This content originally appeared on
A List Apart: The Full Feed and was authored by The fine folks at A List Apart
Feedback, in whichever form it takes, and whatever it may be called, is one of the most effective soft skills that we have at our disposal to collaboratively get our designs to a better place while growing our own skills and perspectives.
Feedback is also one of the most underestimated tools, and often by assuming that we’re already good at it, we settle, forgetting that it’s a skill that can be trained, grown, and improved. Poor feedback can create confusion in projects, bring down morale, and affect trust and team collaboration over the long term. Quality feedback can be a transformative force.
Practicing our skills is surely a good way to improve, but the learning gets even faster when it’s paired with a good foundation that channels and focuses the practice. What are some foundational aspects of giving good feedback? And how can feedback be adjusted for remote and distributed work environments?
On the web, we can identify a long tradition of asynchronous feedback: from the early days of open source, code was shared and discussed on mailing lists. Today, developers engage on pull requests, designers comment in their favorite design tools, project managers and scrum masters exchange ideas on tickets, and so on.
Design critique is often the name used for a type of feedback that’s provided to make our work better, collaboratively. So it shares a lot of the principles with feedback in general, but it also has some differences.
The content
The foundation of every good critique is the feedback’s content, so that’s where we need to start. There are many models that you can use to shape your content. The one that I personally like best—because it’s clear and actionable—is this one from Lara Hogan.
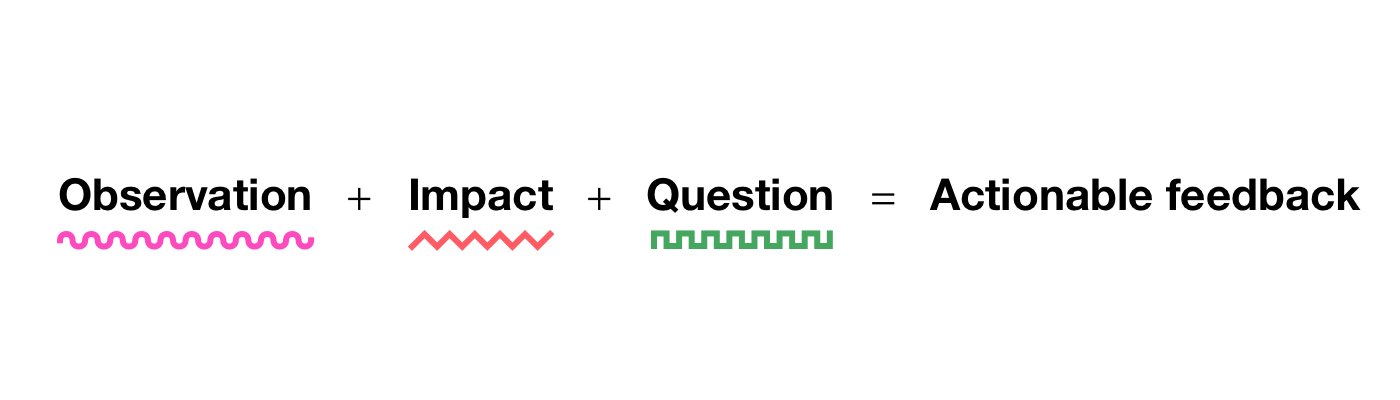
While this equation is generally used to give feedback to people, it also fits really well in a design critique because it ultimately answers some of the core questions that we work on: What? Where? Why? How? Imagine that you’re giving some feedback about some design work that spans multiple screens, like an onboarding flow: there are some pages shown, a flow blueprint, and an outline of the decisions made. You spot something that could be improved. If you keep the three elements of the equation in mind, you’ll have a mental model that can help you be more precise and effective.
Here is a comment that could be given as a part of some feedback, and it might look reasonable at a first glance: it seems to superficially fulfill the elements in the equation. But does it?
Not sure about the buttons’ styles and hierarchy—it feels off. Can you change them?
Observation for design feedback doesn’t just mean pointing out which part of the interface your feedback refers to, but it also refers to offering a perspective that’s as specific as possible. Are you providing the user’s perspective? Your expert perspective? A business perspective? The project manager’s perspective? A first-time user’s perspective?
When I see these two buttons, I expect one to go forward and one to go back.
Impact is about the why. Just pointing out a UI element might sometimes be enough if the issue may be obvious, but more often than not, you should add an explanation of what you’re pointing out.
When I see these two buttons, I expect one to go forward and one to go back. But this is the only screen where this happens, as before we just used a single button and an “×” to close. This seems to be breaking the consistency in the flow.
