This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Arindam Majumder
Introduction
Since COVID, my calendar has been full of stand-ups, team meetings, and client calls.
\ However, scheduling an event and inviting guests are boring tasks. One Friday, after spending too much time on these, I thought –
Why am I spending so much time on this?
Thus, I had the idea to create an Event scheduler to simplify my work!
\ In this article, I'll show you how to create a Nodejs application that can create events and automatically send out email invites with Google Meet links.
\ Excited? Me too.
\ So, without delaying any further!
\ Let's START!
Project Setup:
1. Create Node.js Project:
To start our project, we need to set up a Node.js environment. So, let's create a node project. Run the following command in the Terminal.
npm init -y
\ This will initialize a new Node.js project.
2. Install Dependencies:
Now, we'll install the required dependencies of our project.
npm install express googleapis dotenv
\ This will install the following packages:
- express: a popular web framework for Node.js
\
- dotenv: loads environment variables from a
.envfile.
\
- googleapis: Provides access to various Google APIs
3. Setup Environment Variables:
Next, we'll create a .env folder to securely store our sensitive information such as API credentials.
//.env
PORT = YOUR_PORT || 8000
CLIENT_ID = YOUR_CLIENT_ID
CLIENT_SECRET = YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET
REDIRECT_URL = http://localhost:8000/auth/redirect
API_KEY = YOUR_API_KEY
4. Create Express Server:
Now, we'll create a index.js file in the root directory and set up a basic express server. See the following code:
const express = require("express");
const dotenv = require("dotenv");
dotenv.config();
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 8000;
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Hello World");
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server running on port ${port}`);
});
Here, We're using the "dotenv" package to access the PORT number from the .env file.
\
At the top of the project, we're loading environment variables using dotenv.config() to make it accessible throughout the file.
Setting Up Google Console
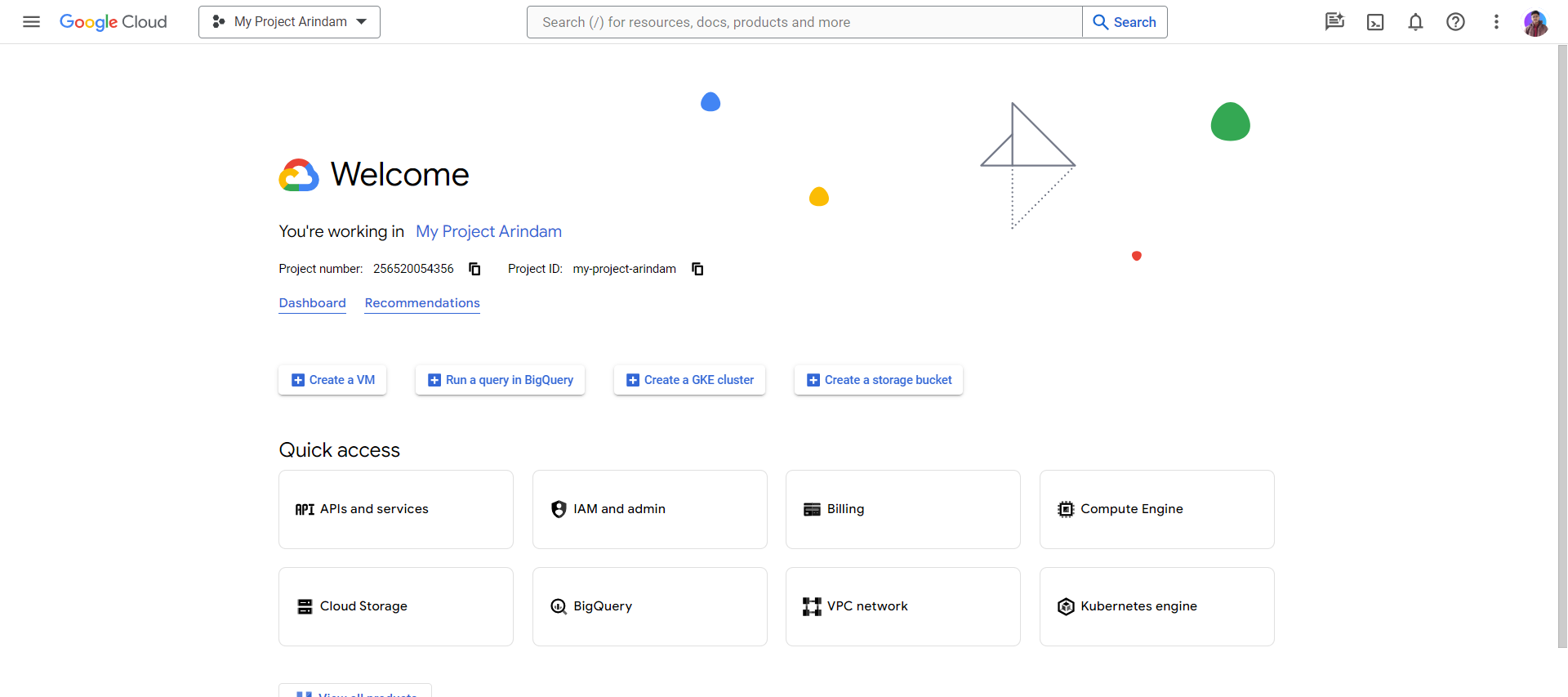
At first, we'll go to the Google Cloud Console.
\ Then we'll get this Dashboard. (I have previously created one project that's why I'm getting this, you might get something else).
