This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by chao huang
As programmers, writing code also requires a lot of writing skills. A good code can be refreshing, easy to understand, comfortable and natural, and at the same time full of a sense of accomplishment. Therefore, I have compiled some JS development skills that I have used in the past three years, hoping to enable you to write refreshing, easy-to-understand, comfortable and natural code.
String Skills
1: Compare time
const time1 = "2022-03-02 09:00:00";
const time2 = "2022-03-02 09:00:01";
const overtime = time1 < time2;
// overtime => true
2: Format money
const ThousandNum = num => num.toString().replace(/\B(?=(\d{3})+(?!\d))/g, ",");
const money = ThousandNum(1000000);
// money => '1,000,000'3: Generate random ID
const RandomId = len => Math.random().toString(36).substr(3, len);
const id = RandomId(10);
// id => "xdeguewg1f"
4: Generate random HEX color values
const RandomColor = () => "#" + Math.floor(Math.random() * 0xffffff).toString(16).padEnd(6, "0");
const color = RandomColor();
// color => "#2cbf89"

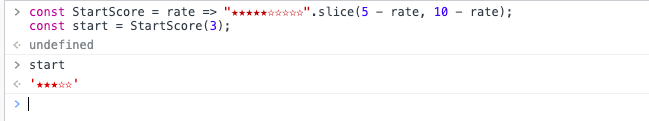
5: Generate star ratings
const StartScore = rate => "★★★★★☆☆☆☆☆".slice(5 - rate, 10 - rate);
const start = StartScore(3);
// start => '★★★☆☆'
6: URL query parameters
const params = new URLSearchParams(location.search.replace(/\?/ig, "")); // location.search = "?name=test&sex=man"
params.has("test"); // true
params.get("sex"); // "man"
Number Skills
7: Arrangement
Substitute Math.floor() for positive numbers and Math.ceil() for negative numbers
const num1 = ~~ 1.19;
const num2 = 2.29 | 0;
const num3 = 3.09 >> 0;
// num1 num2 num3 => 1 2 3
8: Zero padding
const FillZero = (num, len) => num.toString().padStart(len, "0");
const num = FillZero(1234, 5);
// num => "01234"
9: Revolution value
Only valid for null, “”, false, numeric strings
const num1 = +null;
const num2 = +"";
const num3 = +false;
const num4 = +"169";
// num1 num2 num3 num4 => 0 0 0 169
10: Timestamp
const timestamp = +new Date("2022-03-22");
// timestamp => 164790720000011: Exact decimal
const RoundNum = (num, decimal) => Math.round(num * 10 ** decimal) / 10 ** decimal;
const num = RoundNum(1.2345, 2);
// num => 1.23
12: Parity
const OddEven = num => !!(num & 1) ? "odd" : "even";
const num = OddEven(2);
// num => "even"
13: Take min max
const arr = [0, 1, 2, 3];
const min = Math.min(...arr);
const max = Math.max(...arr);
// min max => 0 3
14: Generate range random numbers
const RandomNum = (min, max) => Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
const num = RandomNum(1, 10); // 5
Boolean Skills
15: Short-circuit operator
const a = d && 1; // Fake operation, judge from left to right, return a false value when encountering a false value, and no longer execute it later, otherwise return the last true value
const b = d || 1; // Take the true operation, judge from left to right, return the true value when encountering the true value, and do not execute it later, otherwise return the last false value
const c = !d; // Returns false if a single expression converts to true, otherwise returns true
16: Determine the data type
Determinable types: undefined, null, string, number, boolean, array, object, symbol, date, regexp, function, asyncfunction, arguments, set, map, weakset, weakmap
function DataType(tgt, type) {
const dataType = Object.prototype.toString.call(tgt).replace(/\[object (\w+)\]/, "$1").toLowerCase();
return type ? dataType === type : dataType;
}
DataType("test"); // "string"
DataType(20220314); // "number"
DataType(true); // "boolean"
DataType([], "array"); // true
DataType({}, "array"); // false17: Check if array is empty
const arr = [];
const flag = Array.isArray(arr) && !arr.length;
// flag => true
18: Execute when conditions are met
const flagA = true; // Condition A
const flagB = false; // Condition B
(flagA || flagB) && Func(); // Execute when A or B is satisfied
(flagA || !flagB) && Func(); // Execute when A is satisfied or B is not satisfied
flagA && flagB && Func(); // Execute when both A and B are satisfied
flagA && !flagB && Func(); // Execute when A is satisfied and B is not satisfied
