This content originally appeared on Telerik Blogs and was authored by Dhananjay Kumar
Learn how to add a global error handler service in an Angular app to manage runtime errors throughout the application effectively.
In an Angular application, errors typically fall into two categories:
- Errors related to HTTP operations
- Errors resulting from invalid application operations, like attempting to divide by zero
This blog post delves into incorporating a global error handler in an Angular application to manage runtime errors throughout the application effectively.
When working with Angular applications, it’s common to encounter runtime errors, such as calling methods on undefined variables or objects.
A typical scenario is attempting to call array methods like sort() on a variable that hasn’t been properly initialized or has an undefined value.
For example, consider the below code.
export class AppComponent {
title = 'Global Error Handler Demo';
data:any;
getAverage(){
let a = this.data?.sort().reduce((a:any,b:any)=>a+b)/this.data.length;
console.log(a);
}
}
Angular triggers an error when attempting to call the sort() method on an undefined data variable, as depicted in the following image.
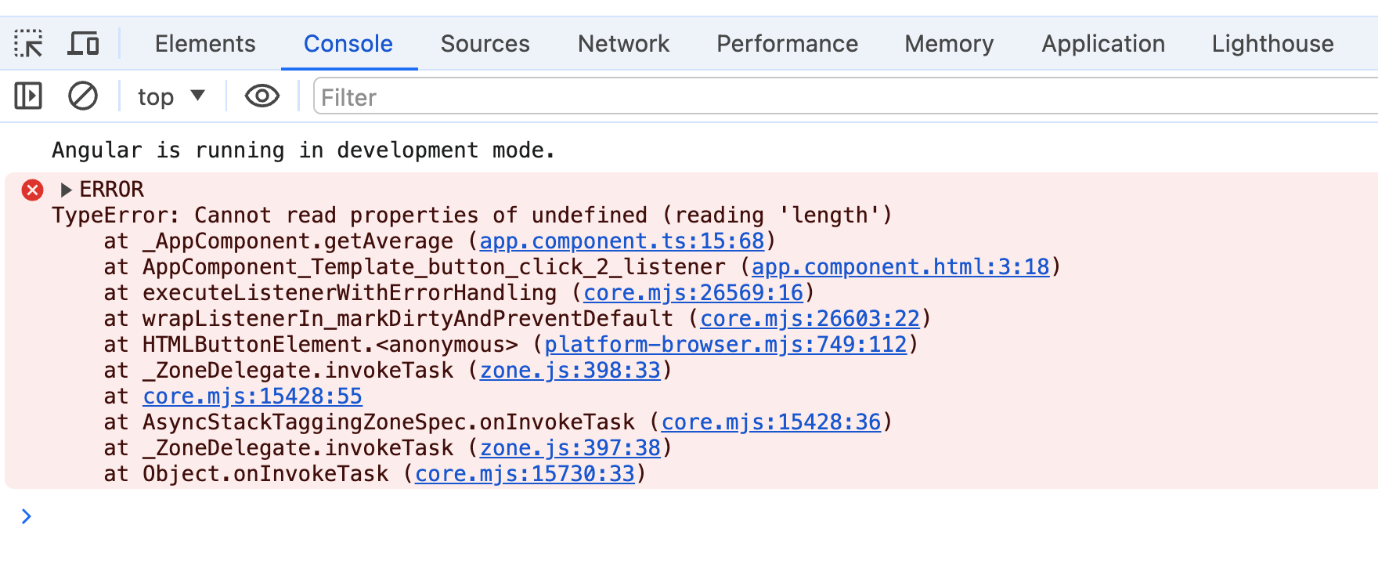
These runtime errors, displayed in red in the browser console, can be enhanced for better usability within the application. To achieve this, we can log these errors and provide meaningful information to the user by overriding the default error handler class.
Angular utilizes the ErrorHandler class to manage run-time errors. To implement global error handling, we can customize the handleError method.
Let’s break down the steps:
Create an Angular Service
To generate an Angular service, run the following CLI command: ng generate service global-error-handler. Once the command runs successfully, you will find the service created as depicted in the code listing below:
import {Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class GlobalErrorHandlerService {
}
To replace the default Error Handler in Angular, you must implement the ErrorHandler interface and redefine the handleError method. This specific method gets triggered whenever an error arises within the application.
import { ErrorHandler, Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class GlobalErrorHandlerService implements ErrorHandler {
handleError(error: any): void {
console.log('handle and log the error here and send it to the server');
// console.error('An error occurred:', error);
//throw error (Keep this line uncommented in development in order to see the error in the console)
}
}
In this method, you are required to code for the following tasks:
- Implement custom error handling.
- Transmit the error log to the server.
- Redirect to an error page if needed.
Provide the Service
To use a custom error handler service across the application:
- It should be provided at the application layer.
- It should be provided for the
ErrorHandlertoken.
For Angular versions 16 and later, you can set up the GlobalErrorHandlerService in the app.config.ts file, as shown below.
import { GlobalErrorHandlerService } from './global-error-handler.service';
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
provideZoneChangeDetection({ eventCoalescing: true }),
{provide:ErrorHandler,useClass:GlobalErrorHandlerService},
provideRouter(routes)
]
};
When Angular triggers an error when attempting to call the sort() method on an undefined data variable, you get an error message, as depicted in the following image.
