This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Rushit Jivani
Discover the Power of Creating Beautiful Home Screen App Widgets with React Native!
Create stunning home screen widgets with React Native + DuoLingo!

Widgets are awesome tools that make your home screen look more attractive and also provide you with quick and useful information. In this post, we’ll show you how to create widgets for both Android and iOS and how to incorporate them into your React Native app.
How does the widget work?
Widget works as an extension of your app. It cannot work as a standalone app itself. Widgets are available in three sizes (Small, Medium, and Large) and could be static or configurable. A widget is limited in terms of interaction. It cannot be scrollable, only tappable. A small widget can only have one type of interaction area whereas a medium and large widget can have multiple tappable areas of interaction.
Why should you develop a widget?
Widgets are commonly created not only to keep users informed with important information and provide access to their applications from their home screen but also to differentiate those applications from competitors and maintain user engagement.
Widgets with React Native
⚠️ Unfortunately, it is not possible to create a home screen widget using React Native. But don’t worry, we have a solution for you! In this guide, we’ll explore how to use a native widget to communicate with your React Native application. Let’s get started!
🛠️ Setup
- Create a new app
react-native init RNWidget
2. Add a dependency that will be creating the bridge between the widget and the app
yarn add react-native-shared-group-preferences
3. For communication with the native module add this code to your App.js
import React, {useState} from 'react';
import {
View,
TextInput,
StyleSheet,
NativeModules,
SafeAreaView,
Text,
Image,
ScrollView,
KeyboardAvoidingView,
Platform,
ToastAndroid,
} from 'react-native';
import SharedGroupPreferences from 'react-native-shared-group-preferences';
import AwesomeButton from 'react-native-really-awesome-button';
import {KeyboardAwareScrollView} from 'react-native-keyboard-aware-scroll-view';
const group = 'group.streak';
const SharedStorage = NativeModules.SharedStorage;
const App = () => {
const [text, setText] = useState('');
const widgetData = {
text,
};
const handleSubmit = async () => {
try {
// iOS
await SharedGroupPreferences.setItem('widgetKey', widgetData, group);
} catch (error) {
console.log({error});
}
const value = `${text} days`;
// Android
SharedStorage.set(JSON.stringify({text: value}));
ToastAndroid.show('Change value successfully!', ToastAndroid.SHORT);
};
return (
<SafeAreaView style={styles.safeAreaContainer}>
<KeyboardAwareScrollView
enableOnAndroid
extraScrollHeight={100}
keyboardShouldPersistTaps="handled">
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.heading}>Change Widget Value</Text>
<View style={styles.bodyContainer}>
<View style={styles.instructionContainer}>
<View style={styles.thoughtContainer}>
<Text style={styles.thoughtTitle}>
Enter the value that you want to display on your home widget
</Text>
</View>
<View style={styles.thoughtPointer}></View>
<Image
source={require('./assets/bea.png')}
style={styles.avatarImg}
/>
</View>
<TextInput
style={styles.input}
onChangeText={newText => setText(newText)}
value={text}
keyboardType="decimal-pad"
placeholder="Enter the text to display..."
/>
<AwesomeButton
backgroundColor={'#33b8f6'}
height={50}
width={'100%'}
backgroundDarker={'#eeefef'}
backgroundShadow={'#f1f1f0'}
style={styles.actionButton}
onPress={handleSubmit}>
Submit
</AwesomeButton>
</View>
</View>
</KeyboardAwareScrollView>
</SafeAreaView>
);
};
export default App;
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
safeAreaContainer: {
flex: 1,
width: '100%',
backgroundColor: '#fafaf3',
},
container: {
flex: 1,
width: '100%',
padding: 12,
},
heading: {
fontSize: 24,
color: '#979995',
textAlign: 'center',
},
input: {
width: '100%',
// fontSize: 20,
minHeight: 50,
borderWidth: 1,
borderColor: '#c6c6c6',
borderRadius: 8,
padding: 12,
},
bodyContainer: {
flex: 1,
margin: 18,
},
instructionContainer: {
margin: 25,
paddingHorizontal: 20,
paddingTop: 30,
borderWidth: 1,
borderRadius: 12,
backgroundColor: '#ecedeb',
borderColor: '#bebfbd',
marginBottom: 35,
},
avatarImg: {
height: 180,
width: 180,
resizeMode: 'contain',
alignSelf: 'flex-end',
},
thoughtContainer: {
minHeight: 50,
borderRadius: 12,
borderWidth: 1,
padding: 12,
backgroundColor: '#ffffff',
borderColor: '#c6c6c6',
},
thoughtPointer: {
width: 0,
height: 0,
borderStyle: 'solid',
overflow: 'hidden',
borderTopWidth: 12,
borderRightWidth: 10,
borderBottomWidth: 0,
borderLeftWidth: 10,
borderTopColor: 'blue',
borderRightColor: 'transparent',
borderBottomColor: 'transparent',
borderLeftColor: 'transparent',
marginTop: -1,
marginLeft: '50%',
},
thoughtTitle: {
fontSize: 14,
},
actionButton: {
marginTop: 40,
},
});let me explain how to use SharedGroupPreferences and SharedStorage in your app. SharedGroupPreferences is imported from the library and you can use it by storing an item with the setItem method, using a key, value, and group. For this example, the key will be widgetKey, the value will be widgetData, a JavaScript object that contains user input, and the group will be the name of the group that will share the information between the app and the widget. We will talk more about this when we get to the Swift code.
Now, for Android, we’ll use SharedStorage. You don’t need to install any additional libraries for this, since it’s included in the React Native package. The value will be a serialized JavaScript object, which will be converted to a string and saved using the set SharedStorage method. Easy peasy, right?
For native code. Let’s start with iOS.
🍏 Implementation for iOS
- Open your app project in Xcode and choose File > New > Target.
