This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by L Javier Tovar
Implementing Social Login: A Step-by-Step Guide

As programmers, we have probably needed to implement social media login at some point and, this is an increasingly common functionality in today’s applications and websites.
Social login allows users to log in to applications or websites using their accounts such as Facebook, Google, Twitter, etc. This saves users time by not having to create an additional account and password as well as taking advantage of the social network’s security measures.
For example, if a user has enabled two-step authentication on their Google account, this security will also apply to the application or website they are using.
In this tutorial, we will implement Github and Google login in a React application with TypeScript. We will use Vite to create our application and pnpm as package manager.
Login with RRSS’s first steps
First of all, to use the authentication services of any platform, we need to create an OAuth application and obtain the necessary keys.
Make sure to keep the keys in a safe place.
After this, we are going to start the development of our application. Since in this application, we will make use of sensitive and private data such as client secret keys, for security reasons it is necessary to create a backend and use it on the server side.
In the post below, I explain more about it:
How to hide your API keys and tokens in React to protect your application
So we will have two applications, backend, and client each one in its directory.
Setting up Backend
We create our application with the following command:
pnpm init -y
We install the dependencies that we will need in the project:
pnpm install express axios cors dotenv tsc ts-node
pnpm install @types/cors @types/express @types/node ts-node-dev typescript -D
After that, we create the following structure for the project:
├── src/
│ ├── routes/
│ │ ├── github-routes.ts
│ │ └── google-routes.ts
│ ├── controllers/
│ │ ├── github-controller.ts
│ │ └── google-controller.ts
│ └── server.ts
├── .env
├── .env-example
Setting up Client
We install the dependencies that we will need in the project:
pnpm install @octokit/auth @react-oauth/google @nextui-org/react axios react-router-dom
After that, we create the following structure for the project:
├── src/
│ ├── assets/
│ │ ├── icons/
│ │ │ ├── Github.tsx
│ │ │ ├── Google.tsx
│ │ │ ├── Logout.tsx
│ │ │ └── index.ts
│ ├── pages/
│ │ ├── home/
│ │ │ ├── services/
│ │ │ │ └── home-services.ts
│ │ │ └── HomePage.tsx
│ │ └── login/
│ │ └── LoginPage.tsx
│ ├── index.tsx
│ ├── App.tsx
│ └── main.tsx
├── .env
├── .env-example
GitHub Login
Backend
- File server.ts:
import express from 'express';
import cors from 'cors';
import githubRoutes from './routes/github-routes';
import googleRoutes from './routes/google-routes';
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 3001
const app = express();
app.use(
cors({
origin: ['http://localhost:5173'],
methods: 'GET,POST',
}),
);
app.use(express.json());
app.use('/api/github', githubRoutes);
app.use('/api/google', googleRoutes);
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log('Server on port', PORT));
This code creates a server application with Express. The application uses the cors library to enable cross-origin access (CORS) and sets the origin and allowed methods.
The application also uses the app.use()function to enable the use of JSON in requests and to define routes for the GitHub service and the Google service.
Finally, the application listens on the port specified in the PORTconstant, or on port 3001 if no port is specified.
- File github-routes.ts:
import express, { Request, Response, Router } from 'express';
import { getAccessToken, getUserData } from '../controllers/github-controller';
const router: Router = express.Router();
router.get('/accessToken', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
const code = req.query.code;
getAccessToken(code as string).then((resp) => res.json(resp));
});
router.get('/userData', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
const accessToken = req.query.accessToken;
getUserData(accessToken as string).then((resp) => res.json(resp));
});
export default router;This code creates an Express router which defines two routes /accessToken y /userData.
The /accessToken route s a GET route that takes a code parameter from the query and calls thegetAccessToken function of the GitHub service.
The/userData rute is a GET route that takes an accessToken parameter from the query and calls the getUserData function of the GitHub service.
- File google-routes.ts:
import express, { Request, Response, Router } from 'express';
import { getUserData } from '../controllers/google-controller';
const router: Router = express.Router();
router.get('/userData', (req: Request, res: Response) => {
const accessToken = req.query.accessToken;
getUserData(accessToken as string).then((resp) => res.json(resp));
});
export default router;This code creates an Express router that defines a GET route called/userData. The route takes anaccessToken parameter from the query and calls the getUserData function of the Google service.