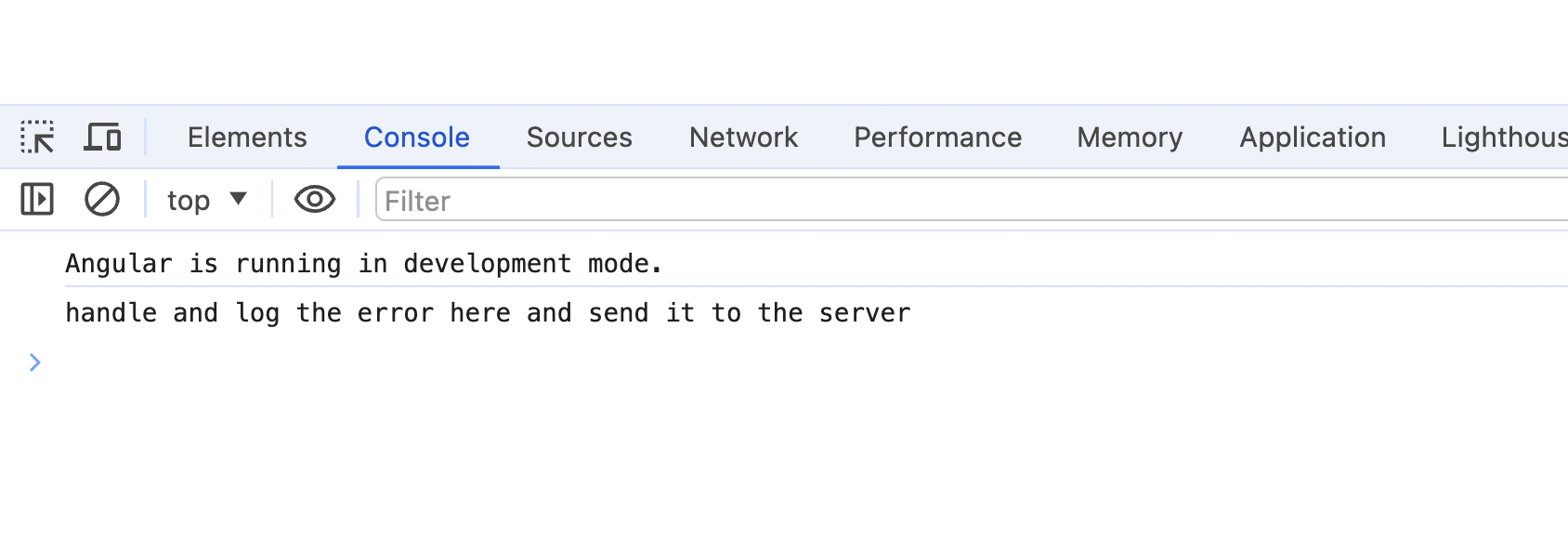
Use StackTrace.js
To use StackTrace.js, you must install it by running the following command.
npm install --save stacktrace-js
Following a successful installation, modify the handleError method to include the usage of stack traces as illustrated below:
import { ErrorHandler, Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import * as StackTrace from 'stacktrace-js';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class GlobalErrorHandlerService implements ErrorHandler {
handleError(error: any): void {
console.log('handle and log the error here and send it to the server');
StackTrace.fromError(error).then(stackframes => {
const stringifiedStack = stackframes
.map(sf => sf.toString())
.join('\n');
console.error(stringifiedStack);
});
}
}
Log the Error
To log meaningful information about run-time errors, create an interface to capture the following information.
- Route: The specific route or endpoint where the error occurred
- Stacktrace: The stack trace or relevant error details
- User: Information about the user (e.g., user ID, username or relevant context)
- Time: Timestamp when the error occurred
The interface can be created as shown below:
export interface LogError {
Time : string;
Route : string;
Message : string;
User : string;
}
Next, create a service to log this information to the server.
export class LogErrorService {
private http = inject(HttpClient);
logError(log: LogError):any {
console.log(log);
this.http.post('http://your-api-url.com', log).subscribe(
response => {
console.log(response);
},
error => {
console.error(error);
}
);
}
}
In the GlobalErrorHandlerService, use LogErrorService as shown below:
import { ErrorHandler, Injectable, inject } from '@angular/core';
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
import * as StackTrace from 'stacktrace-js';
import { LogError } from './LogError';
import { LogErrorService } from './log-error.service';
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class GlobalErrorHandlerService implements ErrorHandler {
router = inject(Router);
logErrorService = inject(LogErrorService);
logError: LogError = {
Message: '',
Time: '',
Route: '',
User: ''
};
handleError(error: any): void {
console.log('handle and log the error here and send it to the server');
StackTrace.fromError(error).then(stackframes => {
const stringifiedStack = stackframes
.map(sf => sf.toString())
.join('\n');
// console.error(stringifiedStack);
console.log('logError is not null');
this.logError.Message = stringifiedStack;
this.logError.Time = new Date().toDateString();
this.logError.Route = this.router.url;
this.logError.User = 'testUser';
this.logErrorService.logError(this.logError);
this.router.navigate(['/error-page']);
});
}
}
You will notice that the service injects two dependencies, Router and LogService. The Router is used to navigate the user to an error page when an error occurs, and the LogService is used to log the error details.
Summary
You learned to add a global error handler service in Angular in this blog post. To do that:
- Create a service.
- Implement the ErrorHandler class.
- Override handleError method.
- Provide the service at the application level.
I hope you find this post helpful. Thanks for reading!
This content originally appeared on Telerik Blogs and was authored by Dhananjay Kumar
Dhananjay Kumar | Sciencx (2024-08-20T08:42:25+00:00) Implementing a Global Error Handler in Angular: A Step-by-Step Guide. Retrieved from https://www.scien.cx/2024/08/20/implementing-a-global-error-handler-in-angular-a-step-by-step-guide/
Please log in to upload a file.
There are no updates yet.
Click the Upload button above to add an update.