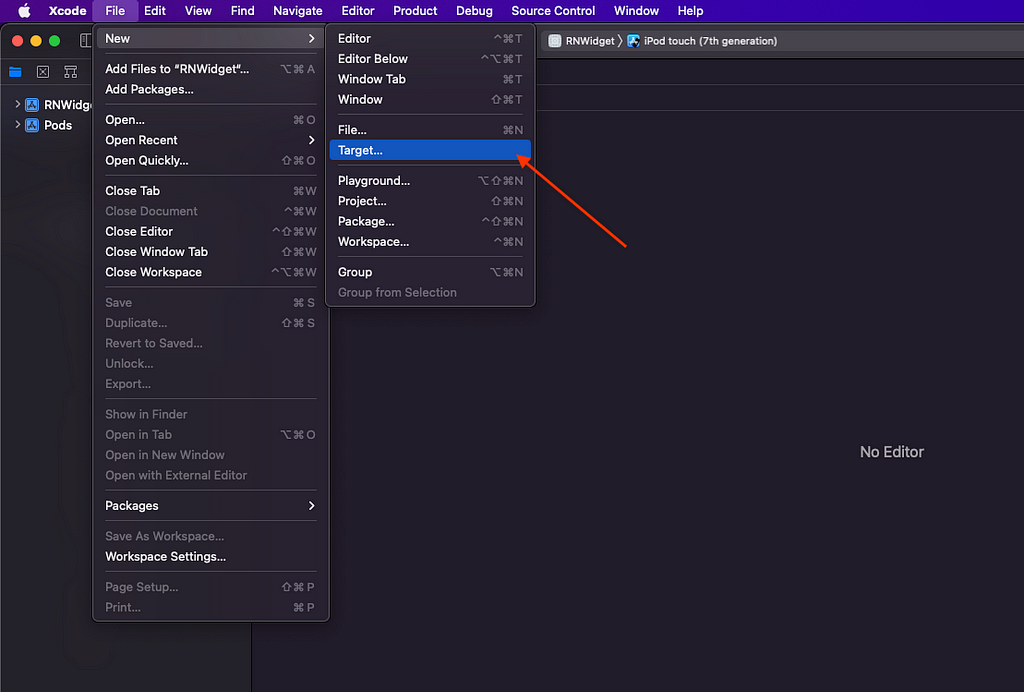
2. From the Application Extension group, select Widget Extension, and then click Next.
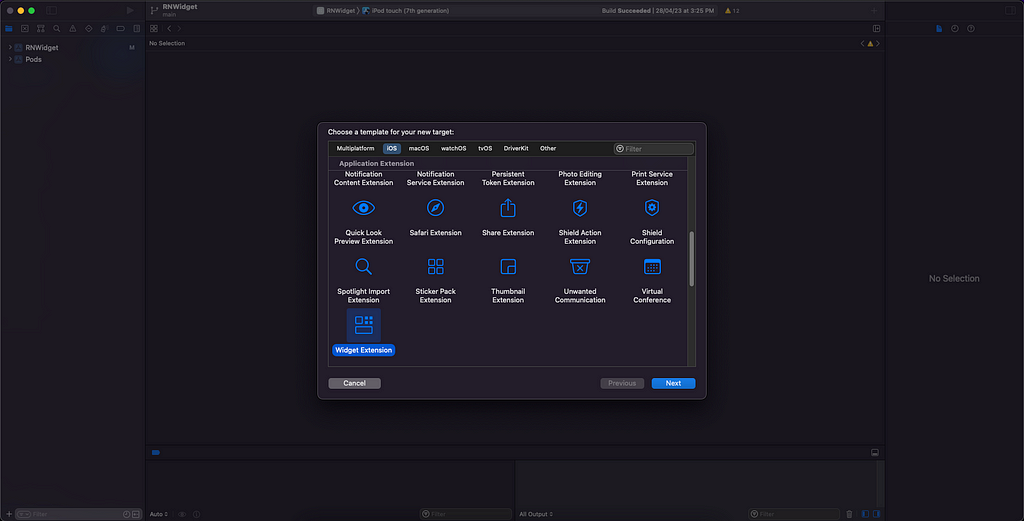
3. Enter the name of your extension.
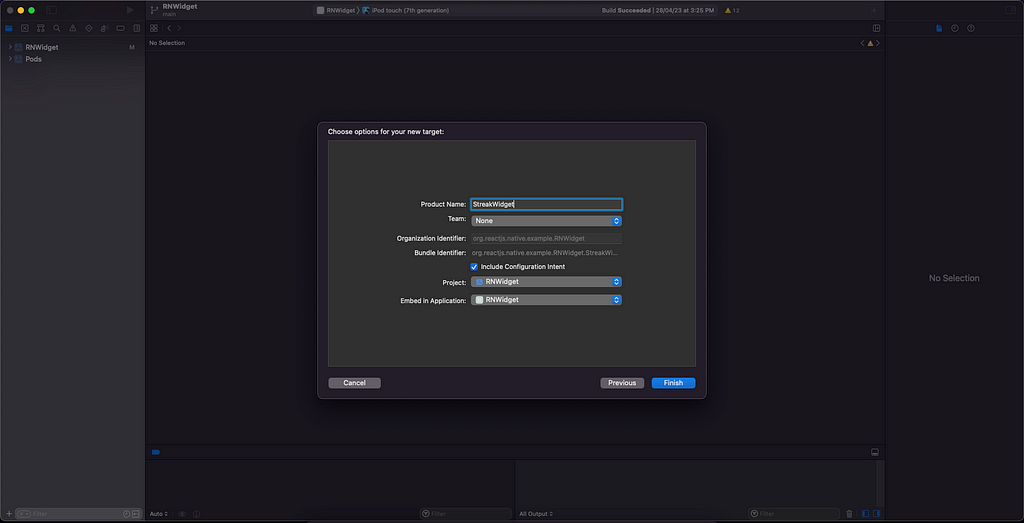
4. If the widget provides user-configurable properties, check the Include Configuration Intent checkbox.
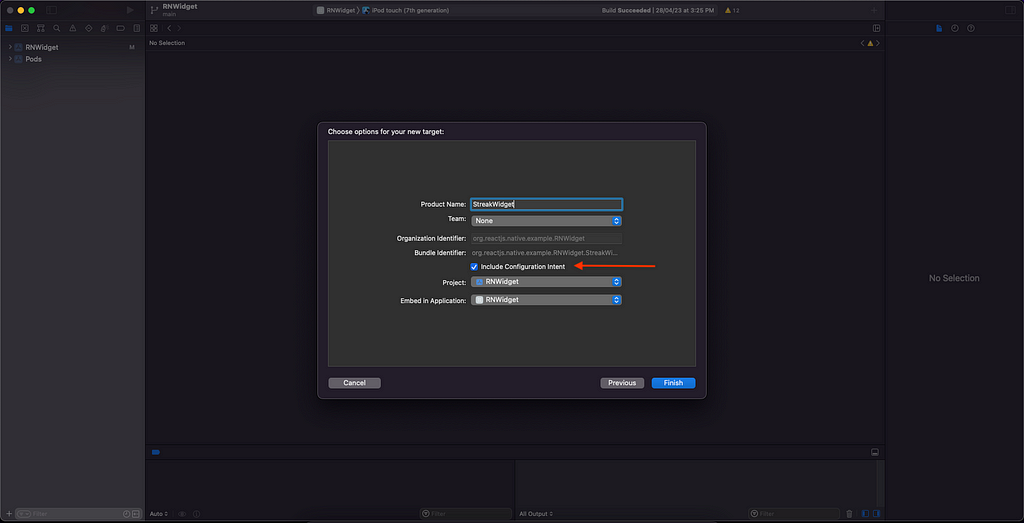
5. Click Finish.
6. If it asks to activate the scheme, click Activate.
7. Your widget is ready to go! You now have a new folder that contains all the essential files for your widget.
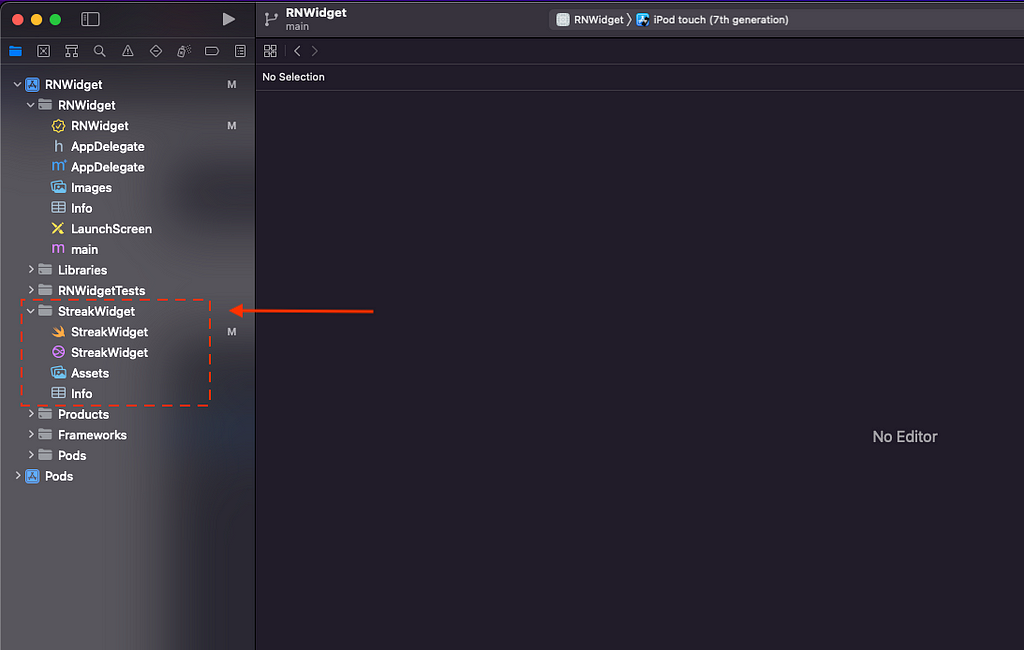
8. Before we move on to the next step, let’s test out your basic widget. To do this, simply open up your terminal and run the app using the following command
react-native run-ios
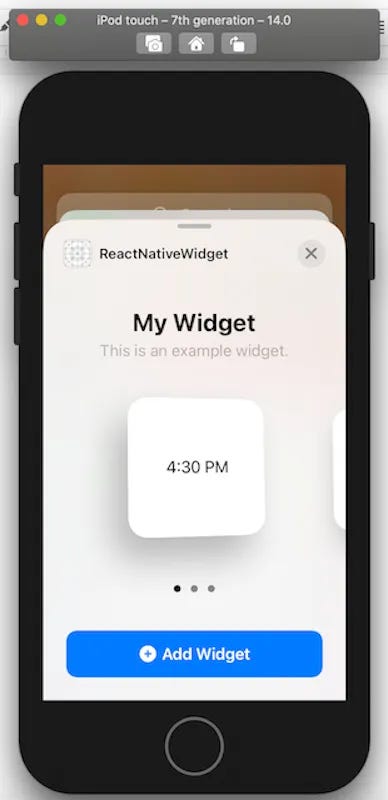
9. To add a widget you have to tap and hold the home screen until a ➕ appears in the upper left corner. When you click on the icon, a list of apps will appear. Our newly created app should be included.
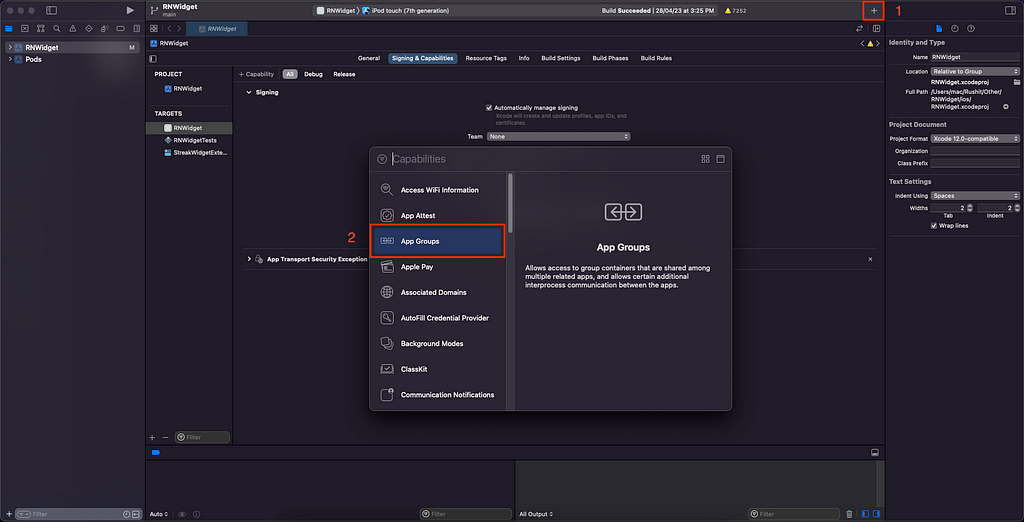
10. To communicate with React Native widget we have to add “App Group”
11. Now for our Streak widget edit StreakWidget.swift with the below code
import WidgetKit
import SwiftUI
import Intents
struct WidgetData: Decodable {
var text: String
}
struct Provider: IntentTimelineProvider {
func placeholder(in context: Context) -> SimpleEntry {
SimpleEntry(date: Date(), configuration: ConfigurationIntent(), text: "Placeholder")
}
func getSnapshot(for configuration: ConfigurationIntent, in context: Context, completion: @escaping (SimpleEntry) -> ()) {
let entry = SimpleEntry(date: Date(), configuration: configuration, text: "Data goes here")
completion(entry)
}
func getTimeline(for configuration: ConfigurationIntent, in context: Context, completion: @escaping (Timeline<SimpleEntry>) -> Void) {
let userDefaults = UserDefaults.init(suiteName: "group.streak")
if userDefaults != nil {
let entryDate = Date()
if let savedData = userDefaults!.value(forKey: "widgetKey") as? String {
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
let data = savedData.data(using: .utf8)
if let parsedData = try? decoder.decode(WidgetData.self, from: data!) {
let nextRefresh = Calendar.current.date(byAdding: .minute, value: 5, to: entryDate)!
