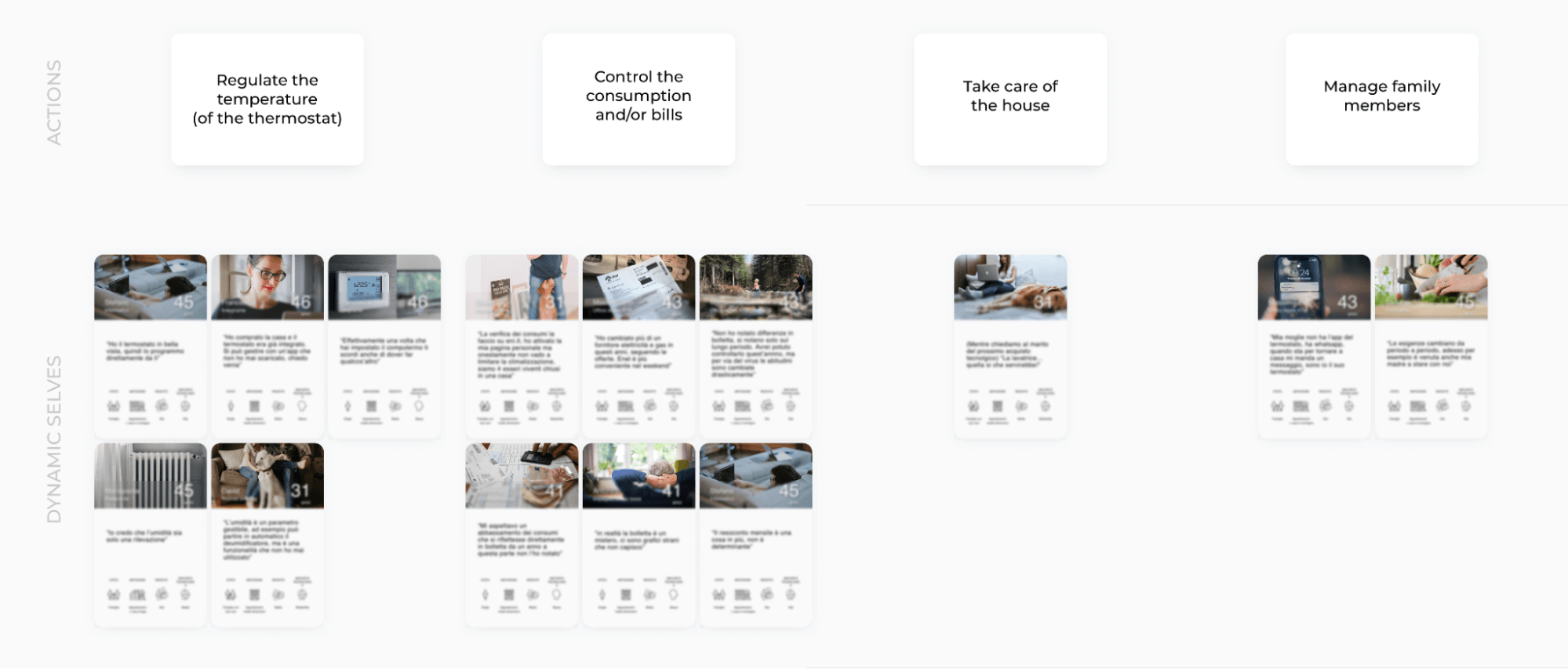
4. Identify design opportunities
Once you have collected all main quotes from the interview transcripts and diaries, and laid them all down as Self cards, you will see patterns emerge. These patterns will highlight the opportunity areas for new product creation, new functionalities, and new services—for new design.
In our example project, there was a particularly interesting insight around the concept of humidity. We realized that people don’t know what humidity is and why it is important to monitor it for health: an environment that’s too dry or too wet can cause respiratory problems or worsen existing ones. This highlighted a big opportunity for our client to educate users on this concept and become a health advisor.
Benefits of Dynamic Selves
When you use the Dynamic Selves approach in your research, you start to notice unique social relations, peculiar situations real people face and the actions that follow, and that people are surrounded by changing environments. In our thermostat project, we have come to know one of the participants, Davide, as a boyfriend, dog-lover, and tech enthusiast.
Davide is an individual we might have once reduced to a persona called “tech enthusiast.” But we can have tech enthusiasts who have families or are single, who are rich or poor. Their motivations and priorities when deciding to purchase a new thermostat can be opposite according to these different frames.
Once you have understood Davide in multiple situations, and for each situation have understood in sufficient depth the underlying reasons for his behavior, you’re able to generalize how he would act in another situation. You can use your understanding of him to infer what he would think and do in the contexts (or scenarios) that you design for.