The question approach is meant to provide open guidance by eliciting the critical thinking in the designer receiving the feedback. Notably, in Lara’s equation she provides a second approach: request, which instead provides guidance toward a specific solution. While that’s a viable option for feedback in general, for design critiques, in my experience, defaulting to the question approach usually reaches the best solutions because designers are generally more comfortable in being given an open space to explore.
The difference between the two can be exemplified with, for the question approach:
When I see these two buttons, I expect one to go forward and one to go back. But this is the only screen where this happens, as before we just used a single button and an “×” to close. This seems to be breaking the consistency in the flow. Would it make sense to unify them?
Or, for the request approach:
When I see these two buttons, I expect one to go forward and one to go back. But this is the only screen where this happens, as before we just used a single button and an “×” to close. This seems to be breaking the consistency in the flow. Let’s make sure that all screens have the same pair of forward and back buttons.
At this point in some situations, it might be useful to integrate with an extra why: why you consider the given suggestion to be better.
When I see these two buttons, I expect one to go forward and one to go back. But this is the only screen where this happens, as before we just used a single button and an “×” to close. This seems to be breaking the consistency in the flow. Let’s make sure that all screens have the same two forward and back buttons so that users don’t get confused.
Choosing the question approach or the request approach can also at times be a matter of personal preference. A while ago, I was putting a lot of effort into improving my feedback: I did rounds of anonymous feedback, and I reviewed feedback with other people. After a few rounds of this work and a year later, I got a positive response: my feedback came across as effective and grounded. Until I changed teams. To my shock, my next round of feedback from one specific person wasn’t that great. The reason is that I had previously tried not to be prescriptive in my advice—because the people who I was previously working with preferred the open-ended question format over the request style of suggestions. But now in this other team, there was one person who instead preferred specific guidance. So I adapted my feedback for them to include requests.
One comment that I heard come up a few times is that this kind of feedback is quite long, and it doesn’t seem very efficient. No… but also yes. Let’s explore both sides.
No, this style of feedback is actually efficient because the length here is a byproduct of clarity, and spending time giving this kind of feedback can provide exactly enough information for a good fix. Also if we zoom out, it can reduce future back-and-forth conversations and misunderstandings, improving the overall efficiency and effectiveness of collaboration beyond the single comment. Imagine that in the example above the feedback were instead just, “Let’s make sure that all screens have the same two forward and back buttons.” The designer receiving this feedback wouldn’t have much to go by, so they might just apply the change. In later iterations, the interface might change or they might introduce new features—and maybe that change might not make sense anymore. Without the why, the designer might imagine that the change is about consistency… but what if it wasn’t? So there could now be an underlying concern that changing the buttons would be perceived as a regression.
Yes, this style of feedback is not always efficient because the points in some comments don’t always need to be exhaustive, sometimes because certain changes may be obvious (“The font used doesn’t follow our guidelines”) and sometimes because the team may have a lot of internal knowledge such that some of the whys may be implied.
So the equation above isn’t meant to suggest a strict template for feedback but a mnemonic to reflect and improve the practice. Even after years of active work on my critiques, I still from time to time go back to this formula and reflect on whether what I just wrote is effective.
The tone
Well-grounded content is the foundation of feedback, but that’s not really enough. The soft skills of the person who’s providing the critique can multiply the likelihood that the feedback will be well received and understood. Tone alone can make the difference between content that’s rejected or welcomed, and it’s been demonstrated that only positive feedback creates sustained change in people.
Since our goal is to be understood and to have a positive working environment, tone is essential to work on. Over the years, I’ve tried to summarize the required soft skills in a formula that mirrors the one for content: the receptivity equation.
