This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Prathibha Perera
Basic knowledge you need when dealing with the RE

A regular expression is a searching pattern that contains a sequence of characters. Regular expressions are useful for extracting information from a text by searching for one or more matches of a specific search pattern. When we are working with regular expressions there are common things that are needed to deal with. They can be categorized as follows.
- Basic pattern
- [] operator
- () operator
- Character classes
- Negation
- ^ and $
- OR operator - |
- Operator based (*, +, ?, .)
- Numerical range
- Boundaries
I use regexr.com to practice regular expressions. You can practice one by one to get the basic knowledge about the RE as follows.
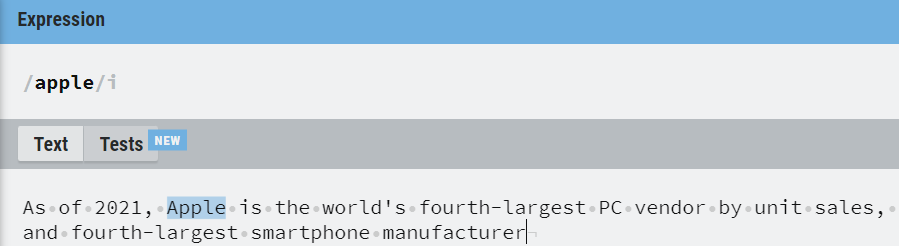
1. Basic pattern
It is the simplest regular expression form that is the character sequence itself, used to match a sequence of characters within a given sentence or paragraph.

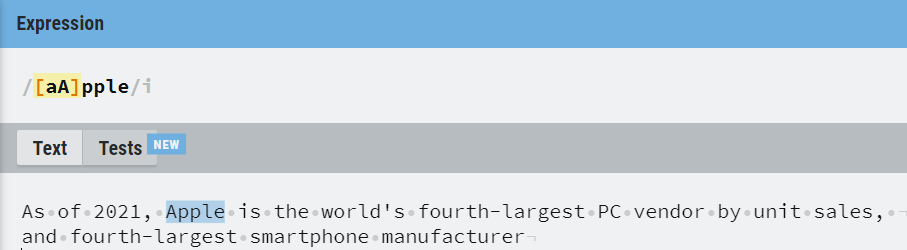
2. [] Operator
Square braces specify a disjunction of characters to match
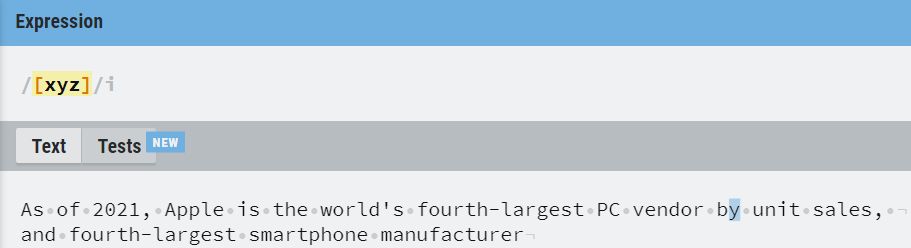

