This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Computational
:::info Authors:
(1) Xiaofan Yu, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California, USA (x1yu@ucsd.edu);
(2) Anthony Thomas, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California, USA (ahthomas@ucsd.edu);
(3) Ivannia Gomez Moreno, CETYS University, Campus Tijuana, Tijuana, Mexico (ivannia.gomez@cetys.edu.mx);
(4) Louis Gutierrez, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, California, USA (l8gutierrez@ucsd.edu);
(5) Tajana Šimunić Rosing, University of California San Diego, La Jolla, USA (tajana@ucsd.edu).
:::
Table of Links
8 Evaluation of LifeHD semi and LifeHDa
9 Discussions and Future Works
10 Conclusion, Acknowledgments, and References
4 PROBLEM DEFINITION
Before diving into our method, we first rigorously formulate the unsupervised lifelong learning problem using streaming sources, driven by real-world IoT applications.
\ Streaming Data. To represent continuously changing environment, we assume a well-known class-incremental model in lifelong learning, in which new classes emerge in a sequential manner [46]. We also allow data distribution shift within one class. This setting models a scenario in which a device is continuously sampling data while the surrounding environment may change implicitly over time, e.g., the self-driving vehicle as shown in Fig. 1. We require that all samples appear only once (i.e., single-pass streams).
\

\ Learning Protocol. Our goal is to build a classification algorithm that maps X → Y. For evaluation, we use the common evaluation protocol in state-of-the-art lifelong learning works [13, 14, 54], in which we construct an iid dataset E = {(𝑋𝑘 , 𝑦𝑘 )} for periodic testing, by sampling labeled examples from each class in a manner that preserves the overall (im)balance between the classes. Note, that even when one class has not appeared in the training data stream, it is always included in E. Hence E is a global view of all classes that can potentially exist in the environment.
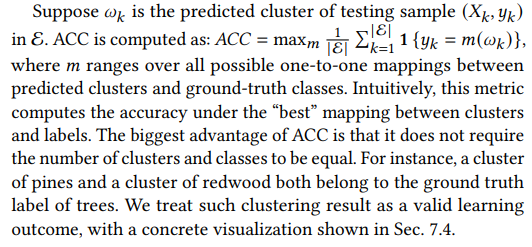
\ Unsupervised Clustering Accuracy. Since we do not give class labels or the total number of classes during training, the predicted label can be different from the ground-truth label. Therefore, for evaluation metric, we cannot adopt the simple prediction accuracy that requires exact label matching. Instead, we employ a widely used clustering metric known as unsupervised clustering accuracy (ACC) [63], which mirrors the conventional accuracy evaluation but within an unsupervised context.
\
\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 DEED license.
:::
\
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Computational
Computational | Sciencx (2024-07-24T15:00:21+00:00) Lifelong Intelligence Beyond the Edge using Hyperdimensional Computing: Problem Definition. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2024/07/24/lifelong-intelligence-beyond-the-edge-using-hyperdimensional-computing-problem-definition/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