let entry = SimpleEntry(date: nextRefresh, configuration: configuration, text: parsedData.text)
let timeline = Timeline(entries: [entry], policy: .atEnd)
completion(timeline)
} else {
print("Could not parse data")
}
} else {
let nextRefresh = Calendar.current.date(byAdding: .minute, value: 5, to: entryDate)!
let entry = SimpleEntry(date: nextRefresh, configuration: configuration, text: "No data set")
let timeline = Timeline(entries: [entry], policy: .atEnd)
completion(timeline)
}
}
}
}
struct SimpleEntry: TimelineEntry {
let date: Date
let configuration: ConfigurationIntent
let text: String
}
struct StreakWidgetEntryView : View {
var entry: Provider.Entry
var body: some View {
HStack {
VStack(alignment: .leading, spacing: 0) {
HStack(alignment: .center) {
Image("streak")
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
.frame(width: 37, height: 37)
Text(entry.text)
.foregroundColor(Color(red: 1.00, green: 0.59, blue: 0.00))
.font(Font.system(size: 21, weight: .bold, design: .rounded))
.padding(.leading, -8.0)
}
.padding(.top, 10.0)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
Text("Way to go!")
.foregroundColor(Color(red: 0.69, green: 0.69, blue: 0.69))
.font(Font.system(size: 14))
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
Image("duo")
.renderingMode(.original)
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity)
}
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity)
}
}
@main
struct StreakWidget: Widget {
let kind: String = "StreakWidget"
var body: some WidgetConfiguration {
IntentConfiguration(kind: kind, intent: ConfigurationIntent.self, provider: Provider()) { entry in
StreakWidgetEntryView(entry: entry)
}
.configurationDisplayName("My Widget")
.description("This is an example widget.")
}
}
struct StreakWidget_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
StreakWidgetEntryView(entry: SimpleEntry(date: Date(), configuration: ConfigurationIntent(), text: "Widget preview"))
.previewContext(WidgetPreviewContext(family: .systemSmall))
}
}
Basically:
- Read the UserDefaults object from the shared group we created before
let userDefaults = UserDefaults.init(suiteName: "group.streak")
- Get the data (which has been encoded in string form)
let savedData = userDefaults!.value(forKey: "widgetKey")
- Decode into an object
let parsedData = try? decoder.decode(WidgetData.self, from: data!)