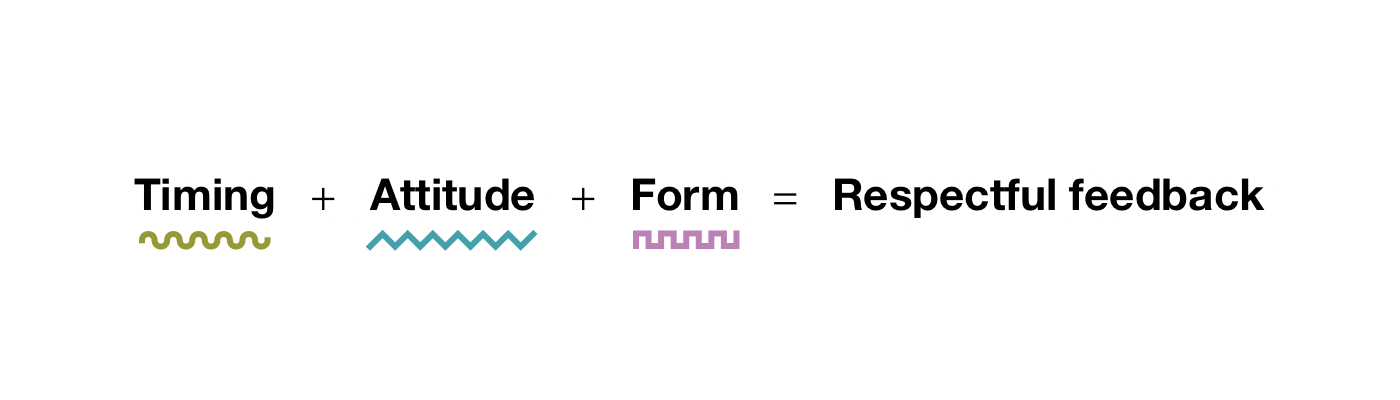
Respectful feedback comes across as grounded, solid, and constructive. It’s the kind of feedback that, whether it’s positive or negative, is perceived as useful and fair.
Timing refers to when the feedback happens. To-the-point feedback doesn’t have much hope of being well received if it’s given at the wrong time. Questioning the entire high-level information architecture of a new feature when it’s about to ship might still be relevant if that questioning highlights a major blocker that nobody saw, but it’s way more likely that those concerns will have to wait for a later rework. So in general, attune your feedback to the stage of the project. Early iteration? Late iteration? Polishing work in progress? These all have different needs. The right timing will make it more likely that your feedback will be well received.
Attitude is the equivalent of intent, and in the context of person-to-person feedback, it can be referred to as radical candor. That means checking before we write to see whether what we have in mind will truly help the person and make the project better overall. This might be a hard reflection at times because maybe we don’t want to admit that we don’t really appreciate that person. Hopefully that’s not the case, but that can happen, and that’s okay. Acknowledging and owning that can help you make up for that: how would I write if I really cared about them? How can I avoid being passive aggressive? How can I be more constructive?
Form is relevant especially in a diverse and cross-cultural work environments because having great content, perfect timing, and the right attitude might not come across if the way that we write creates misunderstandings. There might be many reasons for this: sometimes certain words might trigger specific reactions; sometimes nonnative speakers might not understand all the nuances of some sentences; sometimes our brains might just be different and we might perceive the world differently—neurodiversity must be taken into consideration. Whatever the reason, it’s important to review not just what we write but how.
A few years back, I was asking for some feedback on how I give feedback. I received some good advice but also a comment that surprised me. They pointed out that when I wrote “Oh, […],” I made them feel stupid. That wasn’t my intent! I felt really bad, and I just realized that I provided feedback to them for months, and every time I might have made them feel stupid. I was horrified… but also thankful. I made a quick fix: I added “oh” in my list of replaced words (your choice between: macOS’s text replacement, aText, TextExpander, or others) so that when I typed “oh,” it was instantly deleted.
Something to highlight because it’s quite frequent—especially in teams that have a strong group spirit—is that people tend to beat around the bush. It’s important to remember here that a positive attitude doesn’t mean going light on the feedback—it just means that even when you provide hard, difficult, or challenging feedback, you do so in a way that’s respectful and constructive. The nicest thing that you can do for someone is to help them grow.
We have a great advantage in giving feedback in written form: it can be reviewed by another person who isn’t directly involved, which can help to reduce or remove any bias that might be there. I found that the best, most insightful moments for me have happened when I’ve shared a comment and I’ve asked someone who I highly trusted, “How does this sound?,” “How can I do it better,” and even “How would you have written it?”—and I’ve learned a lot by seeing the two versions side by side.
The format
Asynchronous feedback also has a major inherent advantage: we can take more time to refine what we’ve written to make sure that it fulfills two main goals: the clarity of communication and the actionability of the suggestions.

Let’s imagine that someone shared a design iteration for a project. You are reviewing it and leaving a comment. There are many ways to do this, and of course context matters, but let’s try to think about some elements that may be useful to consider.
In terms of clarity, start by grounding the critique that you’re about to give by providing context. Specifically, this means describing where you’re coming from: do you have a deep knowledge of the project, or is this the first time that you’re seeing it? Are you coming from a high-level perspective, or are you figuring out the details? Are there regressions? Which user’s perspective are you taking when providing your feedback? Is the design iteration at a point where it would be okay to ship this, or are there major things that need to be addressed first?
