This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Ayush Tibra
What is the difference between primitive values and non-primitive values (object references) in JS ?

If you are interviewing for a frontend developer role, there is a high chance that you may be asked this question.
So what exactly are these?
To understand that we need to know how many different types of data type present in Javascript.
**The latest ECMAScript standard defines eight data types:**
- String
- Boolean
- Number
- BigInt
- Null
- Undefine
- Symbol
- Object
Note: Arrays do not belong to this list because they are objects as well. This is a common confusion among developers who assume that arrays are a special data type in Javascript.
Now, these data types are broadly classified into 2 types:
- Primitive:- (String,Boolean,Number,BigInt,Null,Undefined,Symbol )
- Non-Primitive:- Object (array, functions) also called object references.
The fundamental difference between primitives and non-primitive is that primitives are immutable and non-primitive are mutable.
- Mutable values are those which can be modified after creation.
- Immutable values are those which cannot be modified after creation.
Primitives are known as being immutable data types because there is no way to change a primitive value once it gets created.
Example1:-
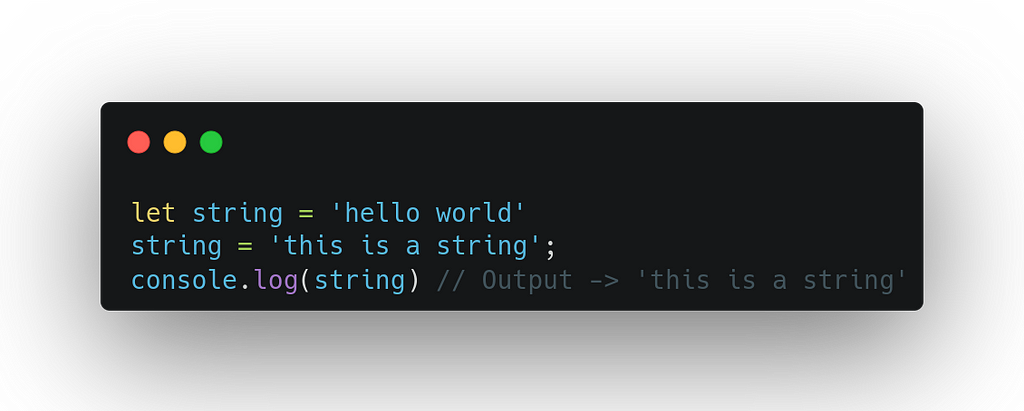
It’s important to note in the above example that a variable that stored primitive value can be reassigned to a new value as shown in the above example but the existing value can’t be changed as shown below:-
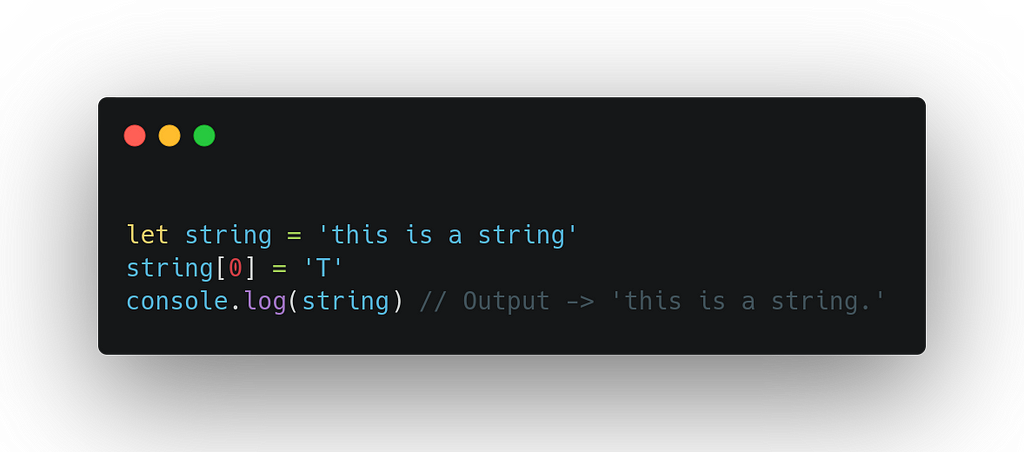
A primitive value can be replaced, but it can’t be directly altered.
Second, Primitive is compared by value. Two values are strictly equal if they have the same value.
const example1 = 'This is a test string';
const example2 = 'This is a test string';
example1 == example2 // True
Non-Primitives are known as mutable data types because we can change the value after creation.