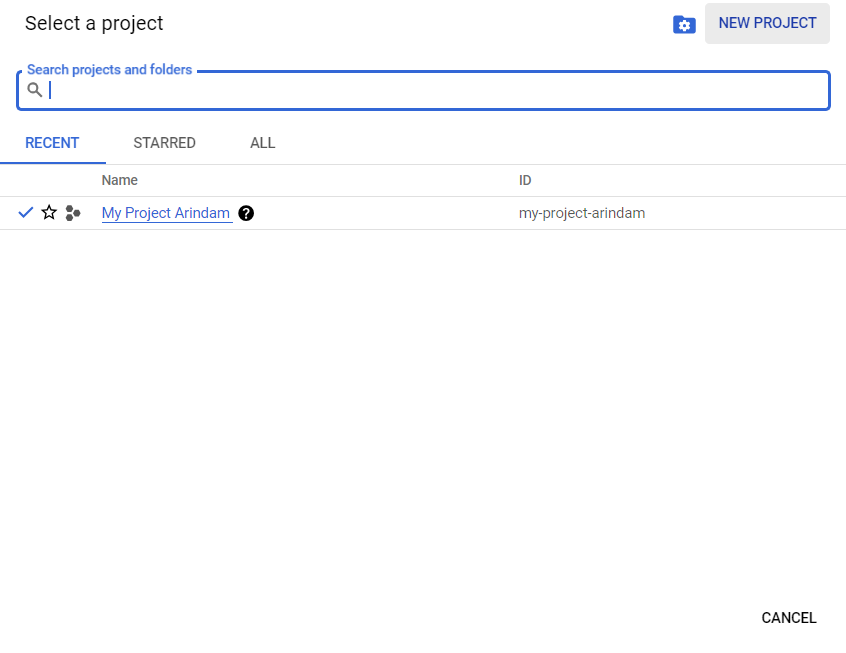
Now, we'll click on the 'New Project' button to start a new project.
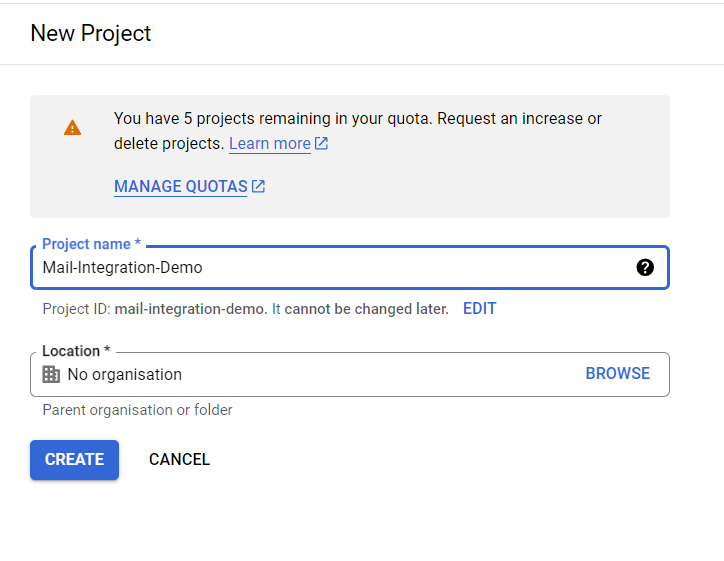
\ Next up, we'll get something like this. Here, we'll add our Project's name and organization. For this project, I'm keeping this as "Mail-integration-Demo." Then we'll click the create button to proceed
\
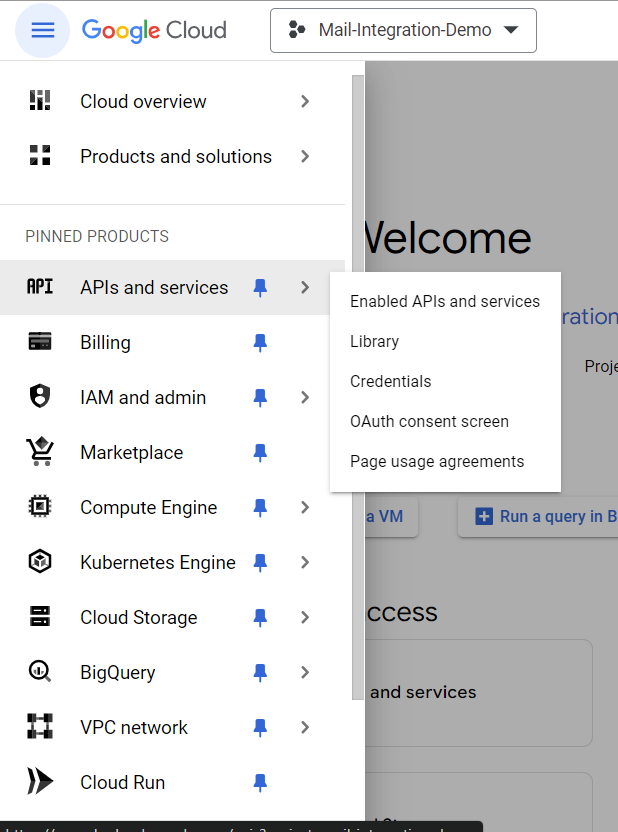
Next, in the side navigation bar, we'll get "APIs and Services." Within this section, there's a submenu to enable APIs and services. We'll click that to proceed.
Next, we'll enable the API that we'll be using in this project, i.e. the Google Calender API.