- Create a timeline of said objects
let nextRefresh = Calendar.current.date(byAdding: .minute, value: 5, to: entryDate)!
Note that the objects added to the Timeline struct must comply with the TimelineEntry protocol, which means they need to have a Date field and nothing else. This is important information to keep in mind.
That’s all there is to it for iOS. Simply run npm start and test your app on either a virtual or real device.
After you’ve installed the app, all you need to do is select the widget from the widget list and put it on your home screen
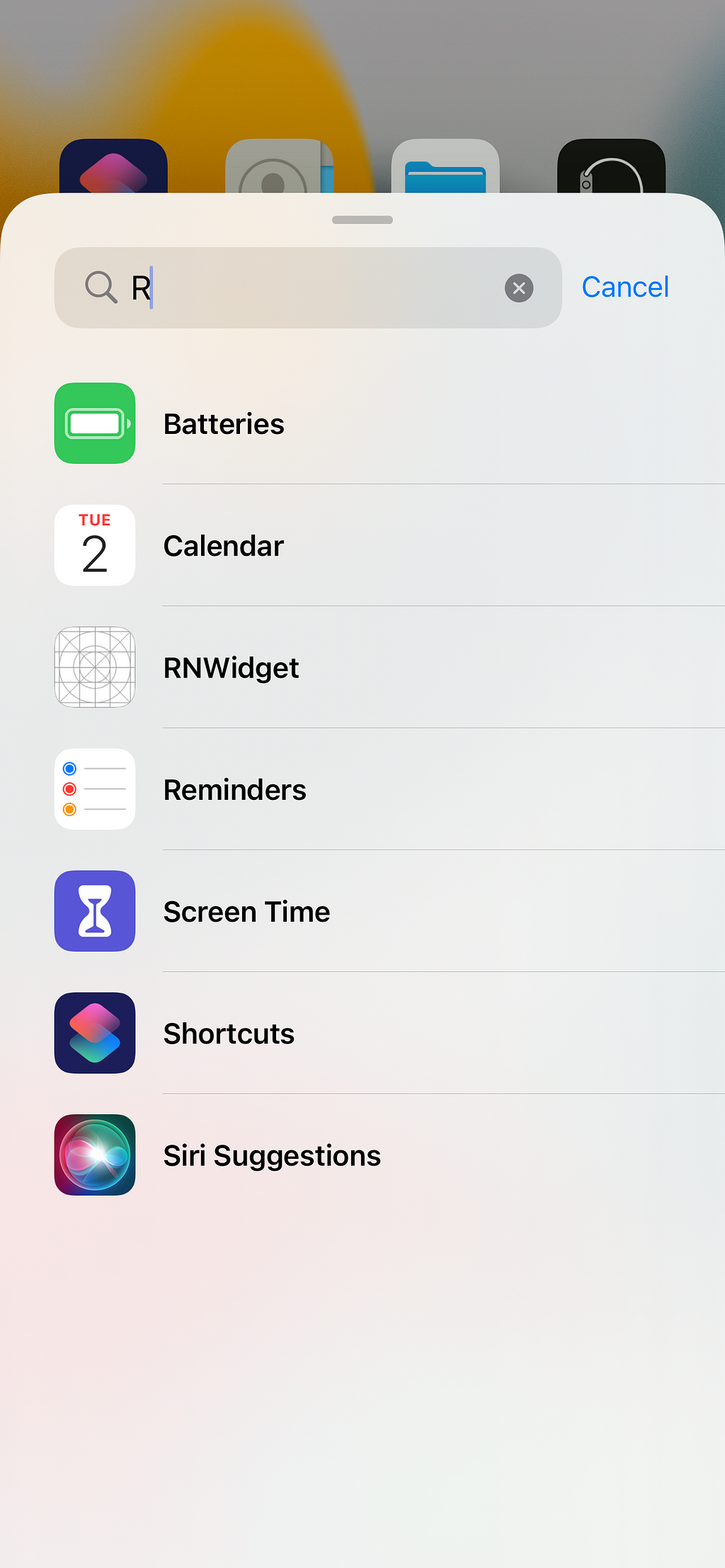
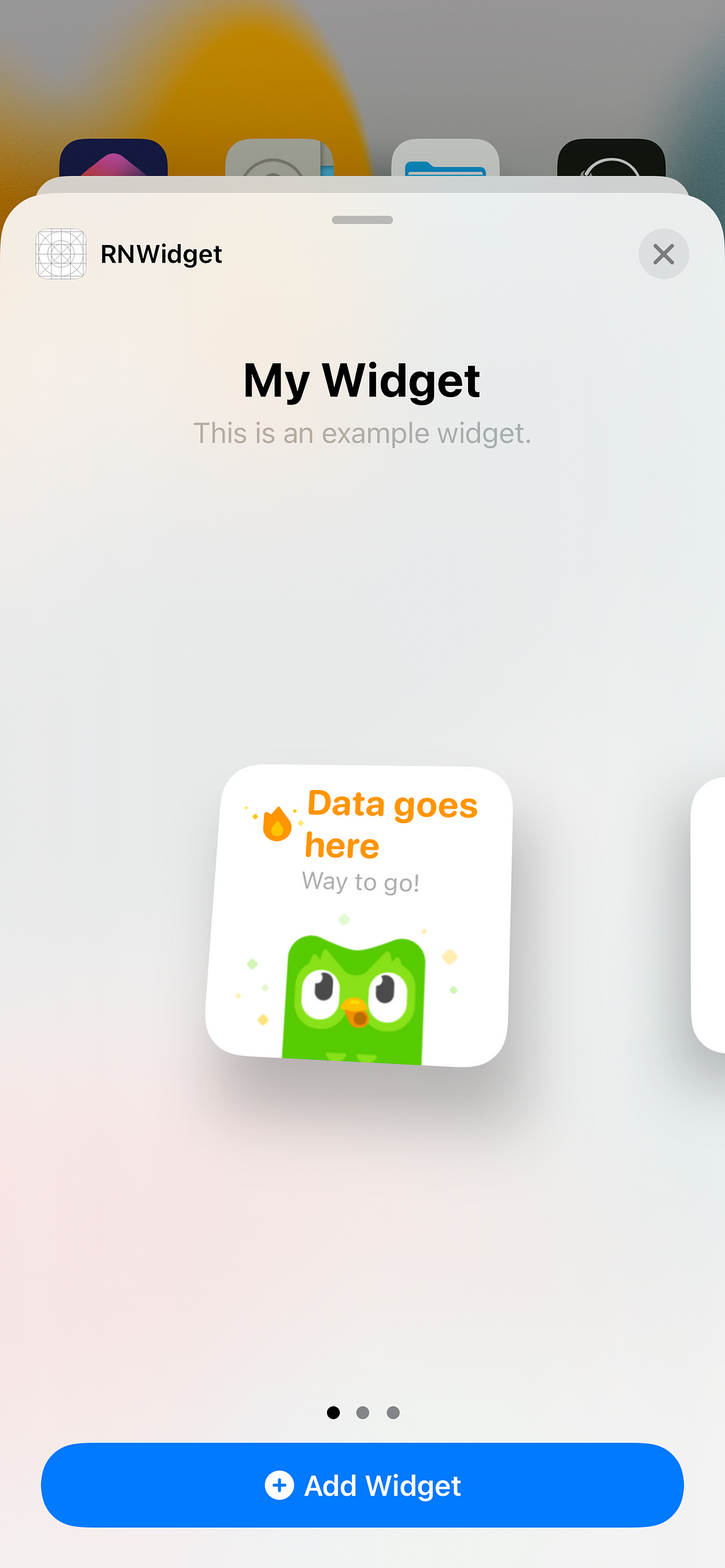
Next, open the app and type something in the input field, press enter, and go back to the home screen.
