This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Arslan Ahmad
A Comprehensive Data Partitioning Guide for Acing System Design Interviews.

Introduction
Data partitioning is an essential technique for optimizing the storage, retrieval, and processing of large datasets. By dividing a dataset into smaller, more manageable parts, it becomes easier to work with and process, leading to improved performance and scalability. In this blog post, we’ll explore different data partitioning methods and illustrate them with real-world examples.
Data partitioning can be done in several ways, including horizontal partitioning, vertical partitioning, and hybrid partitioning.
Partitioning Methods
Designing an effective partitioning scheme can be challenging and requires careful consideration of the application requirements and the characteristics of the data being processed. Below are three of the most popular schemes used by various large-scale applications.
a. Horizontal Partitioning: Also known as sharding, horizontal data partitioning involves dividing a database table into multiple partitions or shards, with each partition containing a subset of rows. Each shard is typically assigned to a different database server, which allows for parallel processing and faster query execution times.
For example, consider a social media platform that stores user data in a database table. The platform might partition the user table horizontally based on the geographic location of the users, so that users in the United States are stored in one shard, users in Europe are stored in another shard, and so on. This way, when a user logs in and their data needs to be accessed, the query can be directed to the appropriate shard, minimizing the amount of data that needs to be scanned.
The key problem with this approach is that if the value whose range is used for partitioning isn’t chosen carefully, then the partitioning scheme will lead to unbalanced servers. For instance, partitioning users based on their geographic location assumes an even distribution of users across different regions, which may not be valid due to the presence of densely or sparsely populated areas.
b. Vertical Partitioning: Vertical data partitioning involves splitting a database table into multiple partitions or shards, with each partition containing a subset of columns. This technique can help optimize performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be scanned, especially when certain columns are accessed more frequently than others.
For example, consider an e-commerce website that stores customer data in a database table. The website might partition the customer table vertically based on the type of data, so that personal information such as name and address are stored in one shard, while order history and payment information are stored in another shard. This way, when a customer logs in and their order history needs to be accessed, the query can be directed to the appropriate shard, minimizing the amount of data that needs to be scanned.

c. Hybrid Partitioning: Hybrid data partitioning combines both horizontal and vertical partitioning techniques to partition data into multiple shards. This technique can help optimize performance by distributing the data evenly across multiple servers, while also minimizing the amount of data that needs to be scanned.
For example, consider a large e-commerce website that stores customer data in a database table. The website might partition the customer table horizontally based on the geographic location of the customers, and then partition each shard vertically based on the type of data. This way, when a customer logs in and their data needs to be accessed, the query can be directed to the appropriate shard, minimizing the amount of data that needs to be scanned. Additionally, each shard can be stored on a different database server, allowing for parallel processing and faster query execution times.
Check Grokking the System Design Interview for a list of common system design interview questions and basics concepts.
Data Sharding techniques
Data sharding, a type of horizontal partitioning, is a technique used to distribute large datasets across multiple storage resources, often referred to as shards. By dividing data into smaller, more manageable pieces, sharding can improve performance, scalability, and resource utilization. Below are several data sharding techniques with examples:
1. Range-based Sharding
In range-based sharding, data is divided into shards based on a specific range of values for a given partitioning key. Each shard is responsible for a specific range, ensuring that the data is distributed in a predictable manner.
Example: An e-commerce platform stores order data and decides to shard it based on order dates. Shards can be created for specific date ranges, such as monthly or yearly intervals. When a query targets a specific date range, only the relevant shard needs to be accessed, which improves query performance.