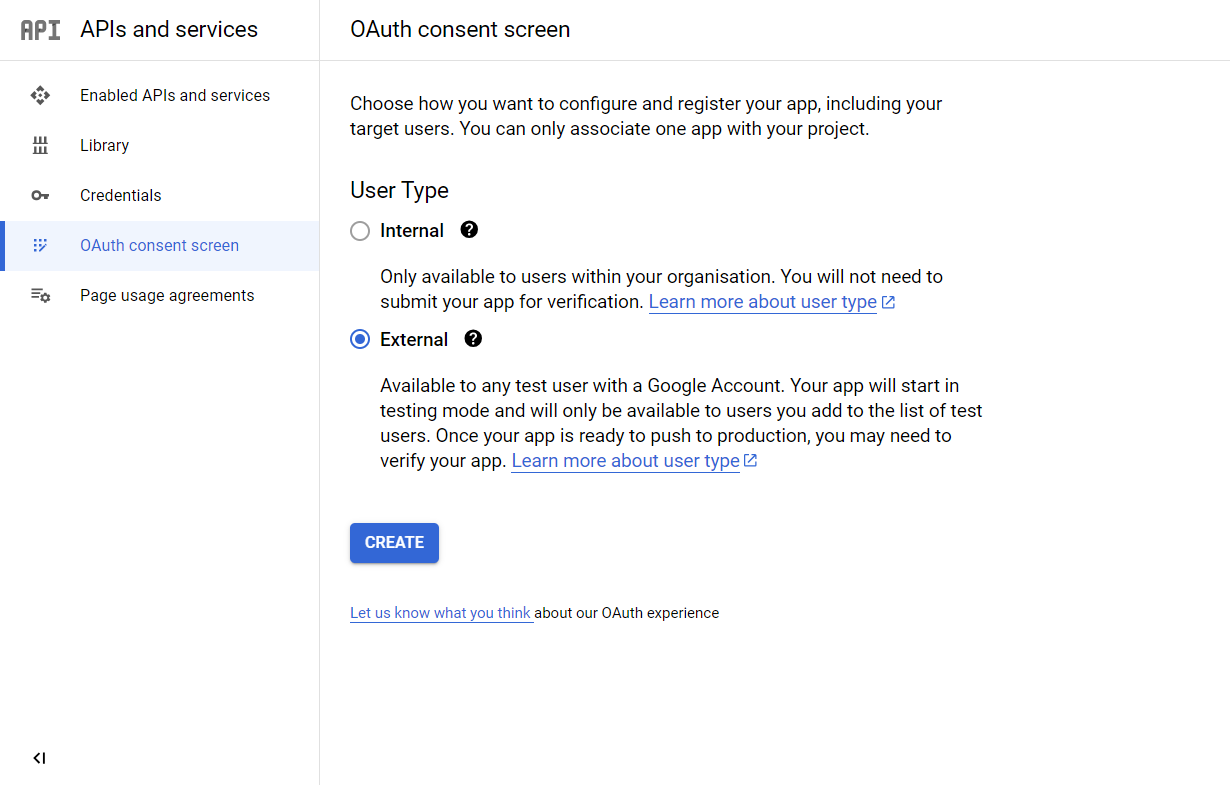
After that, we'll go to the OAuth Consent Screen. Here, we'll select the User Type as External. And we'll press the Create button to proceed.
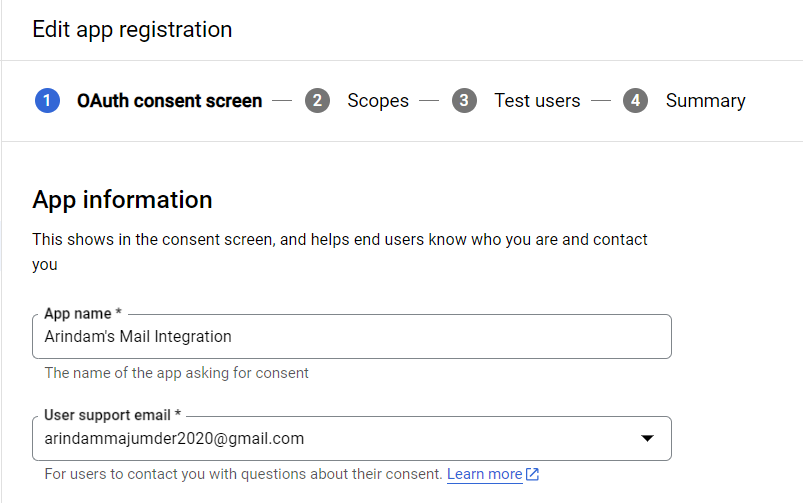
\ Then, we'll go to the app registration page. Here we'll be adding more information about our application. We start by adding the name of our app and an email address for user support.
\ For this project, I'll name it "Arindam's Mail Integration" and use my own email address for support.
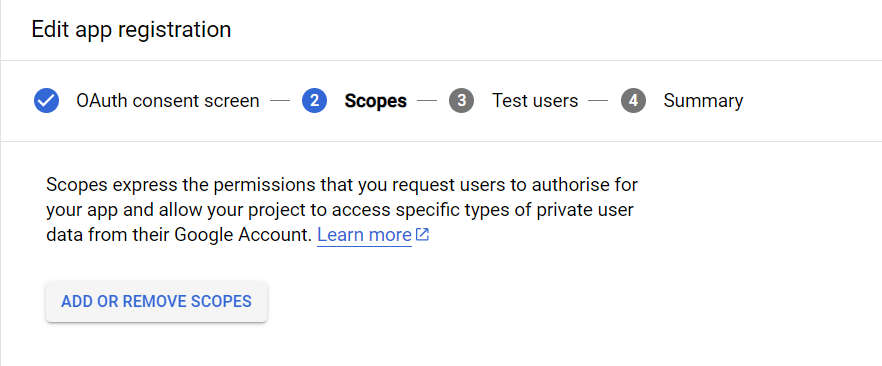
Next, we have to define the scope of the Application.
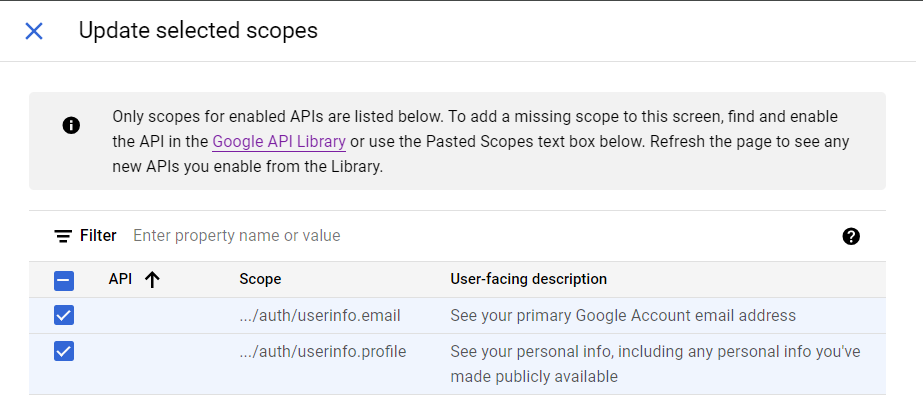
In the Scopes, we'll add necessary permissions such as userinfo.email and userinfo.profile for this project.