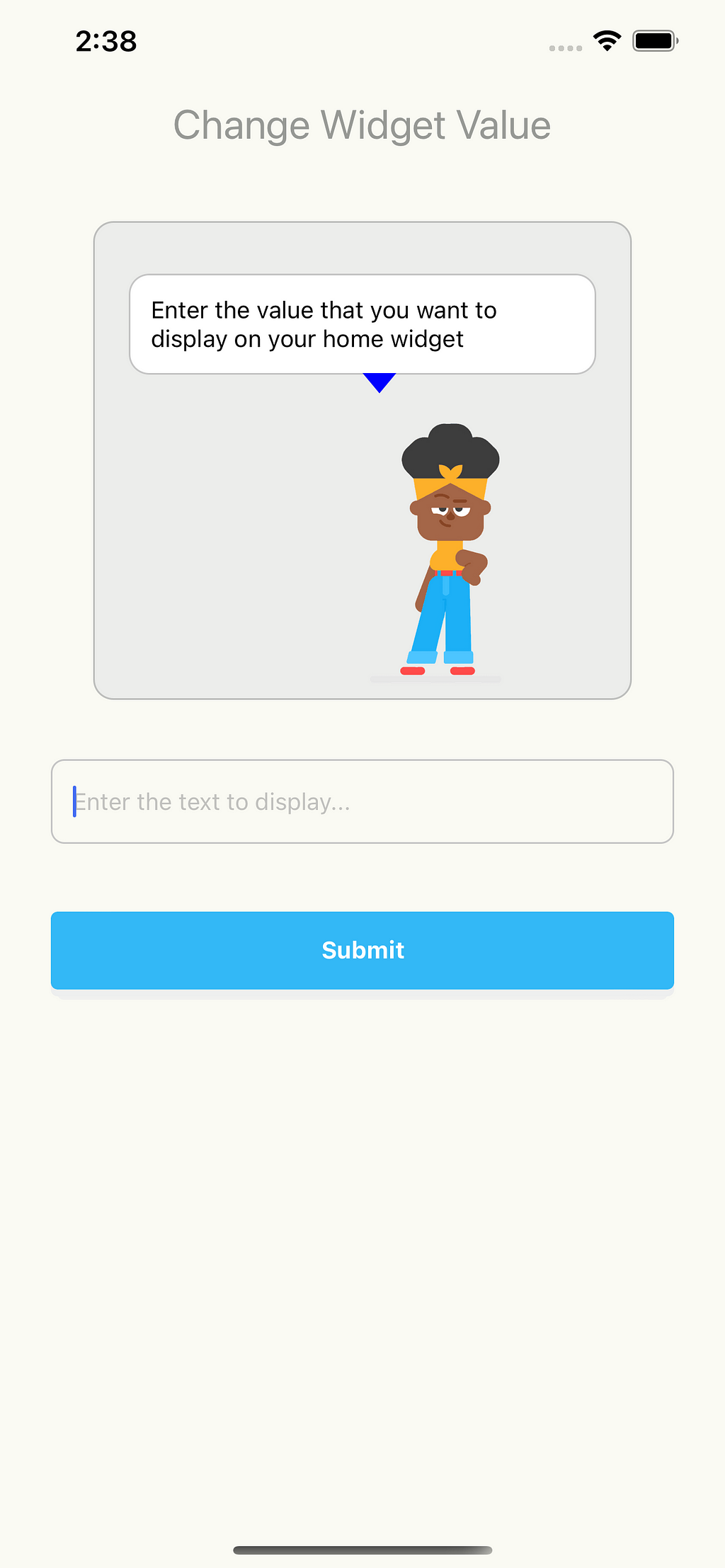
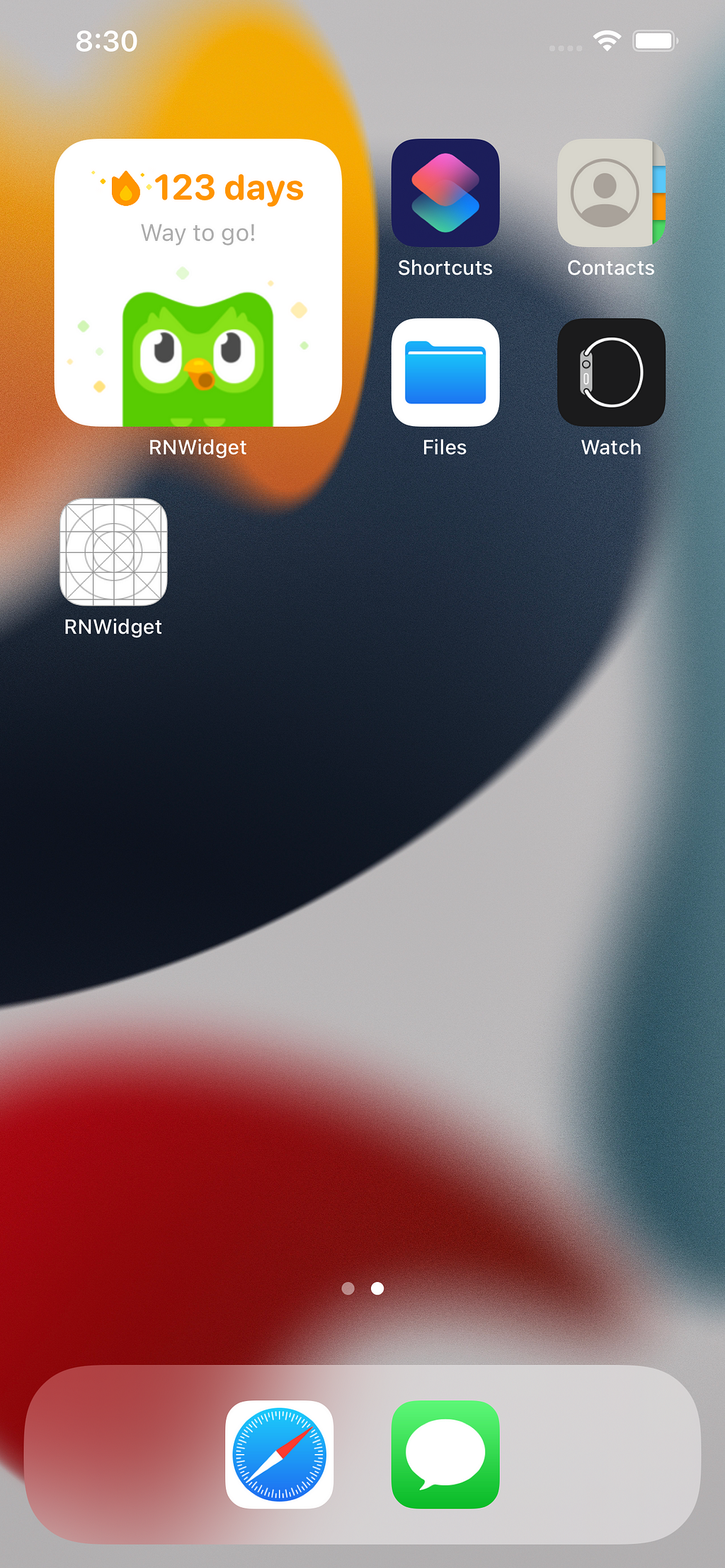
And that’s it for iOS, Now, let’s explore how we can accomplish the same thing on Android.
