This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Tech Media Bias [Research Publication]
Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction 2. Data
3. Measuring Media Slant and 3.1. Text pre-processing and featurization
3.2. Classifying transcripts by TV source
3.3. Text similarity between newspapers and TV stations and 3.4. Topic model
4. Econometric Framework
4.1. Instrumental variables specification
4.2. Instrument first stage and validity
5. Results
6. Mechanisms and Heterogeneity
6.1. Local vs. national or international news content
6.2. Cable news media slant polarizes local newspapers
\ Online Appendices
A. Data Appendix
A.2. Alternative county matching of newspapers and A.3. Filtering of the article snippets
A.4. Included prime-time TV shows and A.5. Summary statistics
B. Methods Appendix, B.1. Text pre-processing and B.2. Bigrams most predictive for FNC or CNN/MSNBC
B.3. Human validation of NLP model
B.6. Topics from the newspaper-based LDA model
C. Results Appendix
C.1. First stage results and C.2. Instrument exogeneity
C.3. Placebo: Content similarity in 1995/96
C.8. Robustness: Historical circulation weights and C.9. Robustness: Relative circulation weights
C.12. Mechanisms: Language features and topics
C.13. Mechanisms: Descriptive Evidence on Demand Side
C.14. Mechanisms: Slant contagion and polarization
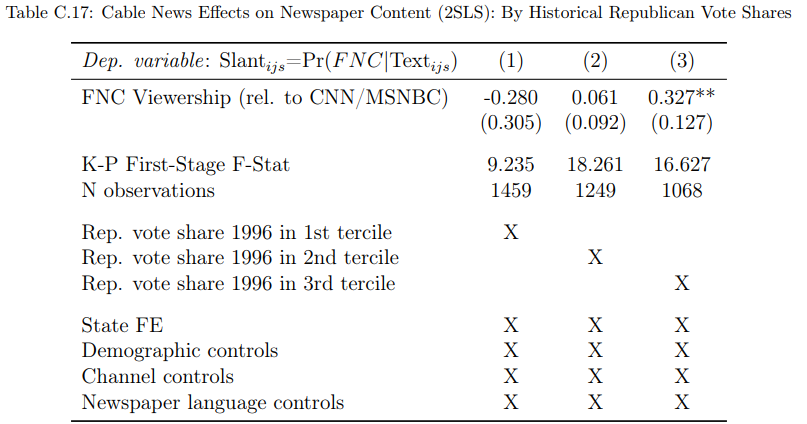
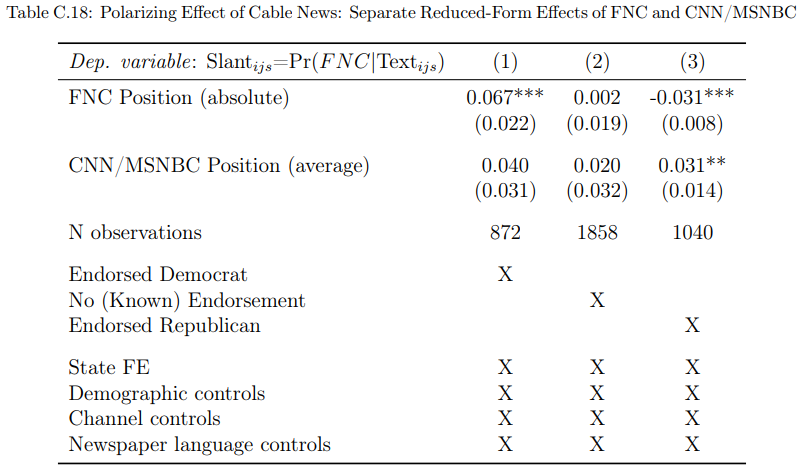
C.14. Mechanisms: Slant contagion and polarization
Here, we replicate Table 4, but instead of pre-FNC/MSNBC era newspaper endorsements, we distinguish observations by the county-level Republican vote share terciles (lowest tercile in the first column, second tercile in middle, and highest tercile in the last column). Qualitatively, we find the same pattern: The relative FNC exposure coefficient is negative in the first column, positive plus relatively small in the second column (coefficients in columns 1 and 2 are not significant), before turning significant, positive, and large in the last column.
\
\
\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC 4.0 license.
:::
:::info Authors:
(1) Philine Widmer, ETH Zürich and philine.widmer@gess.ethz.ch;
(2) Sergio Galletta, ETH Zürich and sergio.galletta@gess.ethz.ch;
(3) Elliott Ash, ETH Zürich and ashe@ethz.ch.
:::
\
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Tech Media Bias [Research Publication]
Tech Media Bias [Research Publication] | Sciencx (2025-02-08T03:16:31+00:00) Media Slant: Slant Contagion and Polarization. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/02/08/media-slant-slant-contagion-and-polarization/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