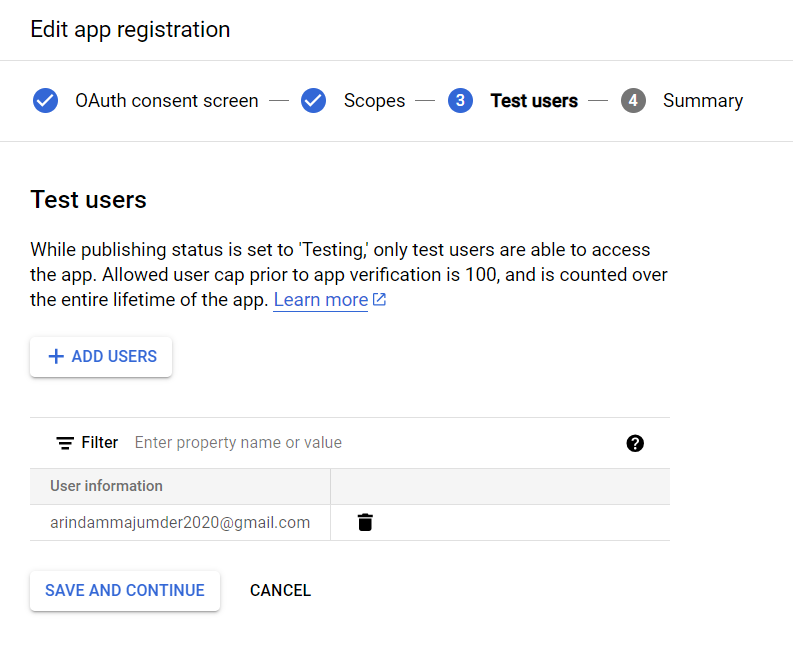
After that, we will add one test user to our application.
That's it. Our application is registered with the platform.
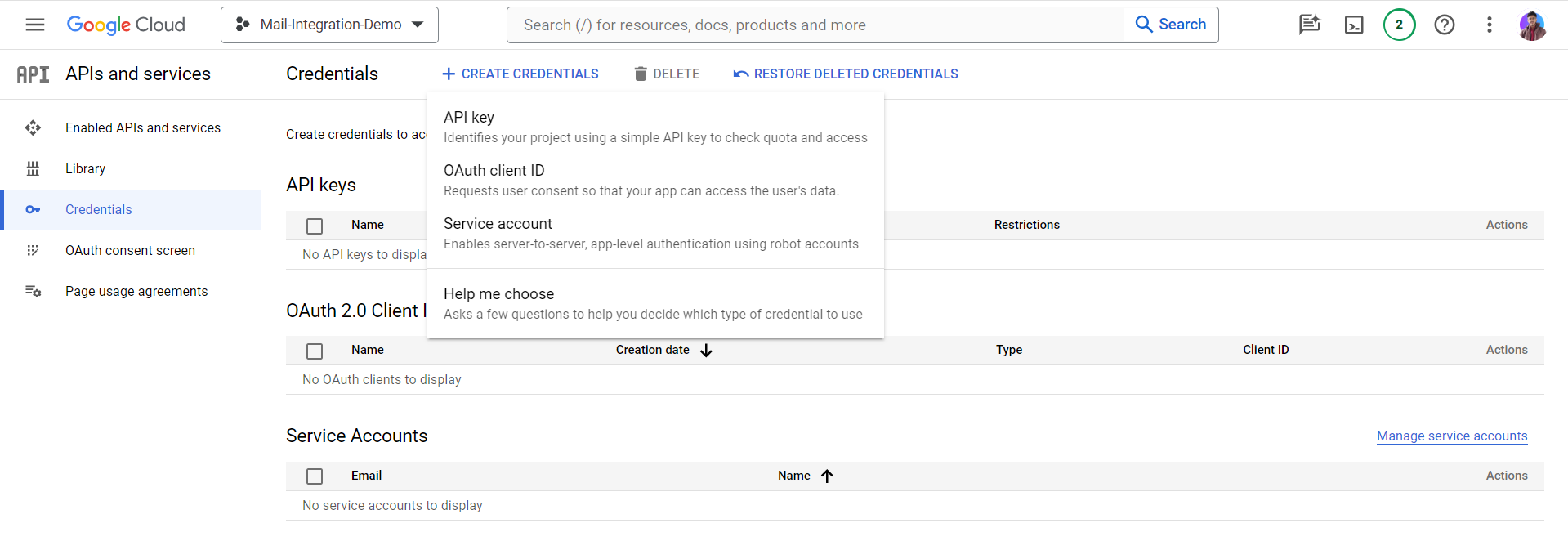
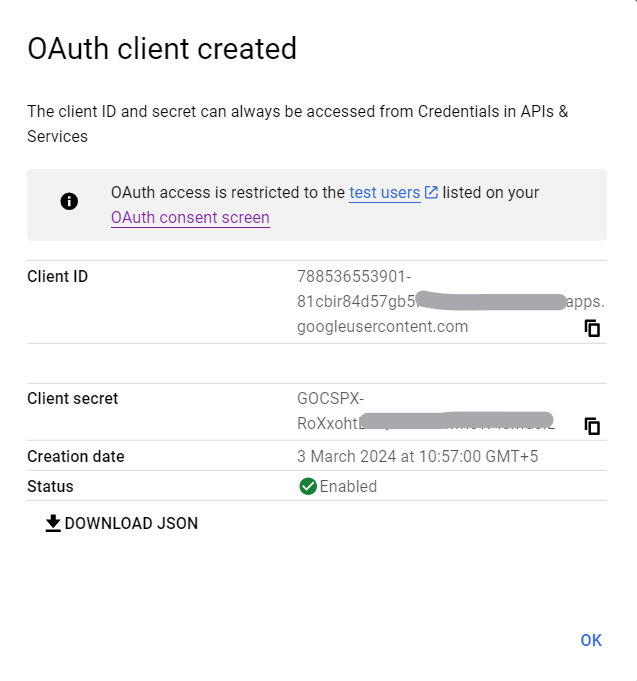
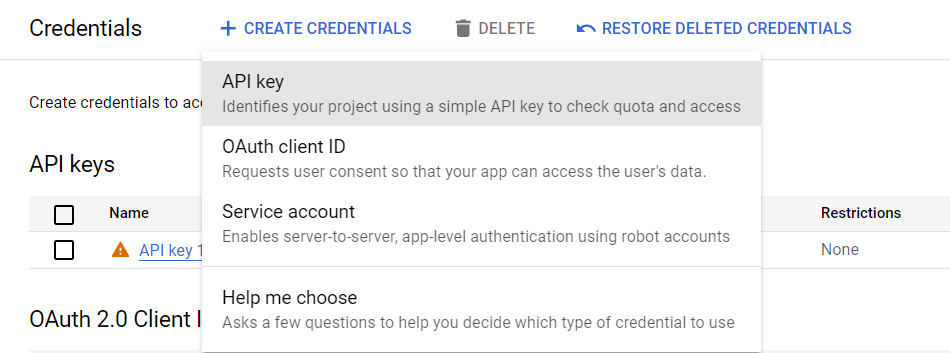
\ Now, we'll create our OAuth Client ID secret. For that, we'll go over to the Create Credential part.