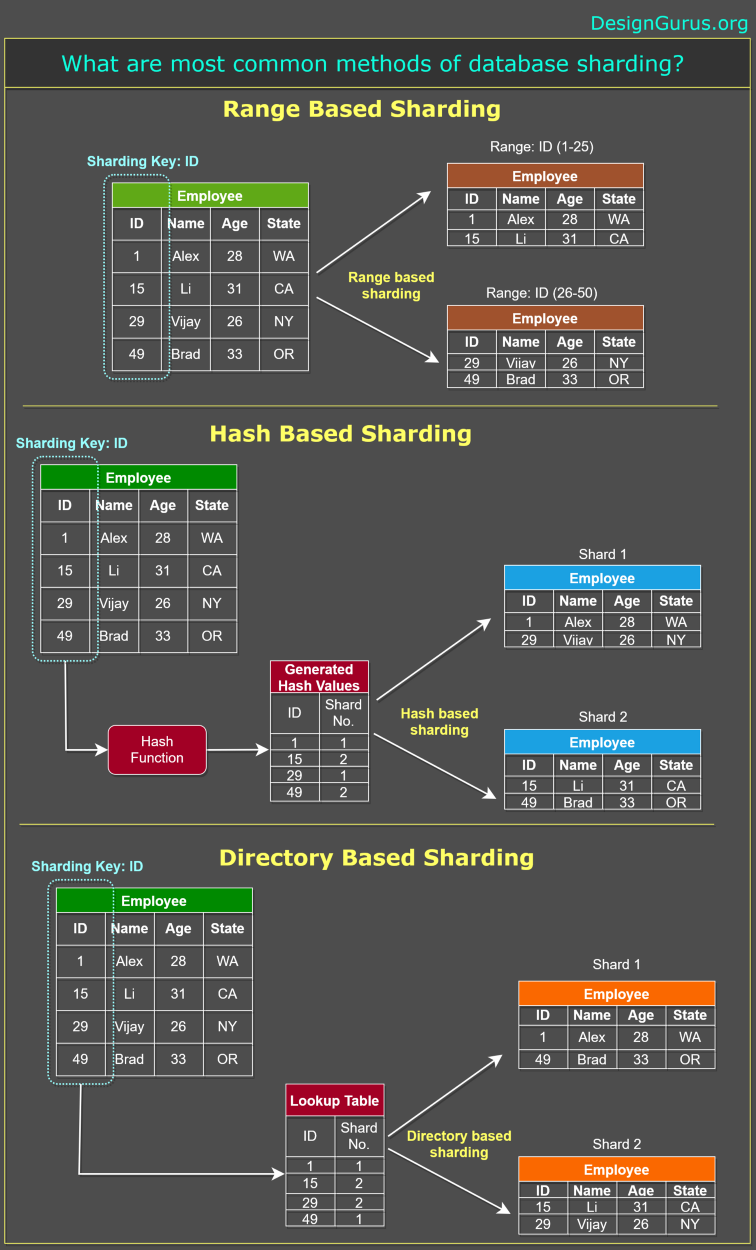
2. Hash-based Sharding
Hash-based sharding involves applying a consistent hash function to the partitioning key, which generates a hash value that determines the destination shard for each data entry. This method ensures an even distribution of data across shards and is particularly useful when the partitioning key has a large number of distinct values or is not easily divided into ranges.
Example: A social media platform stores user data and decides to shard it based on user IDs. The platform applies a hash function to the user ID, generating a hash value that determines the shard for each user’s data. This approach ensures an even distribution of data across shards, optimizing storage efficiency and query performance.
3. Directory-based Sharding
Directory-based sharding uses a lookup table, often referred to as a directory, to map each data entry to a specific shard. This method offers greater flexibility, as shards can be added, removed, or reorganized without the need to rehash or reorganize the entire dataset. However, it introduces an additional layer of complexity, as the directory must be maintained and kept consistent.
Example: An online gaming platform stores player data and decides to use directory-based sharding. The platform maintains a directory that maps each player’s username to a specific shard. When a query targets a specific player’s data, the system first consults the directory to determine the relevant shard, then retrieves the data from that shard.
4. Geographical Sharding
Geographical sharding involves partitioning data based on geographical locations, such as countries or regions. This method can help reduce latency and improve performance for users in specific locations by storing their data closer to them.
Example: A global streaming service stores user data and decides to shard it based on the user’s country. Each shard contains data for users from a specific country, and these shards are stored in data centers located within or near that country. This approach ensures that users can access their data with lower latency, improving the streaming experience.
5. Dynamic Sharding
Dynamic sharding is an adaptive approach that automatically adjusts the number of shards based on the data’s size and access patterns. This method can help optimize resource utilization and performance by creating shards as needed and merging or splitting them as the data grows or shrinks.
Example: An IoT platform collects sensor data from a large number of devices. The platform uses dynamic sharding to automatically adjust the number of shards based on the volume and frequency of incoming data. As more devices are added or removed, the platform can create or merge shards accordingly, ensuring optimal resource utilization and performance.