🤖 Implementation for Android
- Open the Android folder on Android Studio. Then, inside Android Studio, right-click on res > New > Widget > App Widget:
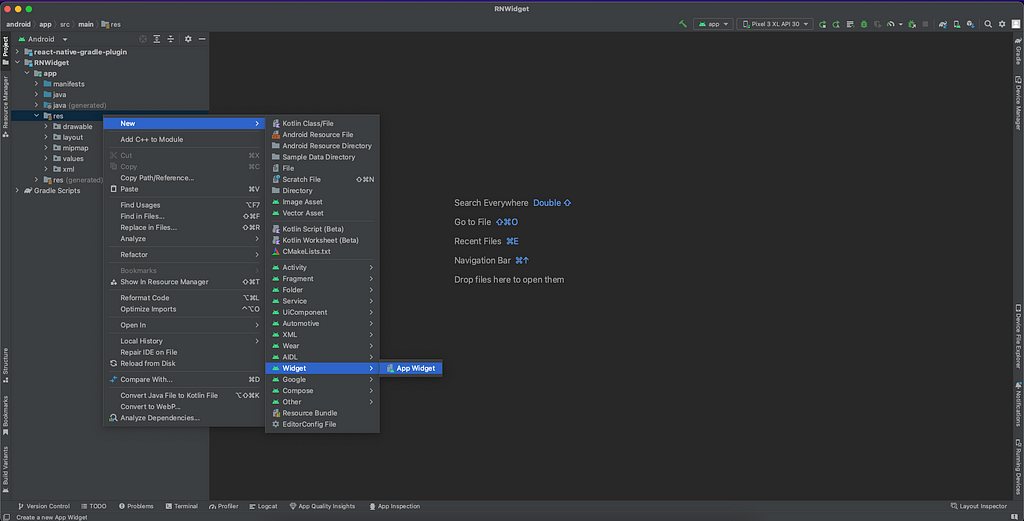
2. Name and configure your widget, and click Finish:
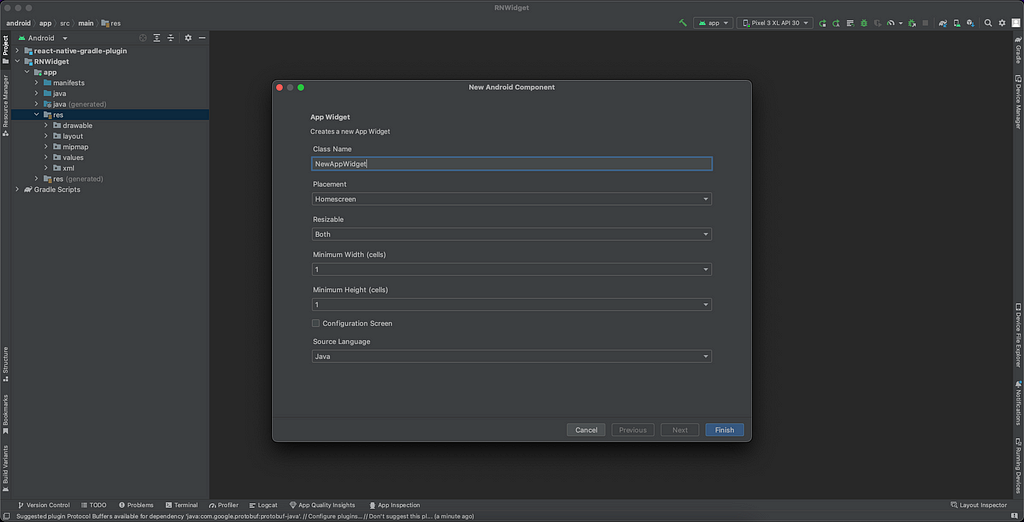
3. Now run the app and you can see the widget available.
4. To communicate between the widget and the React Native app we’ll be using the SharedPreferences Android native module, which is just like UserDefaults for iOS.
This involves adding new SharedStorage.java and SharedStoragePackager.java files to the same directory as your MainApplication.java.
SharedStorage.java
package com.rnwidget;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.NativeModule;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactContext;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactContextBaseJavaModule;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactMethod;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.util.Log;
public class SharedStorage extends ReactContextBaseJavaModule {
ReactApplicationContext context;
public SharedStorage(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
super(reactContext);
context = reactContext;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "SharedStorage";
}
@ReactMethod
public void set(String message) {
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = context.getSharedPreferences("DATA", Context.MODE_PRIVATE).edit();
editor.putString("appData", message);
editor.commit();
Intent intent = new Intent(getCurrentActivity().getApplicationContext(), StreakWidget.class);
intent.setAction(AppWidgetManager.ACTION_APPWIDGET_UPDATE);
int[] ids = AppWidgetManager.getInstance(getCurrentActivity().getApplicationContext()).getAppWidgetIds(new ComponentName(getCurrentActivity().getApplicationContext(), StreakWidget.class));
intent.putExtra(AppWidgetManager.EXTRA_APPWIDGET_IDS, ids);
getCurrentActivity().getApplicationContext().sendBroadcast(intent);
}
}
SharedStoragePackager.java
package com.rnwidget;
import com.facebook.react.ReactPackage;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptModule;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.NativeModule;
import com.facebook.react.bridge.ReactApplicationContext;
import com.facebook.react.uimanager.ViewManager;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class SharedStoragePackager implements ReactPackage {
@Override
public List<ViewManager> createViewManagers(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
@Override
public List<NativeModule> createNativeModules(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
List<NativeModule> modules = new ArrayList<>();
modules.add(new SharedStorage(reactContext));
return modules;
}
}
5. Change the package name for your app as shown in AndroidManifest.xml file inside android > app > src > main.
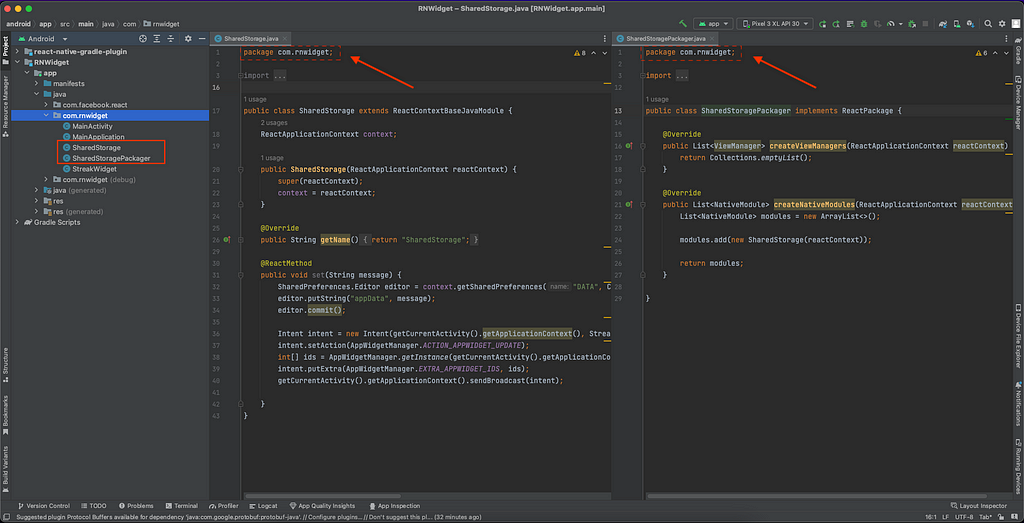
6. After placing those necessary adjustments, go ahead and add this code to your MainApplication.java file within the getPackages method.
packages.add(new SharedStoragePackager());
7. With the bridge set up, let’s move on to receiving data in StreakWidget.java. To update the widget’s content, we’ll need to use SharedPreferences and manage it with the updateAppWidget method. Here’s the code to replace your existing one with:
package com.rnwidget;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetManager;
import android.appwidget.AppWidgetProvider;
import android.content.Context;
import android.widget.RemoteViews;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
/**
* Implementation of App Widget functionality.