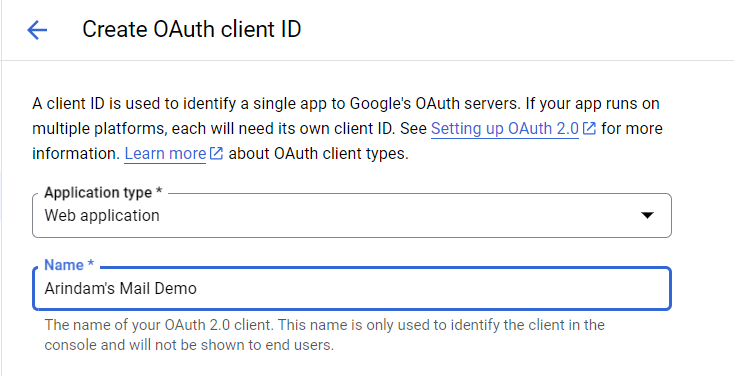
Here, we'll add the type of our application and its name. For this project, it’s a web application, and its name is Arindam's Mail Demo.
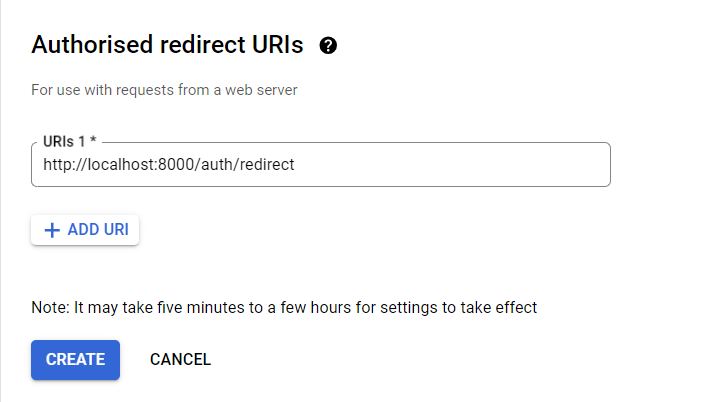
Also, we have added one Redirect URL. For this project, it's going to be http://localhost:8000/auth/redirect.
And then we'll get the OAuth credential.
Next up, we'll create API Keys.
After doing all this, we'll update our .env file with the API keys and the OAuth Credentials that we generated earlier.
\ With this, we have set up our Google Cloud console for this project, now let's move to the next section
OAuth 2 Authentication:
Till now, we have done our basic project setup. Now, we'll integrate OAuth2 Authentication into our Project. This enables our application to interact securely with Google services. For that, first, we'll import the required packages into the index.js file.
const express = require('express');
const { google } = require('googleapis');
const dotenv = require('dotenv');
\ Then we'll define the scope of access required for the Google Calendar API.
const scopes = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar'];
\
Next, we'll configure the OAuth 2 client using the credentials that we have stored in the .env file.
// OAuth 2 configuration
const oauth2Client = new google.auth.OAuth2
(
process.env.CLIENT_ID,
process.env.CLIENT_SECRET,
process.env.REDIRECT_URL
);
\ After the OAuth 2 Configuration, we'll create a Route to Authenticate our Users.
app.get('/auth', (req, res) => {
const url = oauth2Client.generateAuthUrl
({
access_type: 'offline',
scope: scopes
});
res.redirect(url);
}
);
When our users go to this route, they'll be redirected to Google's authentication page where it will ask for specific permissions to our application.
\
After successful authentication, Google will redirect the user to our Redirect URL (/auth/redirect)
app.get("/auth/redirect", async (req, res) => {
const {tokens} = await oauth2Client.getToken(req.query.code);
oauth2Client.setCredentials(tokens);
res.send('Authentication successful! Please return to the console.');
}
);
\
Here, we are getting the refresh tokens from the Query and storing them as credentials in the oauth2Client. These credentials will help us make requests to the Google Calendar API.
\
Here's the complete code for index.js :
//index.js
const express = require('express');
const { google } = require('googleapis');
const dotenv = require('dotenv');
const app = express();
dotenv.config();
const port = process.env.PORT || 8000;
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World');
}
);
// Define the scope of access for the Google Calendar API.
const scopes = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/calendar'];
// OAuth 2 configuration
const oauth2Client = new google.auth.OAuth2
(
process.env.CLIENT_ID,
process.env.CLIENT_SECRET,
process.env.REDIRECT_URL
);
app.get('/auth', (req, res) => {
const url = oauth2Client.generateAuthUrl
({
access_type: 'offline',
scope: scopes
});
res.redirect(url);
}
);
app.get("/auth/redirect", async (req, res) => {
const {tokens} = await oauth2Client.getToken(req.query.code);
oauth2Client.setCredentials(tokens);
res.send('Authentication successful! Please return to the console.');
}
);
Scheduling Events on Google Calendar
Here comes the most important part! In this section, we'll be scheduling an event on Google Calendar!
\ To begin, we'll initialize the Google Calendar API client.
const calendar = google.calendar({
version: 'v3',
auth: oauth2Client
});
\ Next, we'll create an event object where we'll add all the details of the event such as the Summary, Location, Start and End time, etc.
const event = {
summary: 'Tech Talk with Arindam',
location: 'Google Meet',
description: "Demo event for Arindam's Blog Post.",
start: {
dateTime: "2024-03-14T19:30:00+05:30",
timeZone: 'Asia/Kolkata'
},
end: {
dateTime: "2024-03-14T20:30:00+05:30",
timeZone: 'Asia/Kolkata'
},
};
After that we'll create a Route (/create-event ) where we'll create the event.