- File github-controller.ts:
import * as dotenv from 'dotenv';
import axios from 'axios';
dotenv.config();
type AccessTokenData = {
access_token: string;
token_type: string;
scope: string;
} | null;
export const getAccessToken = async (
code: string,
): Promise<AccessTokenData> => {
try {
const params = `?client_id=${process.env.GITHUB_CLIENT_ID}&client_secret=${process.env.GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET}&code=${code}`;
const { data } = await axios.post(
`https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token${params}`,
{},
{
headers: {
Accept: 'application/json',
},
},
);
return data;
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
return null;
}
};
export const getUserData = async (accessToken: string) => {
try {
const { data } = await axios.get('https://api.github.com/user', {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
});
return data;
} catch (error) {
return null;
}
};
ThegetAccessToken function receives the code parameter makes a POST request to the GitHub API to obtain an access token using the provided client_id, client_secret andcode.
ThegetUserData function receives the accessToken parameter and returns the user information from the GitHub API using the access token provided in the request.
- File google-controller.ts:
import axios from 'axios';
export const getUserData = async (accessToken: string) => {
try {
const { data } = await axios.get(
'https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v3/userinfo',
{
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${accessToken}`,
},
},
);
return data;
} catch (error) {
return null;
}
};
ThegetUserData function receives the accessTokenparameter and performs a GET request to the Google OAuth user information API using the access token provided in the authorization header of the request and returns the user information.
Now we already have our backend created with the minimum we need, now let’s go for the frontend.
Client
- File main.tsx:
import { GoogleOAuthProvider } from "@react-oauth/google"
import ReactDOM from "react-dom/client"
import { NextUIProvider } from "@nextui-org/react"
import { darkTheme } from "./themes/darktheme"
const GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID = import.meta.env.VITE_GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID
import App from "./App"
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById("root") as HTMLElement).render(
<NextUIProvider theme={darkTheme}>
<GoogleOAuthProvider clientId={GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID}>
<App />
</GoogleOAuthProvider>
</NextUIProvider>
)In this application we will use Next UI for the styles, you can use any UI library you want.
TheNextUIProvider component provides the dark theme to all the components of the application. The GoogleOAuthProvider component provides the Google login to the application using the provided clientId.
- Component App.tsx:
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Routes } from 'react-router-dom';
import { LoginPage, HomePage } from './pages';
const App = () => {
return (
<Router>
<Routes>
<Route path="/home" element={<HomePage />}></Route>
<Route path="/" element={<LoginPage />}></Route>
</Routes>
</Router>
);
};
export default App;In the App component we will create the routes of the pages that we will use and we assign the corresponding component.
- Component LoginPage.tsx
import { useGoogleLogin } from "@react-oauth/google"
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom"
import { Card, Spacer, Button, Text, Container } from "@nextui-org/react"
import { IconGitHub, IconGoogle } from "../../assets/icons"
const GITHUB_CLIENT_ID = import.meta.env.VITE_GITHUB_CLIENT_ID
const LoginPage = () => {
const navigate = useNavigate()
const loginToGithub = () => {
localStorage.setItem("loginWith", "GitHub")
window.location.assign(`https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize?client_id=${GITHUB_CLIENT_ID}`)
}
const loginToGoogle = useGoogleLogin({
onSuccess: tokenResponse => {
localStorage.setItem("loginWith", "Google")
localStorage.setItem("accessToken", tokenResponse.access_token)
navigate("/home")
},
})
return (
<Container display='flex' alignItems='center' justify='center' css={{ minHeight: "100vh" }}>
<Card css={{ mw: "420px", p: "20px" }}>
<Text
size={24}
weight='bold'
css={{
as: "center",
mb: "20px",
}}
>
Login with
</Text>
<Spacer y={1} />
<Button color='gradient' auto ghost onClick={() => loginToGithub()}>
<IconGitHub />
<Spacer x={0.5} />
GitHub
</Button>
<Spacer y={1} />
<Button color='gradient' auto ghost onClick={() => loginToGoogle()}>
<IconGoogle />
<Spacer x={0.5} />
Google
</Button>
</Card>
</Container>
)
}
export default LoginPageWhen the user clicks the GitHub login button, the user is redirected to the GitHub login page and a key is stored in the browser’s local storage indicating that the user is logging in with GitHub.
When the user clicks the Google login button, the useGoogleLogin function of @react-oauth/google is used to log in with Google. If the login is successful, a key is stored in the browser’s local storage indicating that the user is signing in with Google.