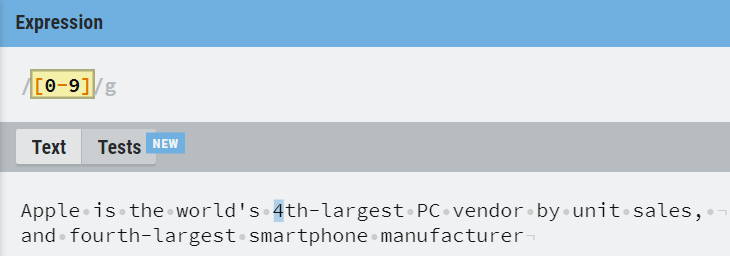
Dash (-) with [] is used to specify any one character in a range
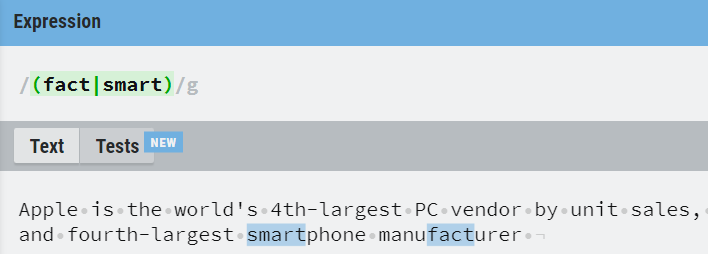
3. () Operator
It constructs a grouping construct to establish a precedence order and parenthesis is also useful for OR’ing two expressions with the bar | character.
4. Character classes
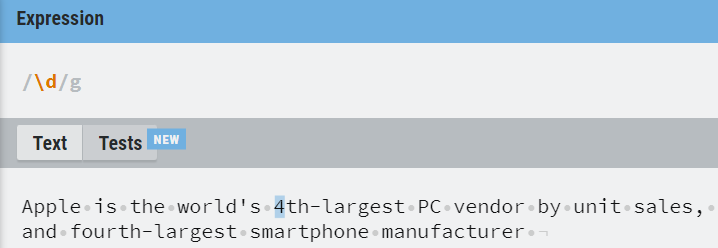
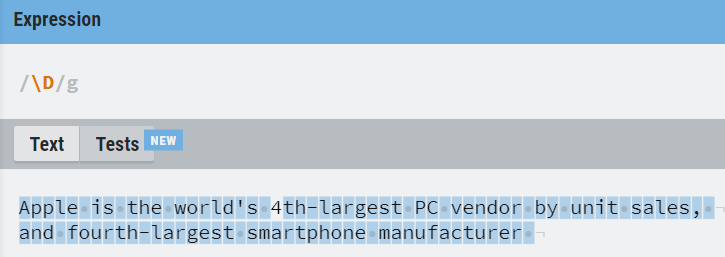
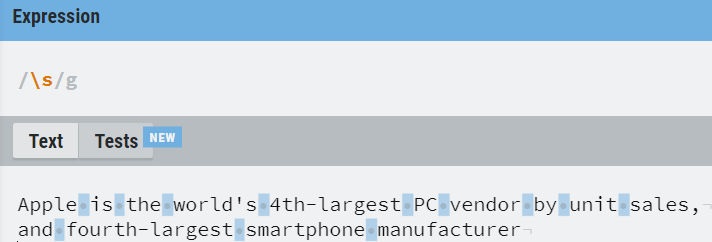
The following table has mentioned the basic character classes that are useful for you to deal with RE.
+---------------+----------------------------------------------+
| Metacharacter | Behavior |
+---------------+----------------------------------------------+
| \d | Match any digit character [0-9] |
| \D | Match any non-digit character |
| \n | Match a new line |
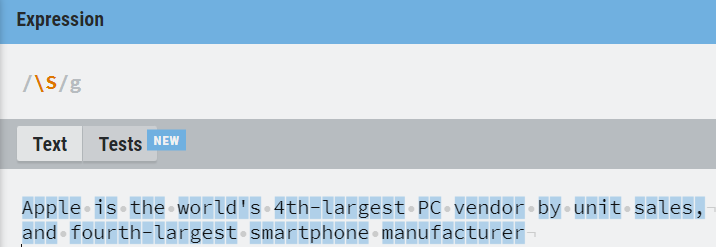
| \s | Match white spaces |
| \S | Match non-white spaces |
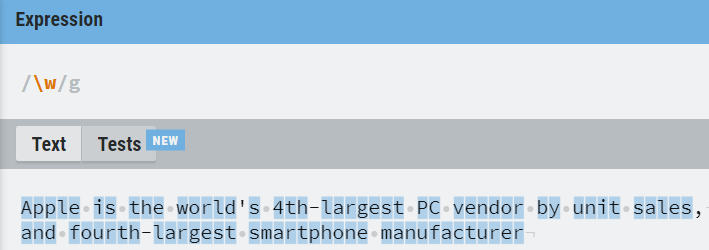
| \w | Match word characters (includes a-z and 0–9) |
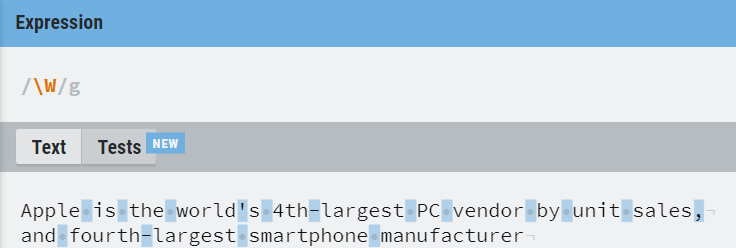
| \W | Match non-word characters |
| | |
+---------------+----------------------------------------------+
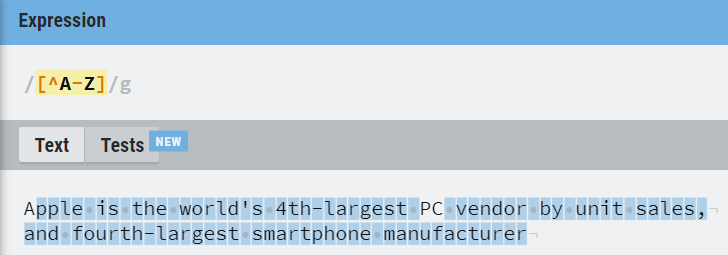
5. Negation
If the ^ caret symbol is the first symbol after opening the square brace, it specifies the negation operation.
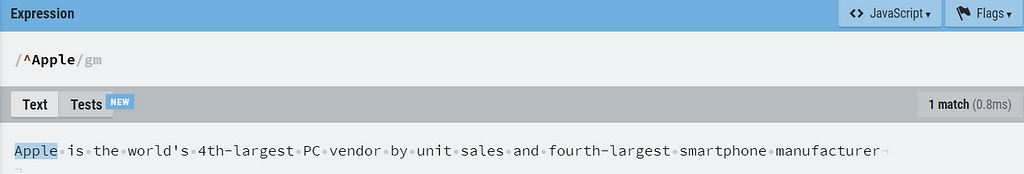
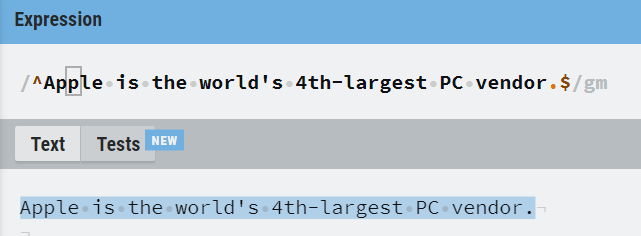
6. ^ and $
^ and $ can be called as most common anchors in regular expressions. ^ matches the start of a line and $ matches the end of the line.
Here examples match with the multiline flag enabled.