\
Here we are inserting an event in the user's Calendar using the calendar.events.insert() method.
app.get('/create-event', async (req, res) => {
try {
const result = await calendar.events.insert({
calendarId: 'primary',
auth:oauth2Client,
resource: event
});
res.send({
status: 200,
message: 'Event created',
});
} catch (err) {
console.log(err);
res.send(err);
}
}
);
With this, we can dynamically schedule events on Google Calendar.
Adding Google Meet Link:
Till now, we have explored how to create a simple event on Google Calendar. In this section, we'll explore how to add a Google Meet Link to that Event!
\
For that, we'll be updating the event object that we have created in the previous section. We'll add a conferenceData property to specify the creation request for a Google Meet link.
conferenceData: {
createRequest: {
requestId: uuid(),
}
},
\
We'll also add an attendees property to invite guests to the Event. Here's a simple example of that:
attendees: [
{email: 'arindammajumder2020@gmail.com'},
]
\ Now, the Event object looks like this:
const event = {
summary: 'Tech Talk with Arindam',
location: 'Google Meet',
description: "Demo event for Arindam's Blog Post.",
start: {
dateTime: "2024-03-14T19:30:00+05:30",
timeZone: 'Asia/Kolkata'
},
end: {
dateTime: "2024-03-14T20:30:00+05:30",
timeZone: 'Asia/Kolkata'
},
colorId: 1,
conferenceData: {
createRequest: {
requestId: uuid(),
}
},
attendees: [
{email: 'arindammajumder2020@gmail.com'},
]
};
\
Next, in the event insertion step, we'll add conferenceDataVersion parameter to it.