- Component HomePage.tsx
import { useEffect, useRef, useState } from "react"
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom"
import { Button, Col, Container, Navbar, Row, Text, User } from "@nextui-org/react"
import { getAccessTokenGithub, getUserDataGithub, getUserDataGoogle } from "./services/home-services"
import { LogOutIcon } from "../../assets/icons"
interface UserDataGithub {
avatar_url: string
login: string
bio: string
}
interface UserdataGoogle {
name: string
picture: string
email: string
}
const HomePage = () => {
const [userDataGithub, setUserDataGithub] = useState<null | UserDataGithub>(null)
const [userDataGoogle, setUserDataGoogle] = useState<null | UserdataGoogle>(null)
const loginWith = useRef(localStorage.getItem("loginWith"))
const navigate = useNavigate()
useEffect(() => {
const queryString = window.location.search
const urlParams = new URLSearchParams(queryString)
const codeParam = urlParams.get("code")
const accessToken = localStorage.getItem("accessToken")
if (codeParam && !accessToken && loginWith.current === "GitHub") {
getAccessTokenGithub(codeParam).then(resp => {
localStorage.setItem("accessToken", resp.access_token)
getUserDataGithub(resp.access_token).then((resp: UserDataGithub) => {
setUserDataGithub(resp)
})
})
} else if (codeParam && accessToken && loginWith.current === "GitHub") {
getUserDataGithub(accessToken).then((resp: UserDataGithub) => {
localStorage.setItem("accessToken", accessToken)
setUserDataGithub(resp)
})
}
}, [loginWith])
useEffect(() => {
const accessToken = localStorage.getItem("accessToken")
if (accessToken && loginWith.current === "Google") {
getUserDataGoogle(accessToken).then(resp => {
setUserDataGoogle(resp)
})
}
}, [loginWith])
const setLogOut = () => {
localStorage.removeItem("accessToken")
localStorage.removeItem("loginWith")
navigate("/")
}
if (!userDataGithub && !userDataGoogle) return null
return (
<>
<Navbar isBordered variant='sticky'>
<Navbar.Brand>
<User
bordered
color='primary'
size='lg'
src={loginWith.current === "GitHub" ? userDataGithub?.avatar_url : userDataGoogle?.picture}
name={loginWith.current === "GitHub" ? userDataGithub?.login : userDataGoogle?.name}
description={loginWith.current === "GitHub" ? userDataGithub?.bio : userDataGoogle?.email}
/>
</Navbar.Brand>
<Navbar.Content>
<Navbar.Item>
<Button
auto
flat
size='sm'
icon={<LogOutIcon fill='currentColor' />}
color='primary'
onClick={() => setLogOut()}
>
Log out
</Button>
</Navbar.Item>
</Navbar.Content>
</Navbar>
<Container gap={0}>
<Row gap={1}>
<Col>
<Text h2>Login with {loginWith.current}</Text>
</Col>
</Row>
</Container>
</>
)
}