Benefits of data partitioning
Data partitioning offers a wide range of benefits that can significantly improve the performance, scalability, and resilience of data-driven systems. By understanding the various advantages and their real-world applications, organizations can effectively implement data partitioning strategies tailored to their specific needs, resulting in more efficient and reliable data management. Here are the top benefits of data partitioning:
1. Improved Query Performance
Benefit: Data partitioning can significantly improve query performance by reducing the amount of data that needs to be processed for a given query. When data is partitioned, queries can be targeted at specific partitions, enabling the system to retrieve only the necessary data and ignore irrelevant partitions.
Example: An online bookstore uses range partitioning to divide its inventory data based on book genres. When a customer searches for mystery novels, the system only needs to query the mystery partition, avoiding the need to search through data for other genres, such as romance or science fiction.
2. Enhanced Scalability
Benefit: Partitioning data across multiple storage resources allows for greater system scalability. As the dataset grows, new partitions can be added to accommodate the additional data, without negatively impacting the performance of existing partitions.
Example: A social media platform uses horizontal partitioning to divide user data based on the user’s registration date. As more users join the platform, new partitions are created to store the data for these new users, ensuring that the system remains scalable and responsive as it grows.
3. Load Balancing
Benefit: Data partitioning helps distribute the workload evenly across multiple storage nodes or servers. This load balancing ensures that no single node becomes a bottleneck, leading to better overall system performance and reliability.
Example: A messaging service uses round-robin partitioning to distribute messages across multiple storage nodes. Each message is assigned to a different node in a cyclic manner, ensuring that the workload is balanced and no single node is overwhelmed with too many messages.
4. Data Isolation
Benefit: Partitioning data can provide a level of data isolation, where the failure or corruption of one partition does not necessarily impact the other partitions. This isolation can help improve the overall robustness and resilience of the system.
Example: A financial institution uses vertical partitioning to separate sensitive customer information, such as social security numbers and account numbers, from less sensitive data, such as transaction history. In the event of a data breach, the impact can be limited to only the affected partition, protecting the remaining data from potential exposure.
5. Parallel Processing
Benefit: Data partitioning enables parallel processing, where multiple partitions can be processed simultaneously by different processors or systems. This parallelism can lead to significant performance improvements, especially for large-scale data processing tasks.
Example: An e-commerce company uses horizontal partitioning to divide customer order data based on geographical regions. During peak sales periods, each regional partition can be processed by a separate server, allowing for faster processing of orders and reduced system bottlenecks.
6. Storage Efficiency
Benefit: By partitioning data based on usage patterns or data relevance, organizations can achieve more efficient storage utilization. Frequently accessed data can be stored on faster, more expensive storage resources, while less critical data can be stored on cheaper, slower storage resources.
Example: A video streaming service uses vertical partitioning to store high-resolution video files separately from lower-resolution versions. By storing high-resolution files on high-performance storage resources and lower-resolution files on more cost-effective storage resources, the service can optimize storage efficiency while maintaining high-quality streaming for users.
7. Simplified Data Management
Benefit: Data partitioning can make data management tasks, such as backup, archiving, and maintenance, more manageable and efficient. By dealing with smaller, more focused partitions, these tasks can be performed more quickly and with less impact on overall system performance.
Example: An online news platform uses range partitioning to store articles based on their publication dates. This approach allows the platform to easily archive older articles or perform backups on specific date ranges without affecting the performance of the entire dataset.
8. Better Resource Utilization
Benefit: Partitioning data based on specific attributes or access patterns can lead to better resource utilization. By aligning the data with the appropriate storage and processing resources, organizations can maximize the performance and efficiency of their data-driven systems.
Example: A weather forecasting service uses horizontal partitioning to store weather data based on geographical locations. This allows the service to allocate more resources to process data for areas with higher user demand, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and in line with user needs.
9. Improved Data Security
Benefit: Data partitioning can help enhance data security by segregating sensitive information from less sensitive data. By isolating sensitive data in separate partitions, organizations can implement stronger security measures for those partitions, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches.
Example: A healthcare provider uses vertical partitioning to separate patient medical records from demographic data. By storing sensitive medical records in a separate partition with strict access controls and encryption, the provider can better protect patient privacy and comply with data protection regulations.
