This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Mahdhi Rezvi
An Introduction to Typed Arrays in JavaScript
We all must be familiar with JavaScript Arrays which are dynamic in nature and can hold any JavaScript object. But if you are familiar with languages such as C, you will know that arrays are not dynamic by nature. And you will only be able to store a specific data type in that array. But this makes sure that the array is more efficient from the performance perspective. But this does not make JavaScript Arrays inefficient. With the help of JavaScript engine optimizations, Arrays in JavaScript are quite fast thanks.
As web applications grew more powerful, there was a need for web applications to handle and manipulate raw binary data. JavaScript Arrays were unable to handle these raw binary data. Hence JavaScript typed arrays were introduced.
Typed Arrays
Typed Arrays are objects which are quite similar to Arrays, but provide a mechanism to write raw binary data into memory buffers. This feature is well supported across all major browsers and with ES6, they were integrated into the core JS framework and received access to Array methods such as map(), filter(), etc. I highly advise you to go through the resources mentioned at the end of this article to gain in-depth knowledge of typed arrays.
Structure
Typed Arrays are implemented in such a way that they are structured as two main components. The two components that work hand-in-hand to implement typed arrays are the Buffer and View.
Buffer
A Buffer is an object that is of type ArrayBuffer which represents a chunk of data. This chunk of raw binary data, cannot be accessed or modified on its own. You might wonder, what is the use of a data object which cannot be accessed or modified. Here is where a View comes into the picture.
View
A View is an object that allows you to access and modify the raw binary content stored in an ArrayBuffer. There are two kinds of Views.
- An instance of the TypedArray object
These types of objects are much similar to the usual Arrays, but only store numerical data of a single type. Types like Int8, Uint8, Int16, Float32 are some of the TypedArray types. The number in the type denotes the number of bits allocated for the data type. For example, Int8 means an integer with 8 bits assigned to it.
You can read the reference docs to know more about TypedArray data types in detail.
- An instance of the DataView object
The DataView is a low-level interface that provides a getter/setter API to read and write arbitrary data to the buffer. This helps you immensely, especially when working with multiple data types in a single TypedArray.
Another advantage of using the DataView is that it lets you control the Endianness of your data. Typed Array use the Endianness of your platform. This will not be an issue if you are working locally, as your device will use the same Endianness as your typed array. In most scenarios, your typed array will be little-endian as Intel uses little-endian. Since Intel is very common amongst computer processors, there will not be an issue most of the time. But if you are transferring a little-endian encoded data to a device that uses big-endian encoding, you will end up with poorly encoded that will probably end up being corrupted. As DataView enables you to control the Endianness, you can use it whenever necessary.
What Makes Them Different From Normal Arrays
As I have mentioned before, ordinary JavaScript arrays are well optimized by JavaScript engines, that you do not need to use Typed Arrays solely for the performance aspect as this would not give you much of an upgrade. But there are certain features that make type arrays different from ordinary arrays, which might be the reason for you opting for them.
- Lets you handle raw binary data
- Since they are working with only a limited number of data types, it is easier for your engine to optimize Typed Arrays when compared with ordinary arrays where it will be a much of a complicated process.
- Optimization of ordinary arrays is never assured as your engine may decide not to do so over various reasons.
Uses in Web Development
XMLHttpRequest API
You can receive the data response in an ArrayBuffer form as per your response type.
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open('GET', exampleUrl);
xhr.responseType = 'arraybuffer';
xhr.onload = function () {
const arrayBuffer = xhr.response;
//handle data
};xhr.send();
Fetch API
Similar to the XMLHttpRequest API, the fetch API also allows you to receive the response in an ArrayBuffer. You just need to use the arrayBuffer() method on your fetch API response and you will receive a Promise that resolves with an ArrayBuffer.
fetch(url)
.then(response => response.arrayBuffer())
.then(arrayBuffer => {
//handle buffer data
});
HTML Canvas
The HTML5 Canvas element lets you render dynamic 2D shapes and bitmap images. This element only acts as a container for your graphics. This graphic should be drawn with the help of JavaScript.
