This content originally appeared on Web Performance Calendar and was authored by Bruno Sabot
Core Web Vitals are well known metrics used to measure your website performance. It’s often the entry point to target what is wrong with someone’s website and measure the progress made optimizing the overall speed and stability.
Some of your clients might have no budget to dig into the various performance tools existing, or maybe no time to test an add it to the website, but they have a Google Analytics tracker set. With a few lines of code added, it is the perfect tool to start monitoring the users performances when browsing the various pages of your client.
Including the tracking code
In my example, I will be using Next.js which is a React SSR framework with a lot of internal optimizations, plus wonderful components such as <Image> and <Script> to improve the scripts and images loading and delaying.
To extract the tracking part, I first have a reusable <Analytics> component to include the two tags required by Google Analytics, and I’m using next environment variables for the customization part.
With the hypothesis I have in the first paragraph, you should not need this to be included since your client already track with this system but you can use it on new projects or existing ones without tracking system.
import Script from "next/script";
function Analytics() {
if (typeof window === "undefined") return null;
return (
<>
<Script
strategy="afterInteractive"
src={`https://www.googletagmanager.com/gtag/js?id=${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_ANALYTICS}`}
/>
<Script
id="gtag-init"
strategy="afterInteractive"
dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{
__html: `
window.dataLayer = window.dataLayer || [];
function gtag(){dataLayer.push(arguments);}
gtag('js', new Date());
gtag('config', '${process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_ANALYTICS}', {
page_path: window.location.pathname,
});
`,
}}
/>
</>
);
}
export default Analytics;
Reporting Core Web Vitals with Next.JS also need to add/update the _app.tsx file to add the metrics tracked and the pages view tracked.
Once again, here is the code if you do not already have Google Analytics on the project.
import type { AppProps, NextWebVitalsMetric } from "next/app";
import Script from "next/script";
import { useEffect } from "react";
import { useRouter } from "next/router";
import Analytics from "../components/Analytics";
export function reportWebVitals({
id,
name,
label,
value,
}: NextWebVitalsMetric) {
if (typeof gtag === "undefined") return;
window.gtag("event", name, {
event_category:
label === "web-vital" ? "Web Vitals" : "Next.js custom metric",
value: Math.round(name === "CLS" ? value * 1000 : value),
event_label: id,
non_interaction: true,
});
}
function MyApp({ Component, pageProps }: AppProps) {
const router = useRouter();
useEffect(() => {
const handleRouteChange = (url: string) => {
const ua = process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_GOOGLE_ANALYTICS ?? "";
window.gtag("config", ua, { page_path: url });
};
router.events.on("routeChangeComplete", handleRouteChange);
return () => {
router.events.off("routeChangeComplete", handleRouteChange);
};
}, [router.events]);
return (
<>
<Analytics />
<Component {...pageProps} />
</>
);
}
export default MyApp;
There are two parts in the file to consider here:
- a
reportWebVitalsmethod that is automatically used by Next.JS when it gets a Core Web Vital metrics. If you are not using Next.JS, you should look at the NPM web-vital package to see the right method in your case. - a
MyAppcomponent that includes the<Analytics>component presented earlier and a (bonus) hook to track the page change in Analytics. This one is to be used only if your client does not already have Google Analytics installed or you might duplicate the page change events sent to the server.
You now just need to add your UA value to the .env file or as an environment variable and you are ready!
Viewing data directly in Google Analytics
After few days collecting, you will see the events (in green on the screenshot) appearing in Google Analytics in the Behavior (in blue) > Events (in purple) > Top Events (in red) > Event action (in orange) menu.
