This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Laszlo Fazekas
One of the most important new features in the latest (2.2) version of the Bee client is the support for access control. This feature is long coveted by the power users and was delivered by Solarpunk Ltd. an ecosystem company pushing the boundaries of Swarm.
\ Ethereum Swarm is a decentralized storage and communication engine that, thanks to a well-designed incentive system, aims to optimize the use of available storage and bandwidth. A fundamental aspect of this is the immutable storage, which enables efficient caching. As a result, Swarm is an ideal content delivery network and could serve as a foundation for streaming services. In Swarm, data is distributed optimally and redundantly across the network. Implementing access control in such a system is not a trivial task.
\ Node-level access control cannot be implemented in such a decentralized system; the only option is to store the data in encrypted form and distribute the key to authorized users. Ethereum Swarm's solution for distributing decryption keys is the ACT (Access Control Trie). The essence of the solution is illustrated in the following diagram:
\
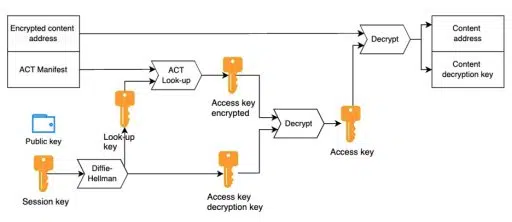
\ If we want to protect content with access control, Swarm creates a special chunk that contains the real content address in encrypted form, along with the ACT manifest. The entry point to access controlled content is the encrypted reference. Those who can decrypt it can then access the reference and the decryption key, which allows them to read the content.
\ Access control allows publishers to grant access to identities as long as they have their public keys. The core notion is the session key, which is the shared secret between the publisher and grantee, a key that both parties can produce using their private key and the counterparty's public key.
\ The ACT is a key value table from which users can obtain the decryption key to decipher the encrypted reference to the content. Surely this key is encrypted individually for every grantee under the ACT. Since both the encryption key and the lookup key are generated from this session key, not only is access restricted, but all information about other grantees or even their numbers is obfuscated for participants.
\ The low-level protocol is completely hidden by the Bee API. Content can be uploaded through the usual API calls. By specifying a header parameter, it is possible to protect the content with access control.
\ Accessing the content is completely transparent for authorized users. The content can be retrieved through the usual endpoint. If a user cannot find its entry in the ACT manifest, an authorization error will be returned.
\ Swarm's Access Control solution can be useful in many new areas. One typical use case is content monetization. With a simple, smart contract and minimal backend, we can make our content, such as books, videos, music, etc., available for purchase.
\ As I mentioned in the introduction, Swarm is not only a storage engine but also a content delivery network, making it an ideal foundation for streaming services. This opens up the possibility of creating subscription-based streaming services (video, music, gaming, etc.).
\ Of course, monetization is not the only area where access control can be useful. Combined with Swarm feeds, we can create social networks with closed groups or store sensitive documents on Swarm, which only authorized users can access.
\ As you can see, thanks to the access control feature, services can now be built on top of Swarm's decentralized, censorship-resistant system, which previously was only possible by using cloud services.
\ For those interested in the deeper technical details, you can read more about it on the Solar Punk Blog: https://solarpunk.buzz/introducing-the-access-control-trie-act-in-swarm/
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Laszlo Fazekas
Laszlo Fazekas | Sciencx (2024-09-26T16:48:25+00:00) Understanding Access Control in Ethereum Swarm. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2024/09/26/understanding-access-control-in-ethereum-swarm-2/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