const result = await calendar.events.insert({
calendarId: 'primary',
auth:oauth2Client ,
conferenceDataVersion: 1,
resource: event
});
\ This will create an Event with a Google Meet Link. We can also share the link as a response like this:
res.send({
status: 200,
message: 'Event created',
link: result.data.hangoutLink
});
Sending Reminder to the Attendees:
So, we're almost done with our project, just the final touch is remaining. Till now, our project will directly add the event to the calendar of the invited guests.
\
However, to notify them about these events, we have to send one Mail. For that, we have to add one parameter sendUpdates: 'all', in the event creation part. With this, the application will automatically send emails to the invited guests.
const result = await calendar.events.insert({
calendarId: 'primary',
auth:oauth2Client ,
conferenceDataVersion: 1 ,
sendUpdates: 'all',
resource: event
});
With this addition, our project now seamlessly handles both event creation and email notifications.
Testing the Application:
The coding part of our project is completed. Now, let's see if it's working or not!
\ For that, we'll start the project!
npm run start
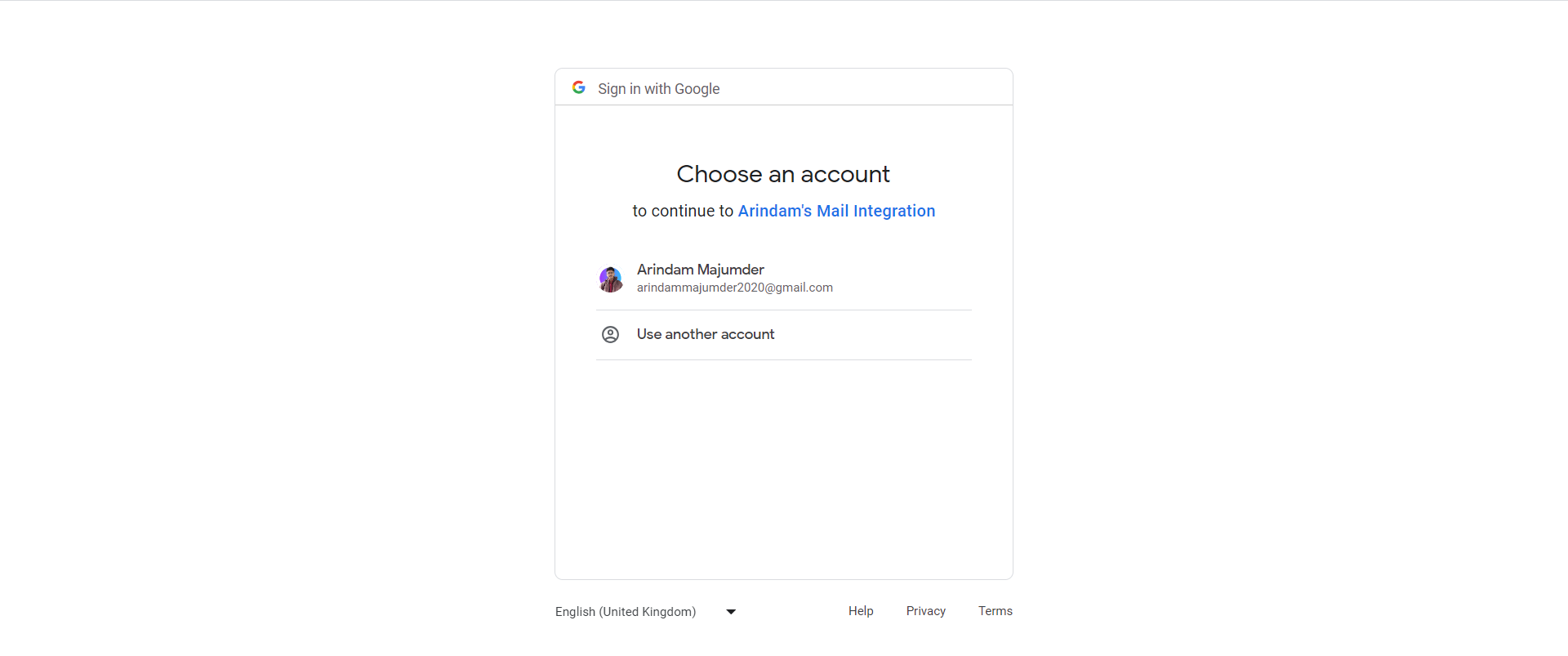
\ And we have started our Server on port 8000! Now, we'll go to the http://localhost:8000/auth/ route to authenticate the user. It will redirect us to something like this:
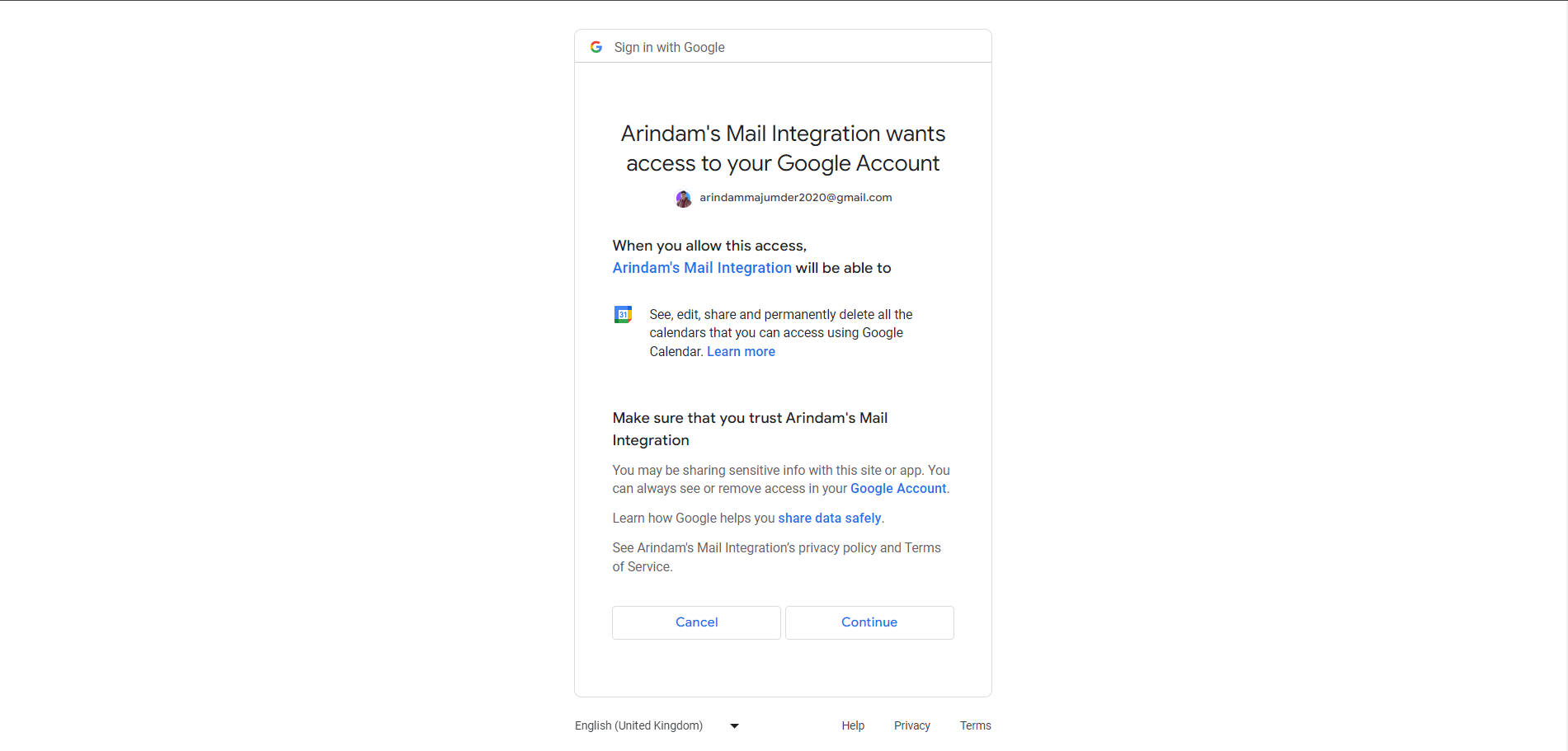
It will ask for some permission for the application.