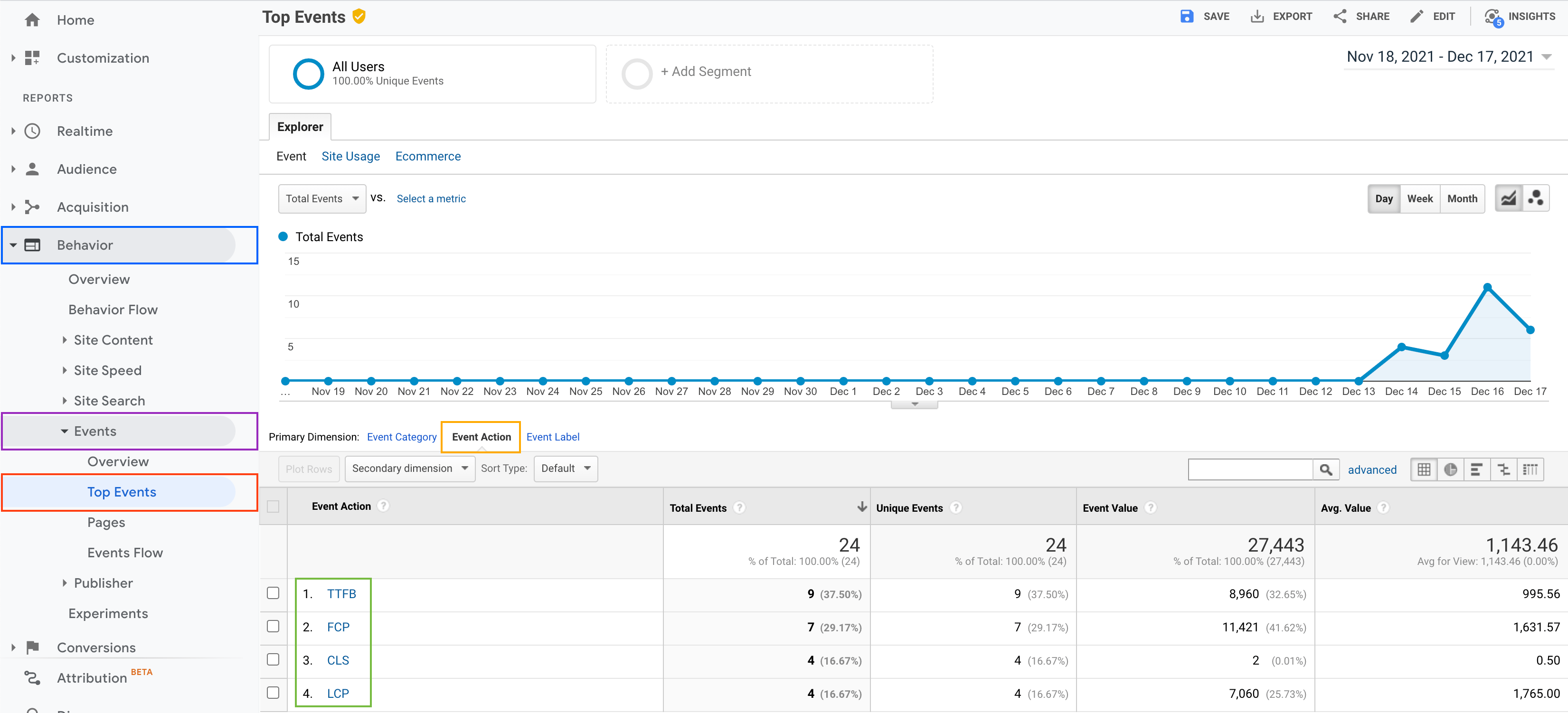
And voilà, now you can report the real performance usage to your client directly in Google Analytics.
Going further by creating custom dashboards
If the previous screen give us the metrics, it is still a combined view where the chart shows all the metrics combined.
To have a very specific view for LCP, FID and CLS, we can create custom dashboard by clicking on the Edit button on the top right od the screen.
Once in the creation page, we need to update three block on the page:
- The Dashboard title (in blue)
- The Tab name (in purple)
- The filters (in red), to Include / Event Action / LCP
Then press the Save button and you are done for the first metric!