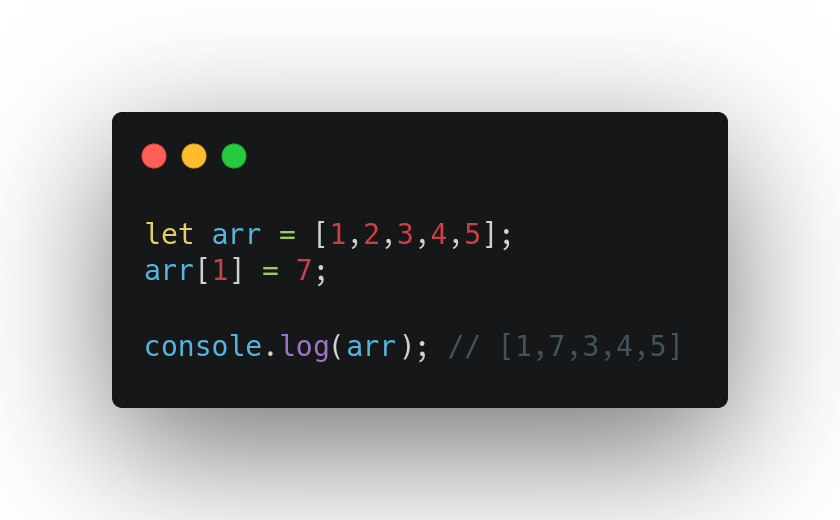
As you can see in the above example we can change the array after creation.
Secondly, Objects are not compared by value, they are being compared by reference.
For example, if two objects have the same key-value pair, they are not strictly equal. The same goes for arrays. Even if they have the same elements that are in the same order, they are not strictly equal.
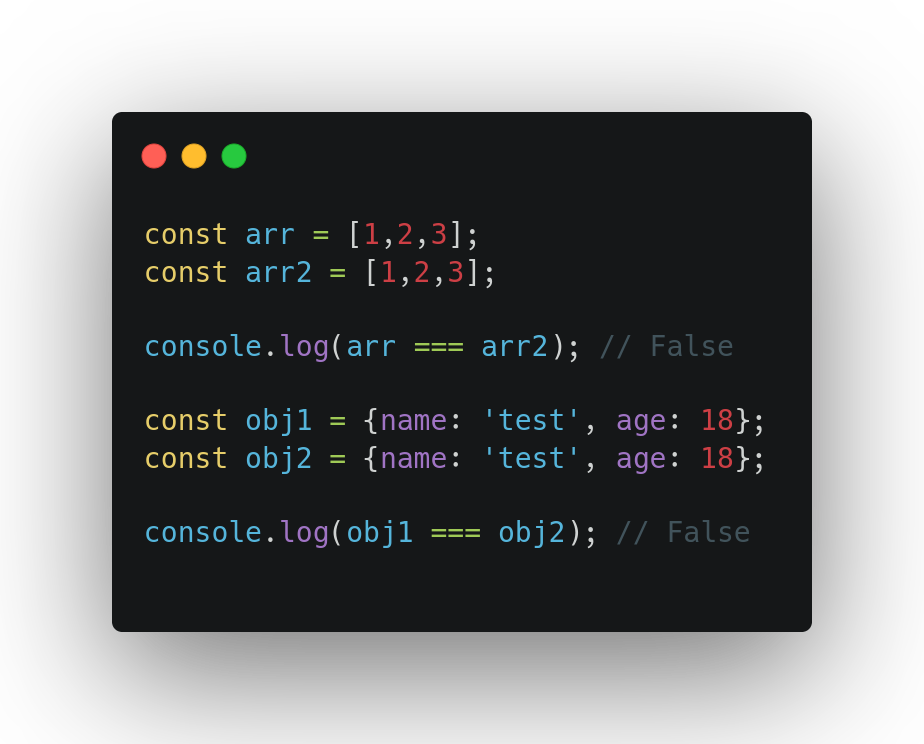
Two objects are only strictly equal if they refer to the same underlying object.
Example:-
let obj1 = {name: 'test', city: 'Jaipur'}
let obj3 = obj1;obj1 === obj3; // True
Differences and Summary
- Primitive values are immutable
- Primitive values compared by value
- Non-primitive values are mutable
- Non-primitive compare by reference not value
Please share your views in the comment section and yeah feedback is appreciated.
Hoping you would like and will share this for better reach
Checkout my other articles on — https://medium.com/@aayushtibra1997
Thanks for reading :)
Primitive vs Non-Primitive Value in Javascript? was originally published in Level Up Coding on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Ayush Tibra
Ayush Tibra | Sciencx (2022-06-15T11:41:26+00:00) Primitive vs Non-Primitive Value in Javascript?. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2022/06/15/primitive-vs-non-primitive-value-in-javascript/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