19: Executed if non-false
const flag = false; // undefined、null、""、0、false、NaN
!flag && Func();
20: Executed when the array is not empty
const arr = [0, 1, 2];
arr.length && Func();
21: Executed when the object is not null
const obj = { a: 0, b: 1, c: 2 };
Object.keys(obj).length && Func();Array Skills
22: Clone array
const _arr = [0, 1, 2];
const arr = [..._arr];
// arr => [0, 1, 2]
23: Merge array
const arr1 = [0, 1, 2];
const arr2 = [3, 4, 5];
const arr = [...arr1, ...arr2];
// arr => [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
24: Deduplicated array
const arr = [...new Set([0, 1, 1, null, null])];
// arr => [0, 1, null]
25: Obfuscated array
const arr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5].slice().sort(() => Math.random() - .5);
// arr => [3, 4, 0, 5, 1, 2]
26: Empty an array
const arr = [0, 1, 2];
arr.length = 0;
// arr => []
27: Truncate array
const arr = [0, 1, 2];
arr.length = 2;
// arr => [0, 1]
28: Exchange assignment
let a = 0;
let b = 1;
[a, b] = [b, a];
// a b => 1 0
29: Filter empty values
Empty values: undefined,null,””,0,false,NaN
const arr = [undefined, null, "", 0, false, NaN, 1, 2].filter(Boolean);
// arr => [1, 2]
30: Insert member at the beginning of the array
let arr = [1, 2];
arr.unshift(0);
arr = [0].concat(arr);
arr = [0, ...arr];
// arr => [0, 1, 2]
31: Insert members at the end of the array
let arr = [0, 1];
arr.push(2);
arr.concat(2);
arr[arr.length] = 2;
arr = [...arr, 2];
// arr => [0, 1, 2]
32: Count number of array members
const arr = [0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2];
const count = arr.reduce((t, v) => {
t[v] = t[v] ? ++t[v] : 1;
return t;
}, {});
// count => { 0: 1, 1: 2, 2: 3 }
33: Destructuring nested array members
const arr = [0, 1, [2, 3, [4, 5]]];
const [a, b, [c, d, [e, f]]] = arr;
// a b c d e f => 0 1 2 3 4 5
34: Destructuring array member aliases
const arr = [0, 1, 2];
const { 0: a, 1: b, 2: c } = arr;
// a b c => 0 1 2
35: Destructuring array member default value
const arr = [0, 1, 2];
const [a, b, c = 3, d = 4] = arr;
// a b c d => 0 1 2 4
36: Get random array member
const arr = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const randomItem = arr[Math.floor(Math.random() * arr.length)];
// randomItem => 1
37: Create an array of specified length
const arr = [...new Array(3).keys()];
// arr => [0, 1, 2]
38: Creates an array of the specified length and equal values
const arr = new Array(3).fill(0);
// arr => [0, 0, 0]
Object Skills
39: Clone object
const _obj = { a: 0, b: 1, c: 2 };
const obj = { ..._obj };
const obj = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(_obj));
// obj => { a: 0, b: 1, c: 2 }40: Merge objects
const obj1 = { a: 0, b: 1, c: 2 };
const obj2 = { c: 3, d: 4, e: 5 };
const obj = { ...obj1, ...obj2 };
// obj => { a: 0, b: 1, c: 3, d: 4, e: 5 }41: Object Variable Properties
const flag = false;
const obj = {
a: 0,
b: 1,
[flag ? "c" : "d"]: 2
};
// obj => { a: 0, b: 1, d: 2 }
42: Create a pure empty object
const obj = Object.create(null);
Object.prototype.a = 0;
// obj => {}
43: Delete object useless properties
const obj = { a: 0, b: 1, c: 2 };
const { a, ...rest } = obj;
// rest => { b: 1, c: 2 }44: Destructuring object property nesting
const obj = { a: 0, b: 1, c: { d: 2, e: 3 } };
const { c: { d, e } } = obj;
// d e => 2 345: Destructuring object property aliases
const obj = { a: 0, b: 1, c: 2 };
const { a, b: d, c: e } = obj;
// a d e => 0 1 246: Destructuring object property default values
const obj = { a: 0, b: 1, c: 2 };
const { a, b = 2, d = 3 } = obj;
// a b d => 0 1 3Function Skills
47: Function self-execution
const Func = function() {}(); // Commonly used(function() {})(); // Commonly used
(function() {}()); // Commonly used
[function() {}()];+ function() {}();
- function() {}();
~ function() {}();
! function() {}();new function() {};
new function() {}();
void function() {}();
typeof function() {}();
delete function() {}();1, function() {}();
1 ^ function() {}();
1 > function() {}();48: One-time function
Good for running some initialization code that only needs to be executed once.