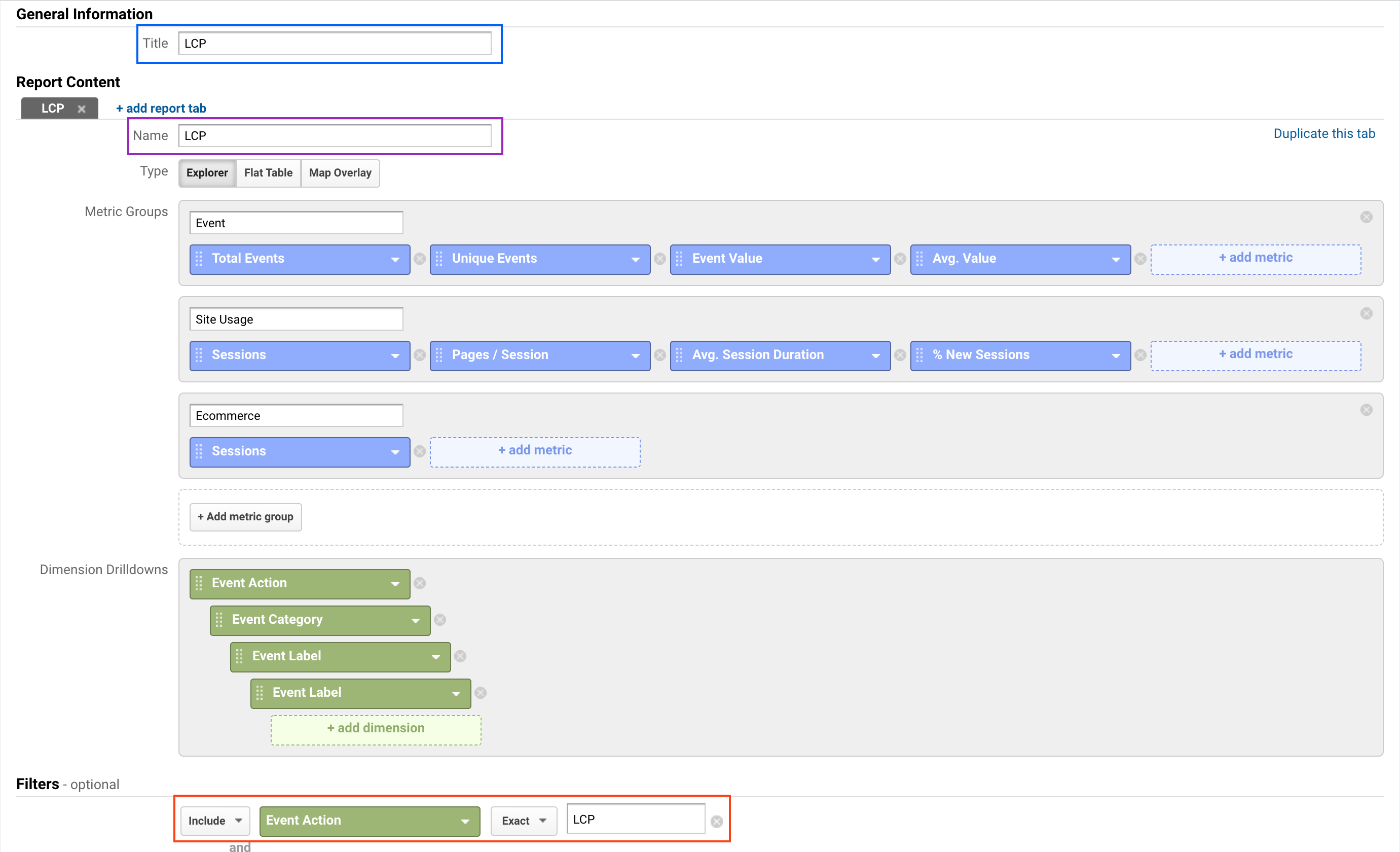
You now just need to reproduce the previous steps for FID and CLS and you will have 3 custom reports with the Realtime User Monitoring (RUM) for your users!
Conclusion
Adding dashboard for Core Web Vitals in Google Analytics is a very easy mean to get a Realtime User Monitoring of your performances.
If the created dashboard are very simple, you can go further thanks to Google Analytics power by adding second dimensions such as pages, device type, and even with conversion custom metrics.
Happy monitoring!
This content originally appeared on Web Performance Calendar and was authored by Bruno Sabot
Bruno Sabot | Sciencx (2021-12-18T18:10:00+00:00) Core Web Vitals Dashboard On Google Analytics. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2021/12/18/core-web-vitals-dashboard-on-google-analytics/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