10. Faster Data Recovery
Benefit: In the event of a system failure or data loss, partitioning can help speed up the data recovery process. By focusing on recovering specific partitions rather than the entire dataset, organizations can reduce downtime and restore critical data more quickly.
Example: A multinational corporation uses horizontal partitioning to store sales data based on regional markets. If a system failure occurs, the company can prioritize the recovery of the most critical regional partitions, ensuring that essential operations can be resumed as soon as possible.
Common problems associated with data partitioning
While data partitioning offers numerous benefits, it also comes with some disadvantages and challenges that organizations must consider when implementing partitioning strategies. Some of these drawbacks include:
1. Complexity: Data partitioning adds complexity to system architecture, design, and management. Organizations must carefully plan and implement partitioning strategies, taking into account the unique requirements of their data and systems. This added complexity can lead to increased development and maintenance efforts, as well as a steeper learning curve for team members.
2. Data Skew: In some cases, data partitioning can result in uneven data distribution across partitions, known as data skew. This can happen when the chosen partitioning key or method does not distribute data evenly, leading to some partitions being larger or more heavily accessed than others. Data skew can result in reduced performance and resource utilization, negating the benefits of partitioning.
3. Partitioning Key Selection: Choosing the appropriate partitioning key is crucial for achieving the desired benefits of data partitioning. An unsuitable partitioning key can lead to inefficient data distribution, performance bottlenecks, and increased management complexity. Selecting the right key requires a deep understanding of the data and its access patterns, which can be challenging for some organizations.
4. Cross-Partition Queries: When queries need to access data across multiple partitions, performance can suffer, as the system must search through and aggregate data from several partitions. This can result in increased query latency and reduced overall performance, especially when compared to a non-partitioned system.
5. Data Migration: Partitioning can sometimes require significant data migration efforts, especially when changing partitioning schemes or adding new partitions. This can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, potentially causing disruptions to normal system operation.
6. Partition Maintenance: Managing and maintaining partitions can be a challenging and resource-intensive task. As the data grows and evolves, organizations may need to reevaluate their partitioning strategies, which can involve repartitioning, merging, or splitting partitions. This can result in additional maintenance overhead and increased complexity.
7. Cost: Implementing a data partitioning strategy may require additional hardware, software, or infrastructure, leading to increased costs. Furthermore, the added complexity of managing a partitioned system may result in higher operational expenses.
Despite these disadvantages, data partitioning can still offer significant benefits in terms of performance, scalability, and resource utilization when implemented and managed effectively. Organizations must carefully weigh the potential drawbacks against the benefits to determine if data partitioning is the right solution for their specific needs.
Conclusion
Data partitioning is a powerful technique used to manage, store, and process large datasets in modern data-driven systems. By dividing data into smaller, more manageable pieces, organizations can improve query performance, scalability, resource utilization, and overall system efficiency. We have explored various data partitioning methods, such as horizontal partitioning (sharding), vertical partitioning, and hybrid partitioning, each with its unique benefits and applications.
While data partitioning offers numerous advantages, it is essential to consider the potential drawbacks and challenges, such as added complexity, data skew, and partition maintenance. Organizations must carefully assess their data management needs and analyze the potential benefits of each partitioning technique before implementing a partitioning strategy.
As the volume and complexity of data continue to grow, the importance of effective data partitioning cannot be overstated. By understanding the various partitioning methods, their benefits, and their real-world applications, organizations can better prepare themselves to manage and process large datasets, ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of their data-driven systems.
Take a look at Grokking the System Design Interview for system design interview questions. To learn software architecture and practice advanced system design interview questions take a look at Grokking the Advanced System Design Interview.
- System Design Interview Survival Guide (2023): Preparation Strategies and Practical Tips
- Master the Art of Caching for System Design Interviews: A Complete Guide
- System Design Master Template: How to Answer Any System Design Interview Question.
Master the Art of Data Partitioning for System Design Interviews: A Complete Guide was originally published in Level Up Coding on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Level Up Coding - Medium and was authored by Arslan Ahmad
Arslan Ahmad | Sciencx (2023-03-23T23:23:21+00:00) Master the Art of Data Partitioning for System Design Interviews: A Complete Guide. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2023/03/23/master-the-art-of-data-partitioning-for-system-design-interviews-a-complete-guide/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