function Func() {
console.log("x");
Func = function() {
console.log("y");
}
}49: Lazy loading functions
When there are more and more complex judgment branches in the function, the resource overhead can be greatly saved.
function Func() {
if (a === b) {
console.log("x");
} else {
console.log("y");
}
}
// replace with
function Func() {
if (a === b) {
Func = function() {
console.log("x");
}
} else {
Func = function() {
console.log("y");
}
}
return Func();
}50: Detect non-null parameters
function IsRequired() {
throw new Error("param is required");
}
function Func(name = IsRequired()) {
console.log("I Love " + name);
}
Func(); // "param is required"
Func("You"); // "I Love You"51: String creation function
const Func = new Function("name", "console.log(\"I Love \" + name)");52: Handle error messages gracefully
try {
Func();
} catch (e) {
location.href = "https://stackoverflow.com/search?q=[js]+" + e.message;
}53: Handle Async/Await parameters gracefully
function AsyncTo(promise) {
return promise.then(data => [null, data]).catch(err => [err]);
}
const [err, res] = await AsyncTo(Func());54: Handle multiple function return values gracefully
function Func() {
return Promise.all([
fetch("/user"),
fetch("/comment")
]);
}
const [user, comment] = await Func();DOM Skills
55: Show all DOM borders
[].forEach.call($$("*"), dom => {
dom.style.outline = "1px solid #" + (~~(Math.random() * (1 << 24))).toString(16);
});56: Responsive pages
The page is based on a design drawing but needs to be adapted to multiple models, and the element size is set using rem.
function AutoResponse(width = 750) {
const target = document.documentElement;
target.clientWidth >= 600
? (target.style.fontSize = "80px")
: (target.style.fontSize = target.clientWidth / width * 100 + "px");
}57: Filter XSS
function FilterXss(content) {
let elem = document.createElement("div");
elem.innerText = content;
const result = elem.innerHTML;
elem = null;
return result;
}58: Access LocalStorage
const love = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem("love"));
localStorage.setItem("love", JSON.stringify("I Love You"));Build composable web applications
Don’t build web monoliths. Use Bit to create and compose decoupled software components — in your favorite frameworks like React or Node. Build scalable and modular applications with a powerful and enjoyable dev experience.
Bring your team to Bit Cloud to host and collaborate on components together, and speed up, scale, and standardize development as a team. Try composable frontends with a Design System or Micro Frontends, or explore the composable backend with serverside components.
