This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Michal Gasparik
A tutorial on how you can create and implement web components into your Angular app.
Web Components are a set of standardized web technologies that allow developers to create reusable components. These components can be used across different web applications, regardless of the underlying framework or technology used (Angular, React, Vue, Svelte…).
💡 Note: You can use an open-source platform such as Bit to publish, share and reuse your components. With Bit, you can pack your web components into independent packages, which can be shared and reused across the entire project, helping to maintain consistency in design.
Moreover, for building web components with Lit or Stencil, Bit provides an integrated dev environment (compiler, tester, linter, documentation, CI, dev server, and packaging/dependency management/bundler all-in-one).
Learn more here:
- Introducing Lit Component Development Environment
- Introducing Stencil Component Development Environment

This feature comprises three main technologies: Custom Elements, Shadow DOM, and HTML Templates. Custom Elements allow developers to define new HTML elements, complete with their own encapsulated behavior and properties.
Shadow DOM provides a way to encapsulate and isolate the styles and markup of a component, preventing interference with other parts of the page. HTML Templates enable developers to define reusable chunks of markup that can be instantiated multiple times with different data.
Simple Example of Web Component
class HelloWorldWebComponent extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this._message= 'Hello World, from Web Component!';
}
connectedCallback() {
this.render();
}
render() {
this.innerHTML = `
<style>
.container {
border: 1px solid #000;
padding: 1rem;
}
</style>
<div class="container">
<h2>${this._message}</h2>
</div>
`;
}
}
customElements.define('wc-hello-world', HelloWorldWebComponent);Simple Example of Web Component with Attributes
class AttributesComponent extends HTMLElement {
static get observedAttributes() {
return ['title', 'description'];
}
constructor() {
super();
}
connectedCallback() {
this.render();
}
attributeChangedCallback(name, oldValue, newValue) {
this.render();
}
render() {
const title = this.getAttribute('title');
const description = this.getAttribute('description');
this.innerHTML = `
<div>
<h1>${title}</h1>
<p>${description}</p>
</div>
`;
}
}
customElements.define('wc-attributes', AttributesComponent);Life Cycle Callbacks
Similar to Angular Lifecycle hooks, Web Components also have their own Life Cycle Callbacks.
connectedCallback() — called by the browser when a custom element is added to the DOM
disconnectedCallback() — ensures that any resources or listeners associated with a custom element are properly cleaned up when the element is removed from the DOM, avoiding memory leaks or other issues.
class IntervalWebComponent extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this._interval = null;
}
// Called when custom element is added to the DOM
connectedCallback() {
this._interval = setInterval(() => {
console.log("Hello, World!");
}, 1000);
}
// Called when custom element is added to the DOM
disconnectedCallback() {
clearInterval(this._interval);
console.log("Cleanup complete!");
}
}
customElements.define("wc-interval", IntervalWebComponent);attributeChangedCallback() — method is called each time a custom element’s defined attribute is added, removed, or changed. It is commonly used to update the state or appearance of the component in response to attribute changes.
class AttributeChangedWebComponent extends HTMLElement {
static get observedAttributes() {
return ['message'];
}
constructor() {
super();
this._message = "Hello, World!";
}
connectedCallback() {
this.render();
}
attributeChangedCallback(name, oldValue, newValue) {
if (name === 'message' && oldValue !== newValue) {
this._message = newValue;
this.render();
}
}
render() {
this.innerHTML = `<p>${this._message}</p>`;
}
}
customElements.define("wc-attribute-changed", AttributeChangedWebComponent);adoptedCallback() — method is called each time a custom element is moved to a new document, and is commonly used to update the component’s state or perform any necessary cleanup or initialization tasks.
class AdoptedWebComponent extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this._message = "Hello, World!";
}
connectedCallback() {
this.render();
}
adoptedCallback() {
console.log("Component adopted to a new document.");
this.render();
}
render() {
this.innerHTML = `<p>${this._message}</p>`;
}
}
customElements.define("wc-adopted", AdoptedWebComponent);How to import Web Components into the Angular framework?

Add CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA to app.module.ts
import { CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA, NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
AppRoutingModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent],
// Add this line to enable the addition of Web Components.
schemas: [CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA],
})
export class AppModule { }Create a folder web-components in src/app and a file named hello-world.web-component.js and copy this content:
class HelloWorldWebComponent extends HTMLElement {
constructor() {
super();
this._message= 'Hello World, from Web Component!';
}
connectedCallback() {
this.render();
}
render() {
this.innerHTML = `
<style>
.container {
border: 1px solid #000;
padding: 1rem;
}
</style>
<div class="container">
<h2>${this._message}</h2>
</div>
`;
}
}
customElements.define('wc-hello-world', HelloWorldWebComponent);Import Web Component to AppComponent
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
// import Web Components
import './web-components/hello-world.web-component';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.scss']
})
export class AppComponent {}Add Web Component tag (wc-hello-world) into app.component.html
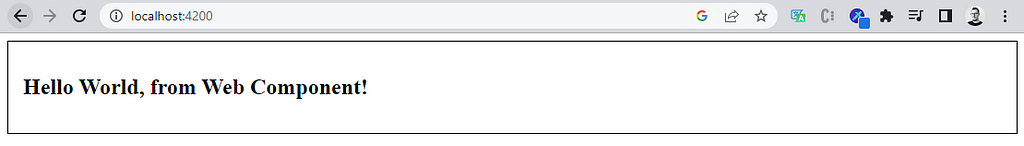
<wc-hello-world></wc-hello-world>
See the result :)
Do you like Angular and Web Components? Claps 👏, follow, and share on social media.
Build Angular Apps with reusable components, just like Lego

Bit’s open-source tool help 250,000+ devs to build apps with components.
Turn any UI, feature, or page into a reusable component — and share it across your applications. It’s easier to collaborate and build faster.
Split apps into components to make app development easier, and enjoy the best experience for the workflows you want:
→ Micro-Frontends
→ Design System
→ Code-Sharing and reuse
→ Monorepo
Learn more:
- Introducing Angular Component Development Environment
- 10 Useful Angular Features You’ve Probably Never Used
- Top 8 Tools for Angular Development in 2023
- Getting Started with a New Angular Project in 2023
- How We Build Micro Frontends
- How to Share Angular Components Between Projects and Apps
- How we Build a Component Design System
- Creating a Developer Website with Bit components
What are Web Components? How to Create and Implement Them in the Angular Framework was originally published in Bits and Pieces on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Michal Gasparik
Michal Gasparik | Sciencx (2023-05-09T00:59:08+00:00) What are Web Components? How to Create and Implement Them in the Angular Framework. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2023/05/09/what-are-web-components-how-to-create-and-implement-them-in-the-angular-framework/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