The 2D Context of canvas lets you retrieve the bitmap data as an instance of Uint8ClampedArray. Let’s have a look at the sample code given by Dr. Axel.
const canvas = document.getElementById('my_canvas');
const context = canvas.getContext('2d');
const imageData = context.getImageData(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
const uint8ClampedArray = imageData.data;WebGL
WebGL allows you to render high-performance interactive 3D and 2D graphics. It is heavily dependent upon Typed Arrays as it manipulates raw pixel data to output the necessary graphics on the canvas.
You can read more about the basics of WebGL in my article over here.
Web Sockets
Web Sockets allow you to send and receive raw binary data in the form of blobs or arraybuffers.
const socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8080");
socket.binaryType = "arraybuffer";// Listen for messages
socket.addEventListener("message", function(event) {
const view = new DataView(event.data);
//Handle received data
});
// Sending binary data
socket.addEventListener('open', function(event) {
const typedArray = new Uint16Array(7);
socket.send(typedArray.buffer);
});
Although you might not need to know TypedArrays in detail as a beginner, they will be essential when you step into the Intermediate-Advanced JavaScript developer stage. This is mainly because you will probably start developing more complex applications that will require the use of TypedArrays.
To get an in-depth understanding of TypedArrays, please go through the resources attached below.
Thank you for reading and happy coding!!
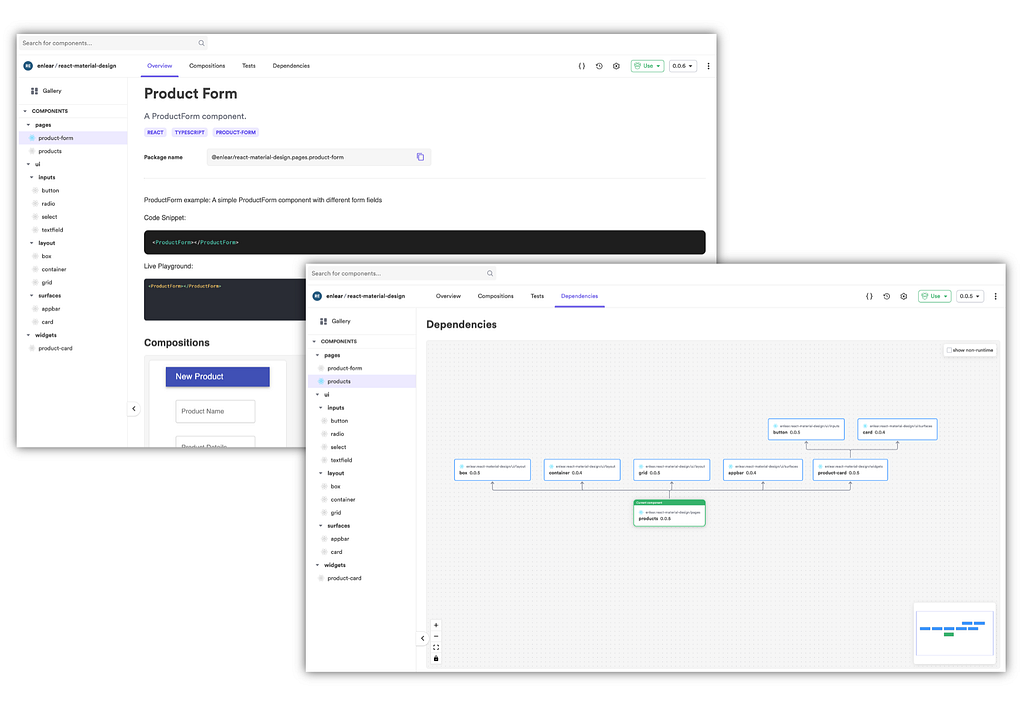
Build & share independent components with Bit
Bit is an ultra-extensible tool that lets you create truly modular applications with independently authored, versioned, and maintained components.
Use it to build modular apps & design systems, author and deliver micro frontends, or simply share components between applications.
Learn More
- The Dark Side of Javascript: A Look at 3 Features You Never Want to Use
- Is It the Beginning of the End for PWAs?
- VSCode Automations for Frontend Developers
Resources
MDN Docs
Exploring JS by Dr. Axel
JavaScript Typed Arrays was originally published in Bits and Pieces on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
This content originally appeared on Bits and Pieces - Medium and was authored by Mahdhi Rezvi
Mahdhi Rezvi | Sciencx (2021-05-04T20:56:15+00:00) JavaScript Typed Arrays. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2021/05/04/javascript-typed-arrays/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
