This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by NANCY CHAUHAN
We encounter load balancers every day. Even when you are reading this medium article, your requests flow through multiple load balancers, before this content reaches your browser.
Load balancing is one of the most important and basic concepts we encounter every single day. It is the process of distributing incoming requests across multiple servers/processes/machines at the backend.
Why do we need load balancing?
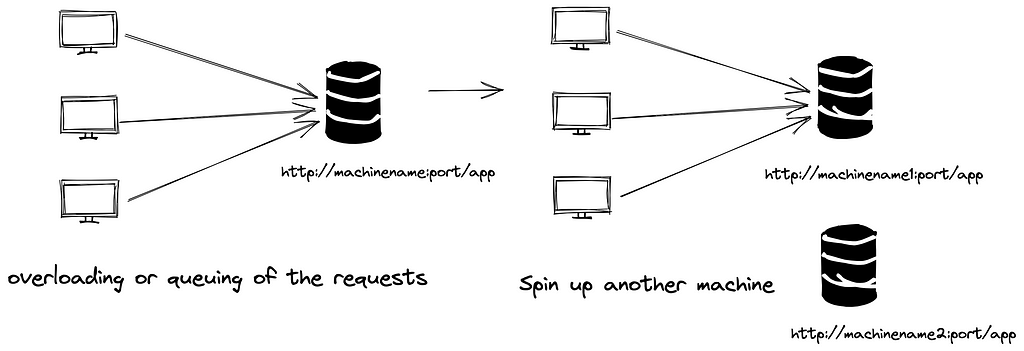
Usually, when we make an application, clients will route their request to one of the backend servers, but as soon as traffic grows, that server will reach its limits. To overcome this, we can spin up another server to share the traffic. But how do we let the clients know to connect to the new machine?
Load balancing is the technique used for discovery and decision-making for this routing. There are two ways of achieving this — server-side load balancing or client-side load balancing.
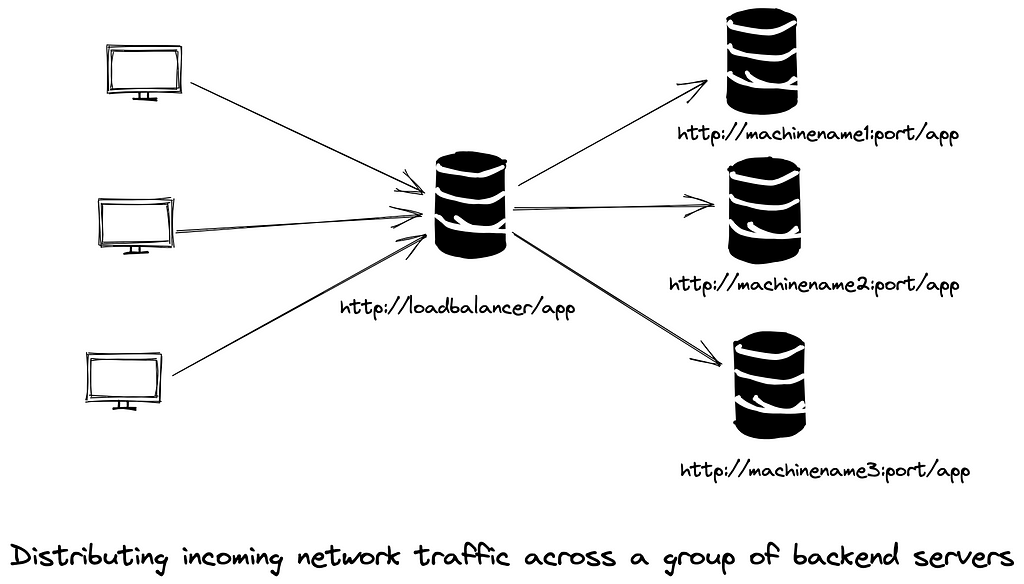
Server-side Load Balancing:
There is a middle layer, a load balancer that forwards the incoming requests to different servers to remove that complexity. All backend servers get registered with a load balancer which then routes to one of the server instances using various algorithms. AWS ELB, Nginx, Envoy are some examples of server-side load balancers.
Advantages
- No need for client-side changes.
- Easy to make changes to load balancing algorithms and backend servers.