Providing context is helpful even if you’re sharing feedback within a team that already has some information on the project. And context is absolutely essential when giving cross-team feedback. If I were to review a design that might be indirectly related to my work, and if I had no knowledge about how the project arrived at that point, I would say so, highlighting my take as external.
We often focus on the negatives, trying to outline all the things that could be done better. That’s of course important, but it’s just as important—if not more—to focus on the positives, especially if you saw progress from the previous iteration. This might seem superfluous, but it’s important to keep in mind that design is a discipline where there are hundreds of possible solutions for every problem. So pointing out that the design solution that was chosen is good and explaining why it’s good has two major benefits: it confirms that the approach taken was solid, and it helps to ground your negative feedback. In the longer term, sharing positive feedback can help prevent regressions on things that are going well because those things will have been highlighted as important. As a bonus, positive feedback can also help reduce impostor syndrome.
There’s one powerful approach that combines both context and a focus on the positives: frame how the design is better than the status quo (compared to a previous iteration, competitors, or benchmarks) and why, and then on that foundation, you can add what could be improved. This is powerful because there’s a big difference between a critique that’s for a design that’s already in good shape and a critique that’s for a design that isn’t quite there yet.
Another way that you can improve your feedback is to depersonalize the feedback: the comments should always be about the work, never about the person who made it. It’s “This button isn’t well aligned” versus “You haven’t aligned this button well.” This is very easy to change in your writing by reviewing it just before sending.
In terms of actionability, one of the best approaches to help the designer who’s reading through your feedback is to split it into bullet points or paragraphs, which are easier to review and analyze one by one. For longer pieces of feedback, you might also consider splitting it into sections or even across multiple comments. Of course, adding screenshots or signifying markers of the specific part of the interface you’re referring to can also be especially useful.
One approach that I’ve personally used effectively in some contexts is to enhance the bullet points with four markers using emojis. So a red square 



Let’s see how this would work by reusing the example that we used earlier as the first bullet point in this list:
Navigation—When I see these two buttons, I expect one to go forward and one to go back. But this is the only screen where this happens, as before we just used a single button and an “×” to close. This seems to be breaking the consistency in the flow. Let’s make sure that all screens have the same two forward and back buttons so that users don’t get confused.
Overall—I think the page is solid, and this is good enough to be our release candidate for a version 1.0.
Metrics—Good improvement in the buttons on the metrics area; the improved contrast and new focus style make them more accessible.
-
Button Style—Using the green accent in this context creates the impression that it’s a positive action because green is usually perceived as a confirmation color. Do we need to explore a different color?
Tiles—Given the number of items on the page, and the overall page hierarchy, it seems to me that the tiles shouldn’t be using the Subtitle 1 style but the Subtitle 2 style. This will keep the visual hierarchy more consistent.
Background—Using a light texture works well, but I wonder whether it adds too much noise in this kind of page. What is the thinking in using that?
What about giving feedback directly in Figma or another design tool that allows in-place feedback? In general, I find these difficult to use because they hide discussions and they’re harder to track, but in the right context, they can be very effective. Just make sure that each of the comments is separate so that it’s easier to match each discussion to a single task, similar to the idea of splitting mentioned above.
One final note: say the obvious. Sometimes we might feel that something is obviously good or obviously wrong, and so we don’t say it. Or sometimes we might have a doubt that we don’t express because the question might sound stupid. Say it—that’s okay. You might have to reword it a little bit to make the reader feel more comfortable, but don’t hold it back. Good feedback is transparent, even when it may be obvious.
There’s another advantage of asynchronous feedback: written feedback automatically tracks decisions. Especially in large projects, “Why did we do this?” could be a question that pops up from time to time, and there’s nothing better than open, transparent discussions that can be reviewed at any time. For this reason, I recommend using software that saves these discussions, without hiding them once they are resolved.
Content, tone, and format. Each one of these subjects provides a useful model, but working to improve eight areas—observation, impact, question, timing, attitude, form, clarity, and actionability—is a lot of work to put in all at once. One effective approach is to take them one by one: first identify the area that you lack the most (either from your perspective or from feedback from others) and start there. Then the second, then the third, and so on. At first you’ll have to put in extra time for every piece of feedback that you give, but after a while, it’ll become second nature, and your impact on the work will multiply.
Thanks to Brie Anne Demkiw and Mike Shelton for reviewing the first draft of this article.
This content originally appeared on
A List Apart: The Full Feed and was authored by The fine folks at A List Apart
The fine folks at A List Apart | Sciencx (2021-06-17T14:00:00+00:00) Asynchronous Design Critique: Giving Feedback. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2021/06/17/asynchronous-design-critique-giving-feedback-685/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