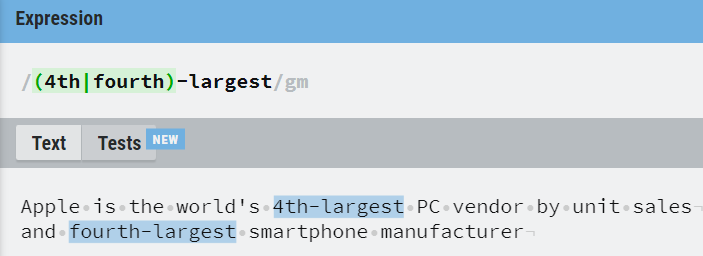
7. OR Operator — |
The OR operator allows us to specify different allowable capture groups
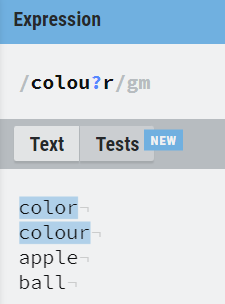
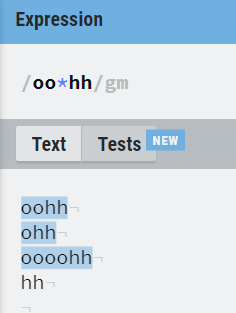
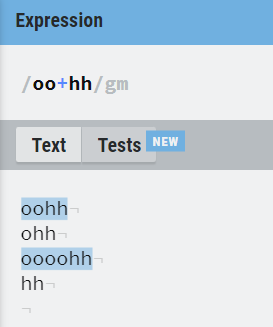
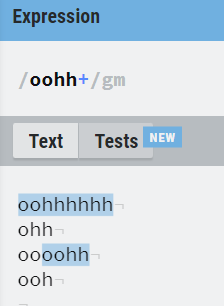
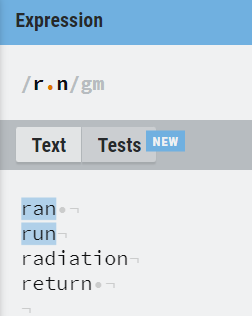
8. Operator based ( *, + , ?, . )
*, +, ? and . are the operators that are used to deal with RE.

9. Numerical range
It is used to specify a quantity range using {low, high}
{n,m} — minimum is n and maximum is m

{n,} — minimum is n and maximum is undefined
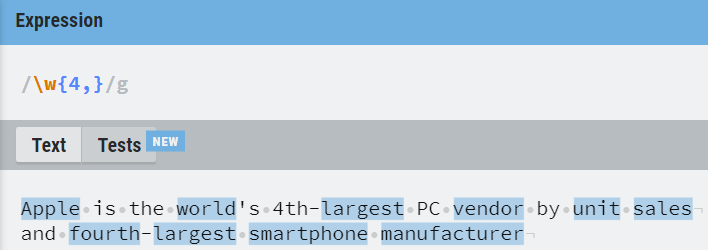
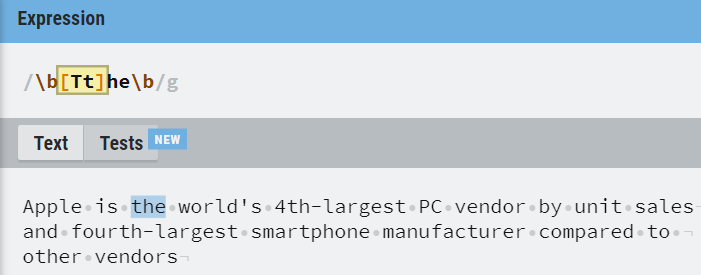
10. Boundaries
\b matches the word boundary and \B is used to identify non-word boundary

OK Cool, Guys 🤗🤗🤗🤗
This is the end of the Regular Expression article and I hope you may grab some important facts about RE. If you enjoy the article and help to improve your knowledge on RE, then hit a clap. 🙌
Thank you for reading !!! 😊
Regular Expressions was originally published in Level Up Coding on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Prathibha Perera
Prathibha Perera | Sciencx (2021-11-04T04:20:58+00:00) Regular Expressions. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2021/11/04/regular-expressions/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