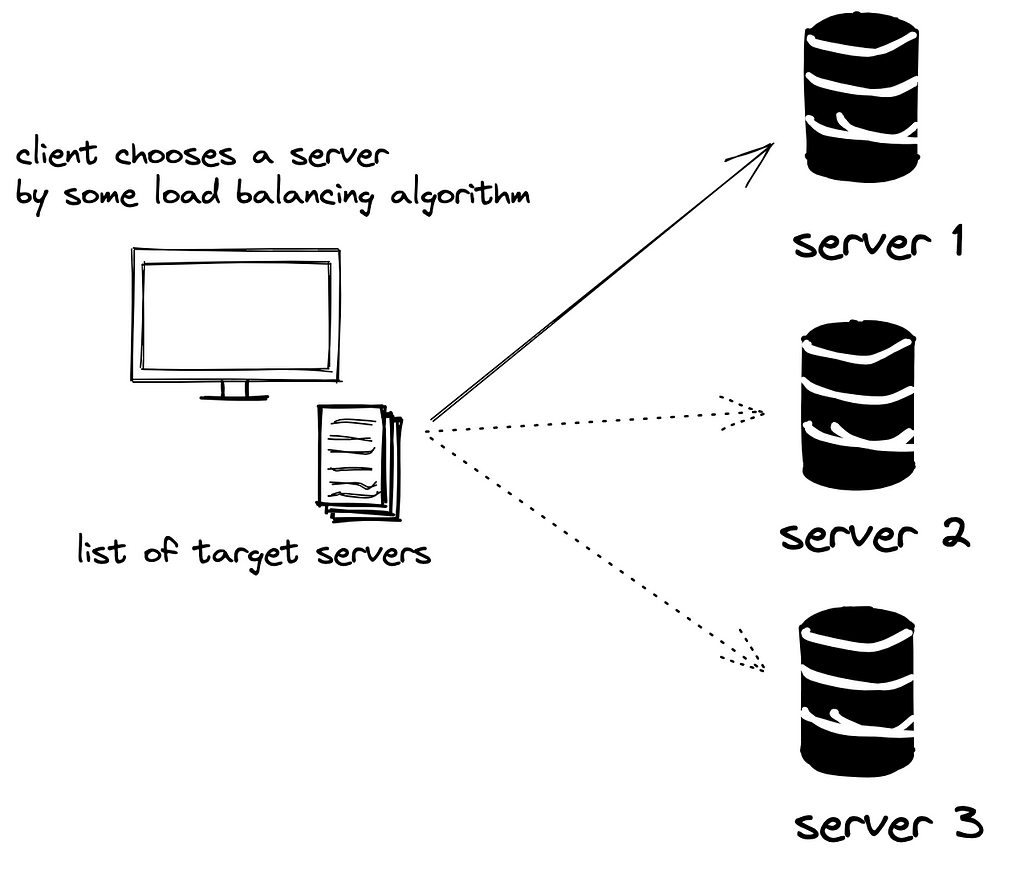
Client-Side Load Balancing:
In client-side load balancing, the client handles the load balancing. Let’s take an abstract look at how this can be achieved. To perform load balancing on the client-side -
- The client should be aware of all available web servers
- A library on the client-side to implement a load balancing algorithm
The client routes the requests to one of the servers using client-side load balancing libraries like Ribbon. Client-side load balancing is also used for service discovery.
Suppose Service A (client-side) wants to access Service B (server-side). Service B has three instances and register all at the discovery server (X). Service A has enabled the Ribbon client which allows doing the client-side load balancing. It fetches the available Service B instances from the discovery server and redirects the traffic from the client-side and constantly listens for any changes.
Here I have implemented client-side load balancing using consul service discovery: https://github.com/Nancy-Chauhan/consul-service-discovery
Advantages
- No need for additional infrastructure.
Benefits of Loadbalancing
Load balancers are the foundation of modern cloud-native applications. The concept of load balancing and the ability to be dynamically configured has created innovations such as service mesh.
Load Balancing was originally published in Level Up Coding on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by NANCY CHAUHAN
NANCY CHAUHAN | Sciencx (2021-09-28T12:13:55+00:00) Load Balancing. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2021/09/28/load-balancing/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