*/
public class StreakWidget extends AppWidgetProvider {
static void updateAppWidget(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager,
int appWidgetId) {
try {
SharedPreferences sharedPref = context.getSharedPreferences("DATA", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
String appString = sharedPref.getString("appData", "{\"text\":'no data'}");
JSONObject appData = new JSONObject(appString);
RemoteViews views = new RemoteViews(context.getPackageName(), R.layout.streak_widget);
views.setTextViewText(R.id.appwidget_text, appData.getString("text"));
appWidgetManager.updateAppWidget(appWidgetId, views);
}catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onUpdate(Context context, AppWidgetManager appWidgetManager, int[] appWidgetIds) {
// There may be multiple widgets active, so update all of them
for (int appWidgetId : appWidgetIds) {
updateAppWidget(context, appWidgetManager, appWidgetId);
}
}
@Override
public void onEnabled(Context context) {
// Enter relevant functionality for when the first widget is created
}
@Override
public void onDisabled(Context context) {
// Enter relevant functionality for when the last widget is disabled
}
}
8. Now, let’s talk about the widget’s appearance. This step is optional, but we’ll use the same design as in the iOS example. In Android Studio, navigate to your app > res > layout > streak_widget.xml file. And you can check out the design preview like this
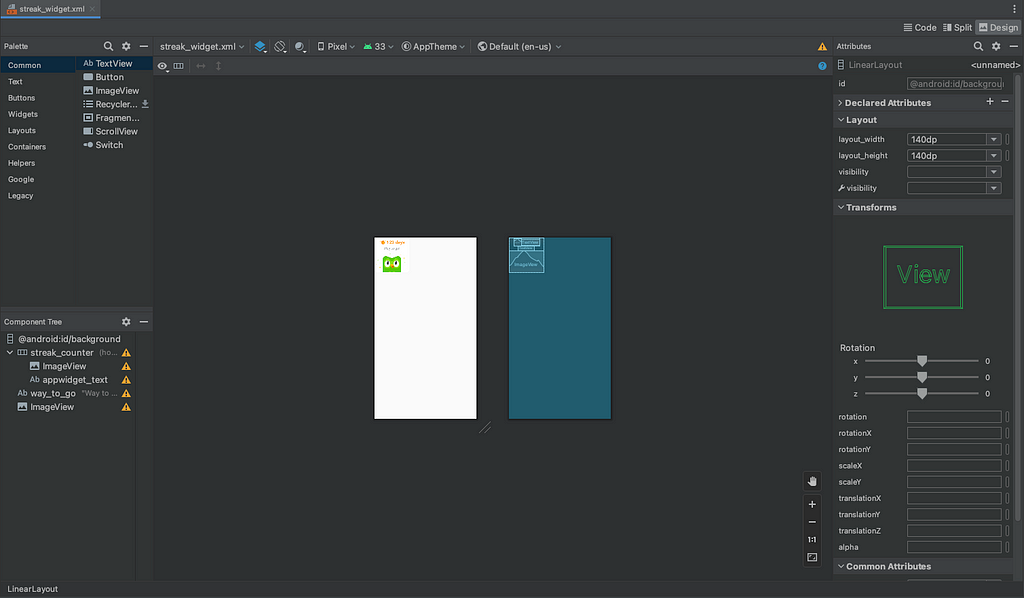