It will redirect to the /auth/redirect route with the code query parameter.
After successfully authenticating the user, we'll go to the http://localhost:8000/create-event route to schedule the Event.
Awesome! It means our event is created with a Google Meet link.
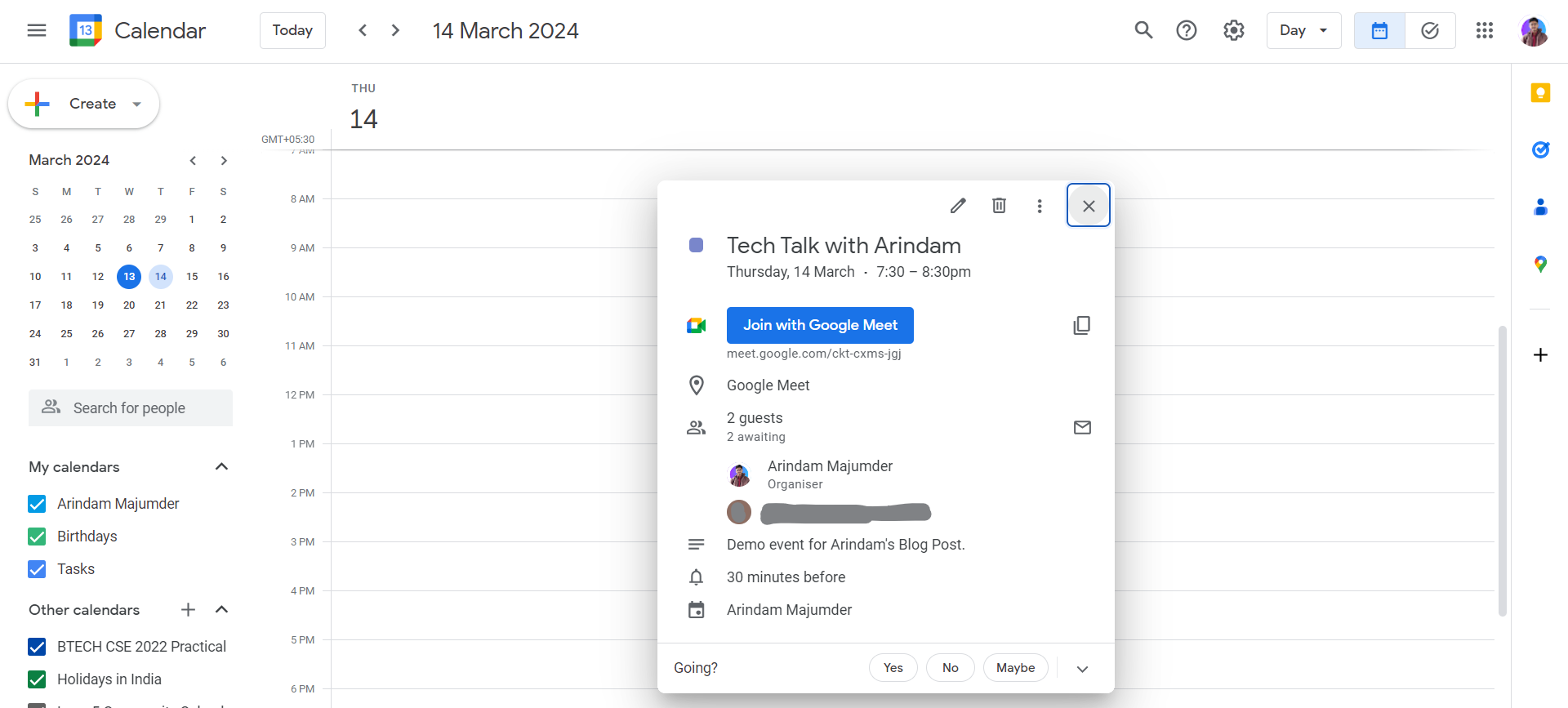
\ To verify that the event creation process is functioning correctly, let's check our Google Calendar
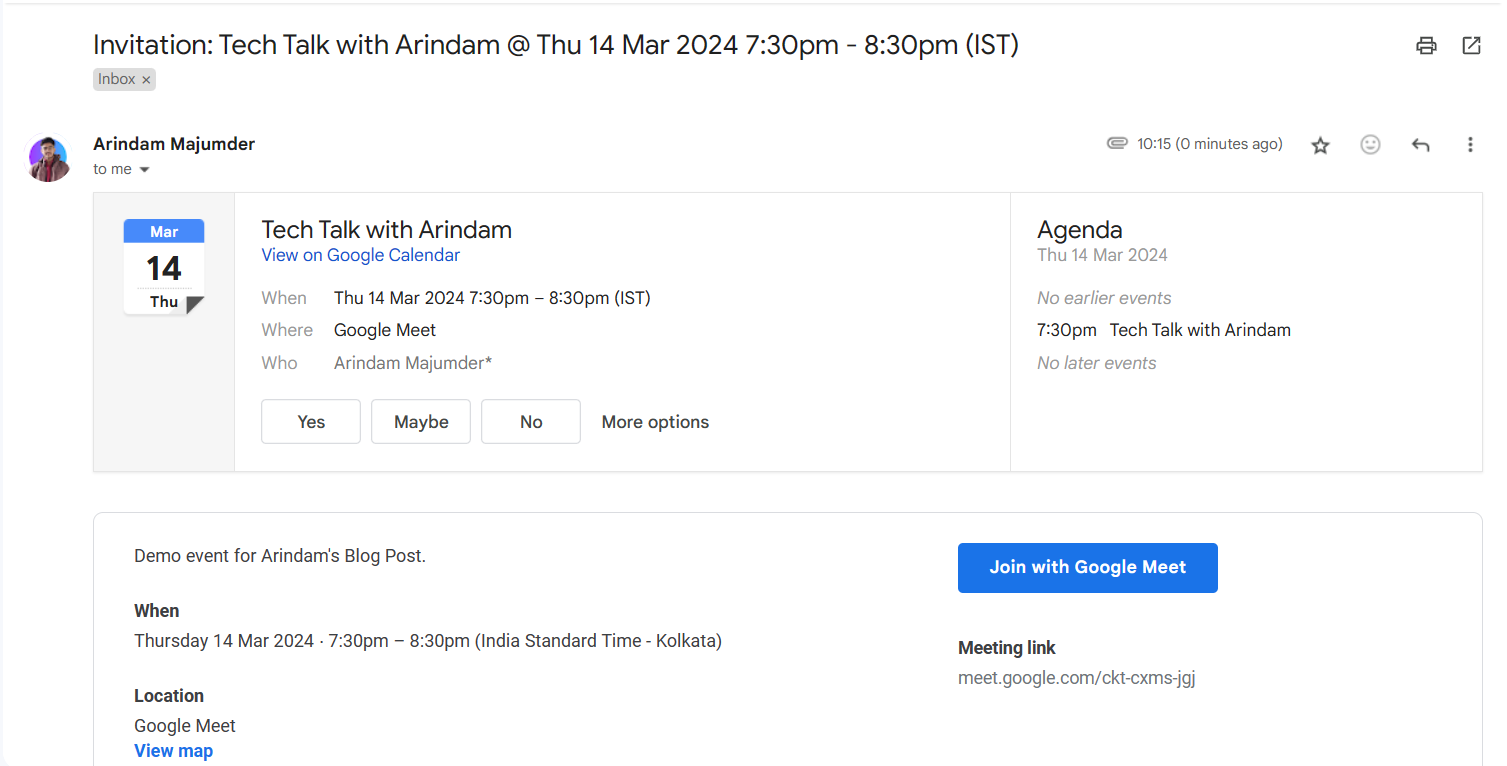
Amazing! Our Event is created which means the Event-creation route is working perfectly! And we also got an Invite mail as well:
Great! Our application is working perfectly!
\ With that, we have integrated Google Calendar into our Node.js app. In the following articles, we'll explore more use cases with Google Calendar.
\ Till then, stay tuned!
Conclusion
If you found this blog post helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit. You can also follow me for more content on Javascript, React, and other web Development topics.
\ For Paid collaboration, mail me at: arindammajumder2020@gmail.com
\ Connect with me on Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, and GitHub.
\ Thank you for Reading :)
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Arindam Majumder
Arindam Majumder | Sciencx (2024-08-18T18:00:19+00:00) How I Built an Event Scheduler in NodeJs. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2024/08/18/how-i-built-an-event-scheduler-in-nodejs/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.