This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Transcompiler: Learn How to Translate Code
Table of Links
B Details of Think-and-Execute
C Prompts Used in Our Experiments
D Human-written Pseudocode Prompts
F Generated Pseudocode Prompts
D Human-written Pseudocode Prompts
D.1 Human-written P of Dyck Languages

D.2 Human-written P of Geometric Shapes

D.3 Human-written P of Navigate
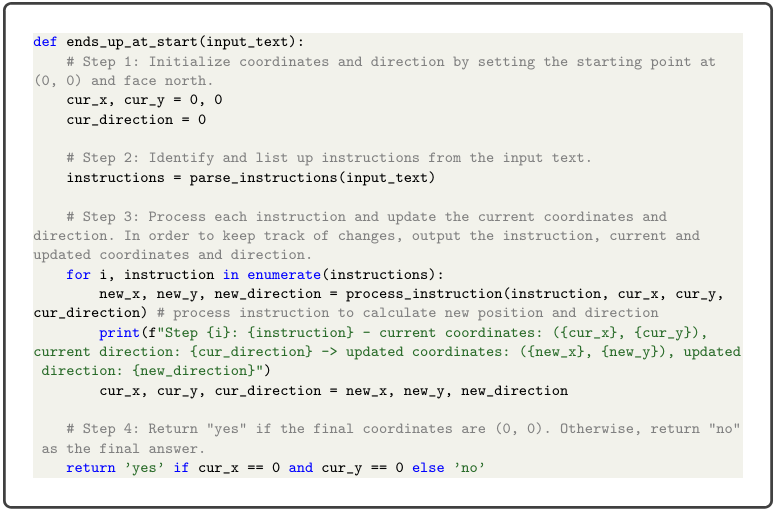
D.4 Human-written P of Reasoning about Colored Objects

D.5 Human-written P of Temporal Sequences

D.6 Human-written P of Tracking Shuffled Objectives

D.7 Human-written P of Web of Lies

\
:::info This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 DEED license.
:::
:::info Authors:
(1) Hyungjoo Chae, Yonsei University;
(2) Yeonghyeon Kim, Yonsei University;
(3) Seungone Kim, KAIST AI;
(4) Kai Tzu-iunn Ong, Yonsei University;
(5) Beong-woo Kwak, Yonsei University;
(6) Moohyeon Kim, Yonsei University;
(7) Seonghwan Kim, Yonsei University;
(8) Taeyoon Kwon, Yonsei University;
(9) Jiwan Chung, Yonsei University;
(10) Youngjae Yu, Yonsei University;
(11) Jinyoung Yeo, Yonsei University.
:::
\
This content originally appeared on HackerNoon and was authored by Transcompiler: Learn How to Translate Code
Transcompiler: Learn How to Translate Code | Sciencx (2025-03-22T01:03:07+00:00) Examples of Human-Written Pseudocode Prompts. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2025/03/22/examples-of-human-written-pseudocode-prompts/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