export default HomePageAfter the user has logged in and is redirected to Home, we will use the useEffecthook to perform a series of actions when the page loads.
First, we get the authorization code from the page URL and, if the user has logged in with GitHub, we get an access token and then we get the user’s data from GitHub. If the user has logged in with Google, we simply get the Google user data.
In addition, we have a “Logout” button that removes the access token and login from local storage and redirects the user to the application’s home page.
That’s it!
Now we can log in to Github or Google. The next steps are to register the user and save the user information in a database or whatever suits you.
The application looks something like this:
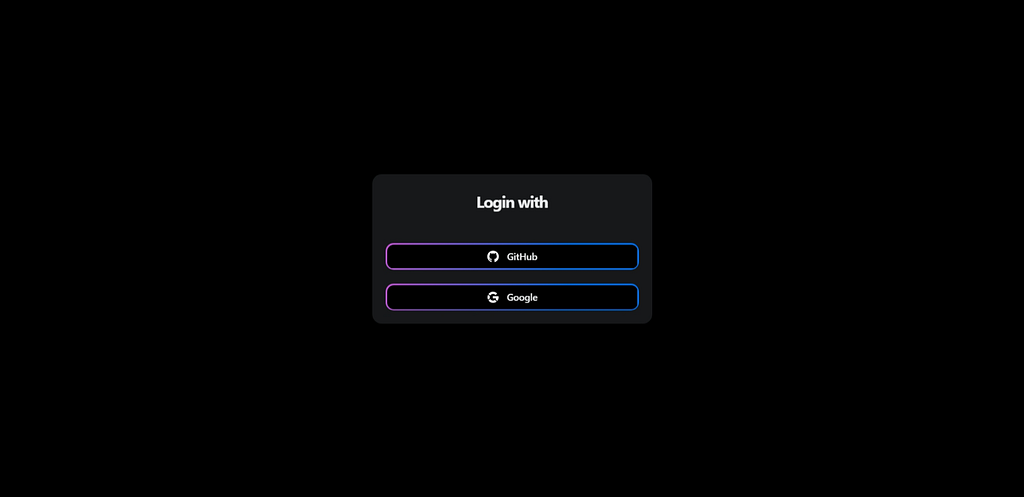
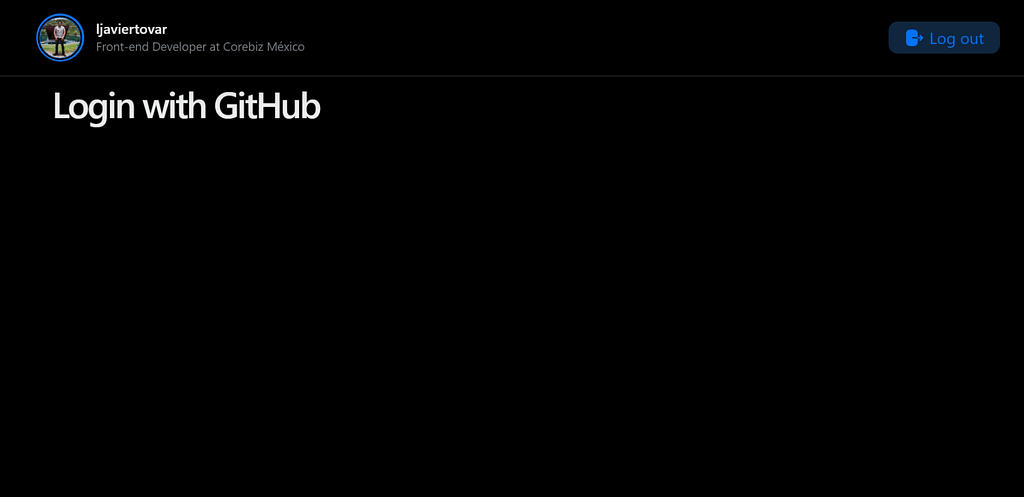
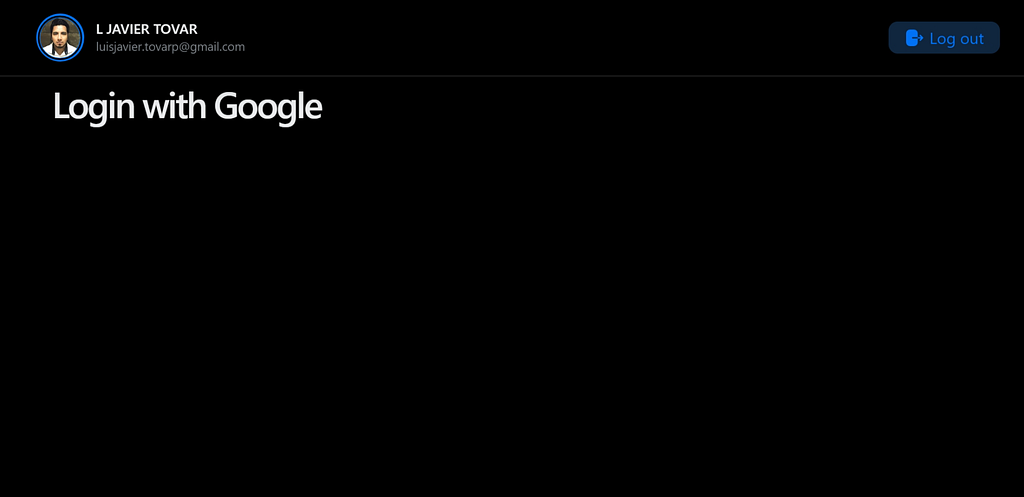
Conclusion
Social login is a feature that offers many advantages for both users and developers. It is simple to integrate and can improve the user experience and security of the application or website. Therefore, it is a good idea to consider using it in your projects.
Read more:
- Avoid Memory Leaks and Improve Performance with Cleanup Functions in React’s useEffect Hook
- Build an Autocomplete Search Component in React and TypeScript
Want to connect with the Author?
Love connecting with friends all around the world on Twitter.
10x your app development building reusable auth components

Bit’s open-source tool help 250,000+ devs to build apps with components.
Turn any UI, feature, or page into a reusable component — and share it across your applications. It’s easier to collaborate and build faster.
Split apps into components to make app development easier, and enjoy the best experience for the workflows you want:
→ Micro-Frontends
→ Design System
→ Code-Sharing and reuse
→ Monorepo
Learn more
- How We Build Micro Frontends
- How we Build a Component Design System
- Bit - Component driven development
- 5 Ways to Build a React Monorepo
- How to Create a Composable React App with Bit
- Sharing JavaScript Utility Functions Across Projects
How to Auth Login with GitHub and Google in a React and Backend app was originally published in Bits and Pieces on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by L Javier Tovar
L Javier Tovar | Sciencx (2023-01-17T07:02:24+00:00) How to Auth Login with GitHub and Google in a React and Backend app. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2023/01/17/how-to-auth-login-with-github-and-google-in-a-react-and-backend-app/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