9. That’s all there is to it! Give it a test run on an Android device
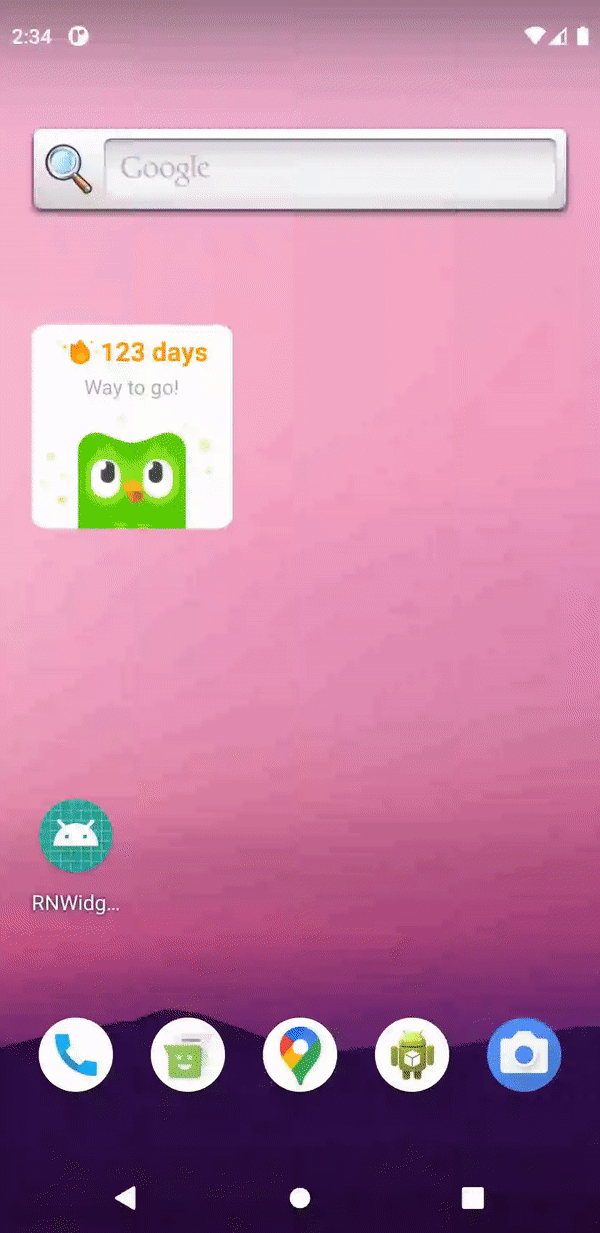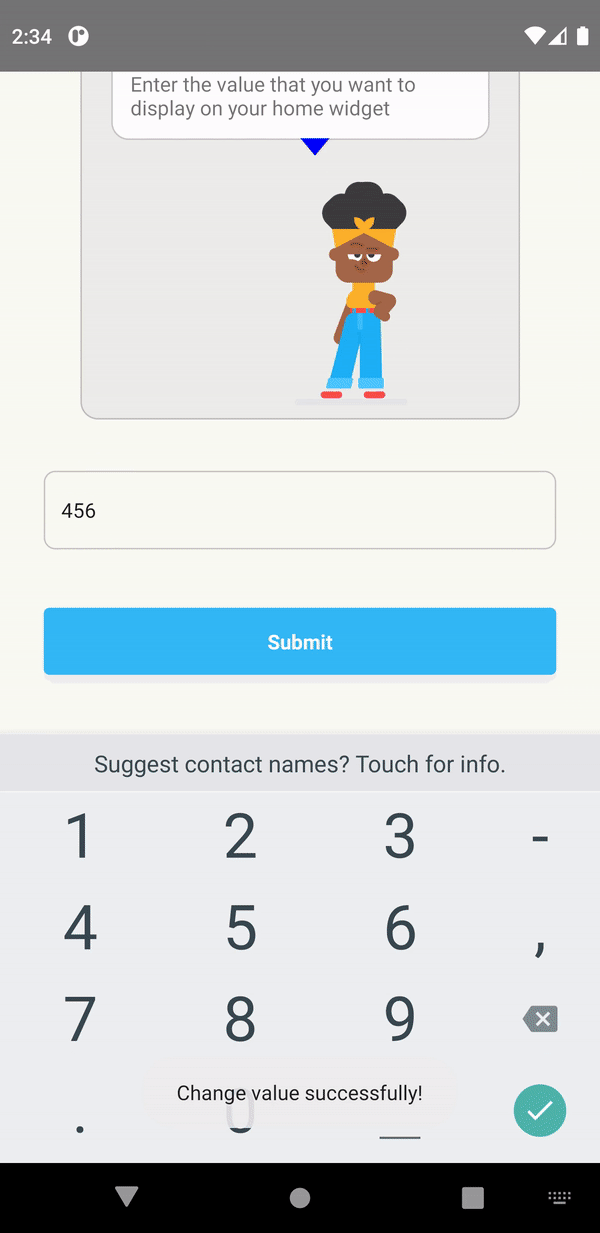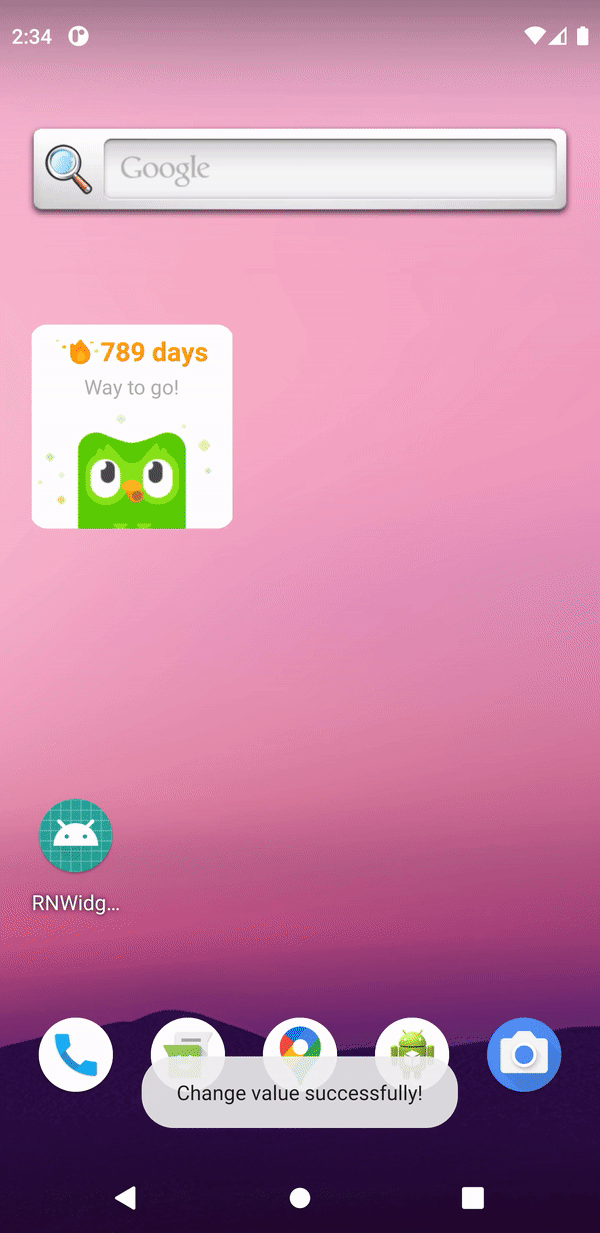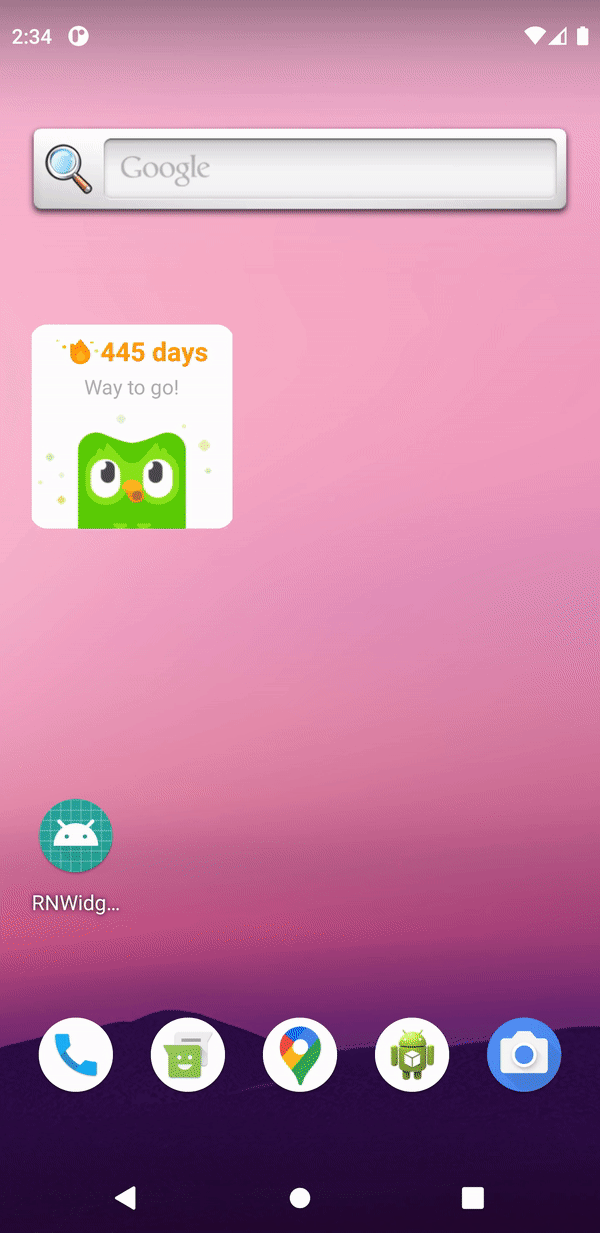
Conclusion
Great job! By learning how to create the AppWidget with React Native, you’ve added a valuable skill to your toolkit. Even if this topic is new to you, don’t worry — it’s straightforward and easy to use in your applications. Keep up the good work!
Kindly give it a clap 👏🏻 and share it with your friends.!!
Please leave a comment with your feedback.
Connect with me on LinkedIn
Level Up Coding
Thanks for being a part of our community! Before you go:
- 👏 Clap for the story and follow the author 👉
- 📰 View more content in the Level Up Coding publication
- 💰 Free coding interview course ⇒ View Course
- 🔔 Follow us: Twitter | LinkedIn | Newsletter
🚀👉 Join the Level Up talent collective and find an amazing job
Discover the Power of Creating Beautiful Home Screen App Widgets with React Native was originally published in Level Up Coding on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Rushit Jivani
Rushit Jivani | Sciencx (2023-05-16T17:18:43+00:00) Discover the Power of Creating Beautiful Home Screen App Widgets with React Native. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2023/05/16/discover-the-power-of-creating-beautiful-home-screen-app-widgets-with-react-native/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