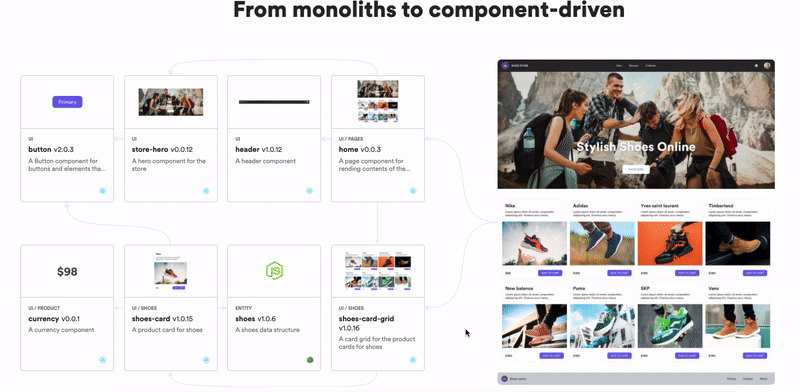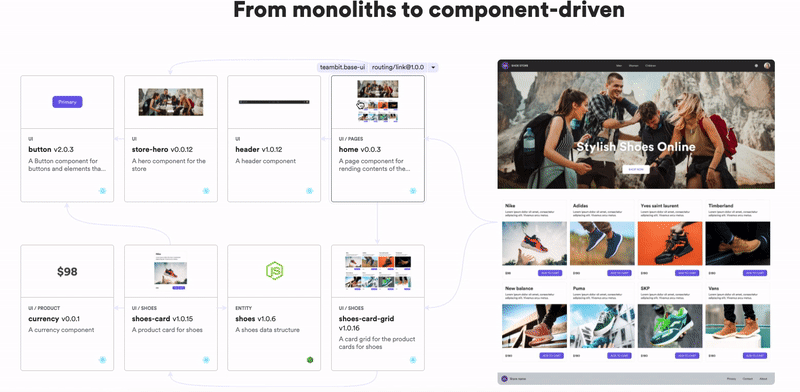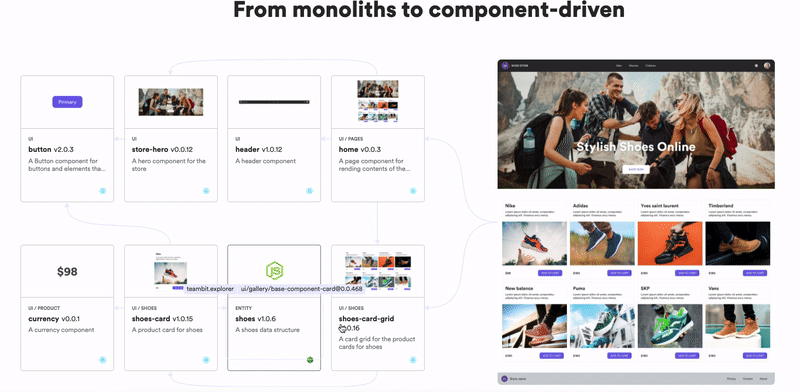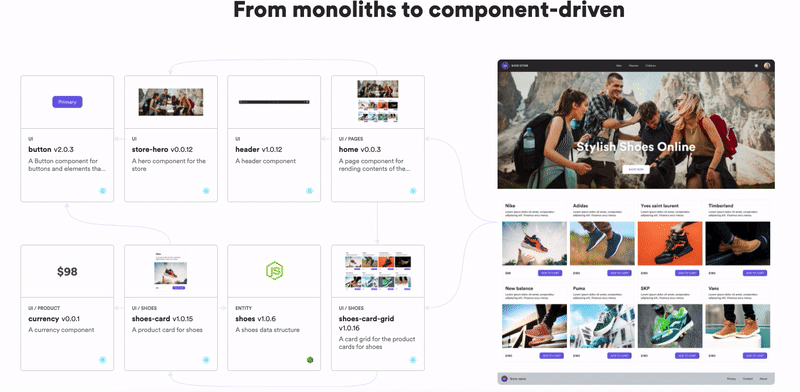
Learn More
- How We Build Micro Frontends
- How we Build a Component Design System
- The Composable Enterprise: A Guide
- 7 Tools for Faster Frontend Development in 2022
58 JavaScript Tips and Tricks for Web Developers was originally published in Bits and Pieces on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by chao huang
chao huang | Sciencx (2022-04-12T09:39:52+00:00) 58 JavaScript Tips and Tricks for Web Developers. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2022/04/12/58-javascript-tips-and-tricks-for-web-developers/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