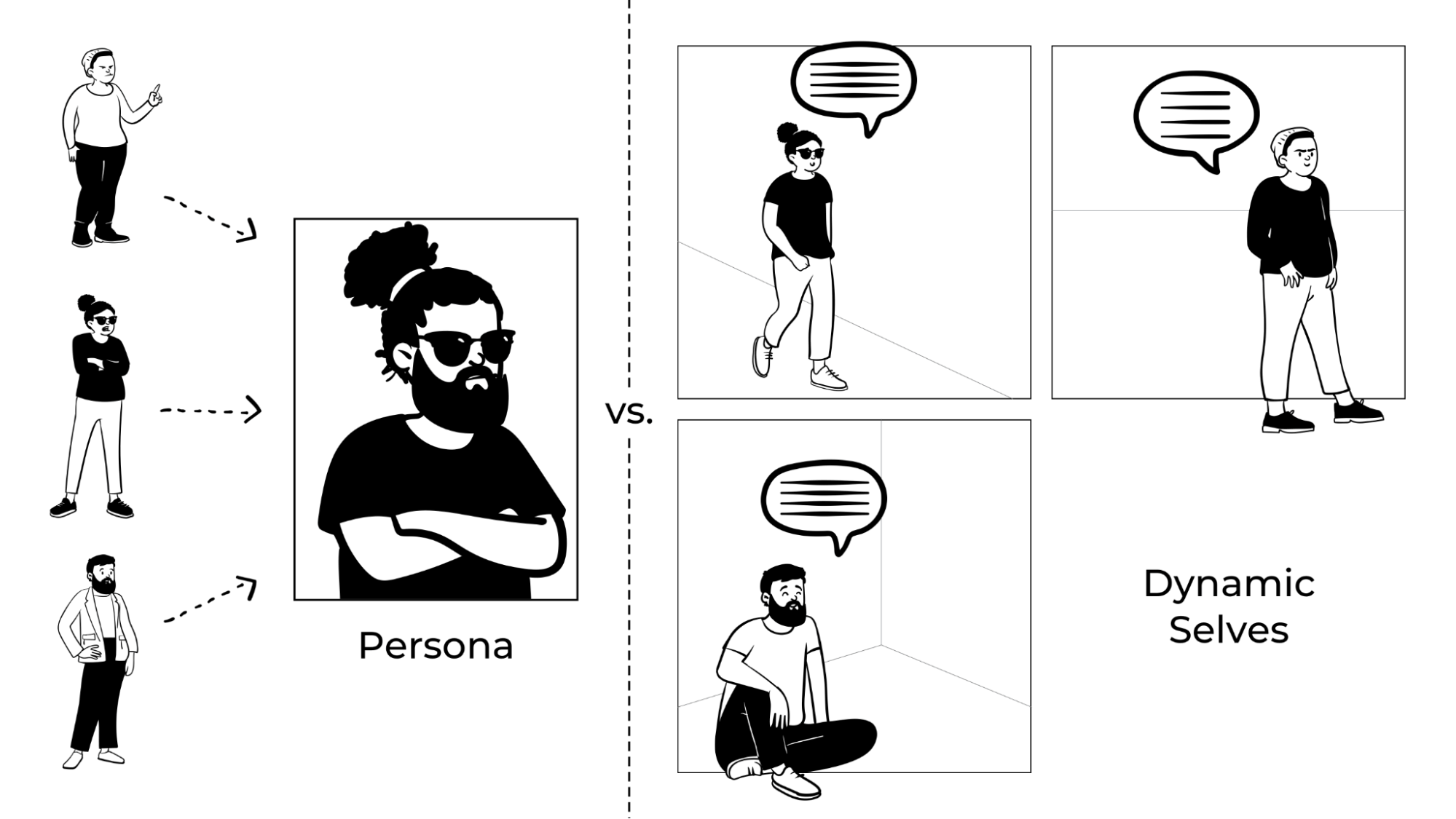
The Dynamic Selves approach aims to dismiss the conflicted dual purpose of personas—to summarize and empathize at the same time—by separating your research summary from the people you’re seeking to empathize with. This is important because our empathy for people is affected by scale: the bigger the group, the harder it is to feel empathy for others. We feel the strongest empathy for individuals we can personally relate to.
If you take a real person as inspiration for your design, you no longer need to create an artificial character. No more inventing details to make the character more “realistic,” no more unnecessary additional bias. It’s simply how this person is in real life. In fact, in our experience, personas quickly become nothing more than a name in our priority guides and prototype screens, as we all know that these characters don’t really exist.
Another powerful benefit of the Dynamic Selves approach is that it raises the stakes of your work: if you mess up your design, someone real, a person you and the team know and have met, is going to feel the consequences. It might stop you from taking shortcuts and will remind you to conduct daily checks on your designs.
And finally, real people in their specific contexts are a better basis for anecdotal storytelling and therefore are more effective in persuasion. Documentation of real research is essential in achieving this result. It adds weight and urgency behind your design arguments: “When I met Alessandra, the conditions of her workplace struck me. Noise, bad ergonomics, lack of light, you name it. If we go for this functionality, I’m afraid we’re going to add complexity to her life.”
Conclusion
Designit mentioned in their article on Mindsets that “design thinking tools offer a shortcut to deal with reality’s complexities, but this process of simplification can sometimes flatten out people’s lives into a few general characteristics.” Unfortunately, personas have been culprits in a crime of oversimplification. They are unsuited to represent the complex nature of our users’ decision-making processes and don’t account for the fact that humans are immersed in contexts.
Design needs simplification but not generalization. You have to look at the research elements that stand out: the sentences that captured your attention, the images that struck you, the sounds that linger. Portray those, use them to describe the person in their multiple contexts. Both insights and people come with a context; they cannot be cut from that context because it would remove meaning.
It’s high time for design to move away from fiction, and embrace reality—in its messy, surprising, and unquantifiable beauty—as our guide and inspiration.
This content originally appeared on
A List Apart: The Full Feed and was authored by The fine folks at A List Apart
The fine folks at A List Apart | Sciencx (2021-05-06T14:00:00+00:00) Beware the Cut ‘n’ Paste Persona. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2021/05/06/beware-the-cut-n-paste-persona-424/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
